Overview
Navigating the world of mortgage payments can feel overwhelming, especially when considering a loan of $500,000. We understand how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way. This article breaks down the process of calculating mortgage payments, addressing the key components that influence your monthly costs.
When you look at a mortgage payment, it’s essential to consider various elements:
- principal
- interest
- taxes
- insurance
Each of these factors plays a significant role in determining your overall financial commitment. For instance, did you know that even slight variations in interest rates or loan terms can lead to substantial differences in what you pay over time?
By exploring these factors, we aim to empower you in your financial planning. Understanding how these components interact can help you make informed decisions that align with your family’s needs. As you consider your options, remember that the right information can guide you toward a more secure financial future.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of a $500,000 mortgage can feel overwhelming. We know how challenging this can be, especially with fluctuating interest rates and a variety of loan options. Understanding how to calculate monthly payments is not just an academic exercise; it’s a vital step in ensuring your financial stability and making informed decisions about homeownership. But how can you effectively break down these costs and anticipate your financial commitments?
This article provides a step-by-step guide to demystifying the mortgage payment calculation process. We will highlight essential components and factors that influence costs, ultimately empowering you to take control of your financial future. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Explore the Basics of Mortgage Payments on a $500,000 Loan
When considering a loan for a , we know how challenging it can be to navigate the financial landscape. It’s essential to understand that your recurring costs are influenced by several factors, including the interest percentage, loan duration, and initial deposit. Typically, loan installments consist of principal and interest, but they may also include property taxes and insurance.
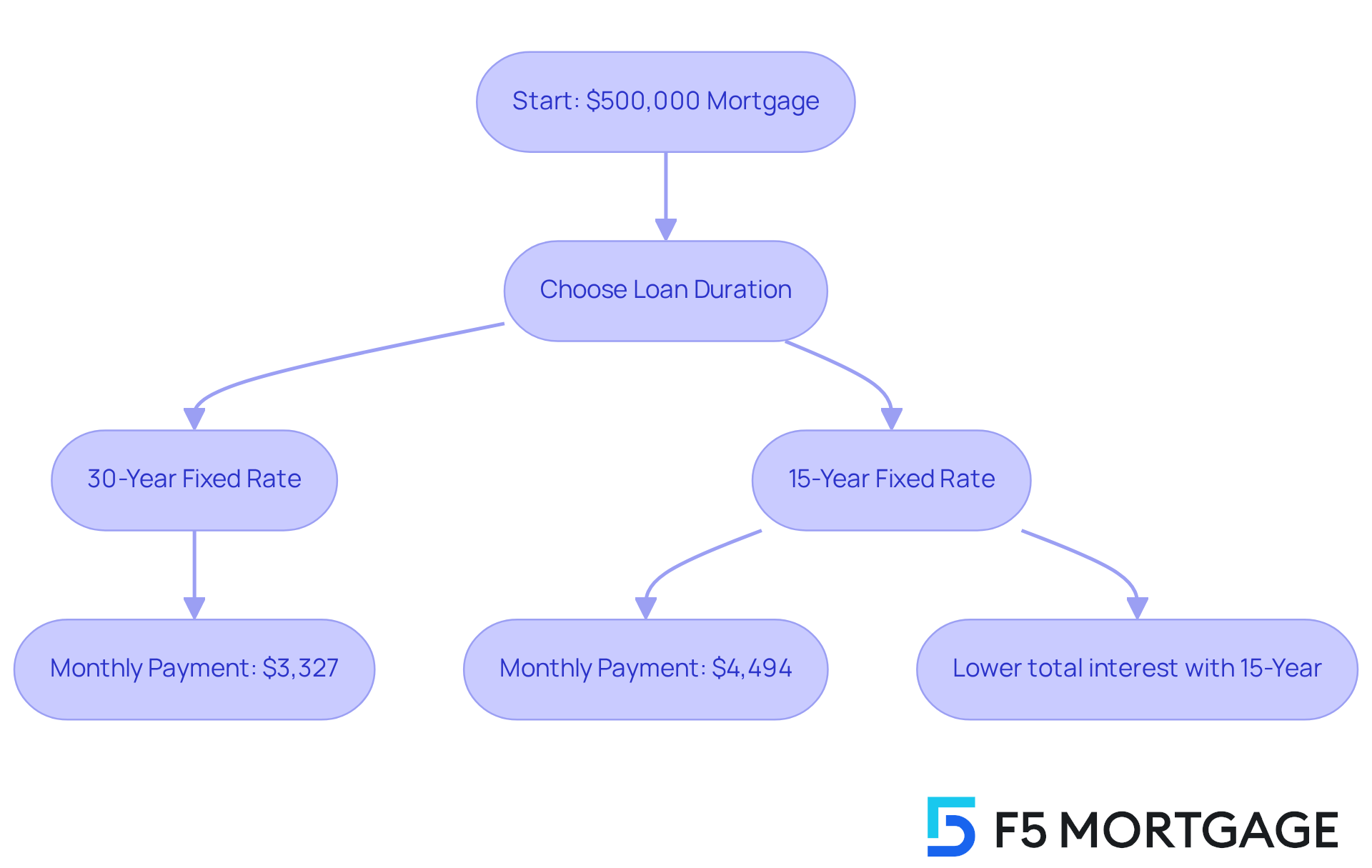
For instance, with a 30-year fixed-rate loan at a 7.00% interest, your 500,000 mortgage payment would be approximately $3,327 per month, not factoring in taxes and insurance. On the other hand, if you opt for a 15-year mortgage at the same interest rate, your 500,000 mortgage payment would be about $4,494. However, this option significantly reduces the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Understanding these basics is crucial as you prepare for the financial responsibilities of homeownership. Interest rates can fluctuate, impacting your overall affordability. As we look ahead to 2025, tracking these rates becomes vital, as they can greatly influence your monthly obligations and long-term financial planning. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Break Down the Components of Your Monthly Mortgage Payment
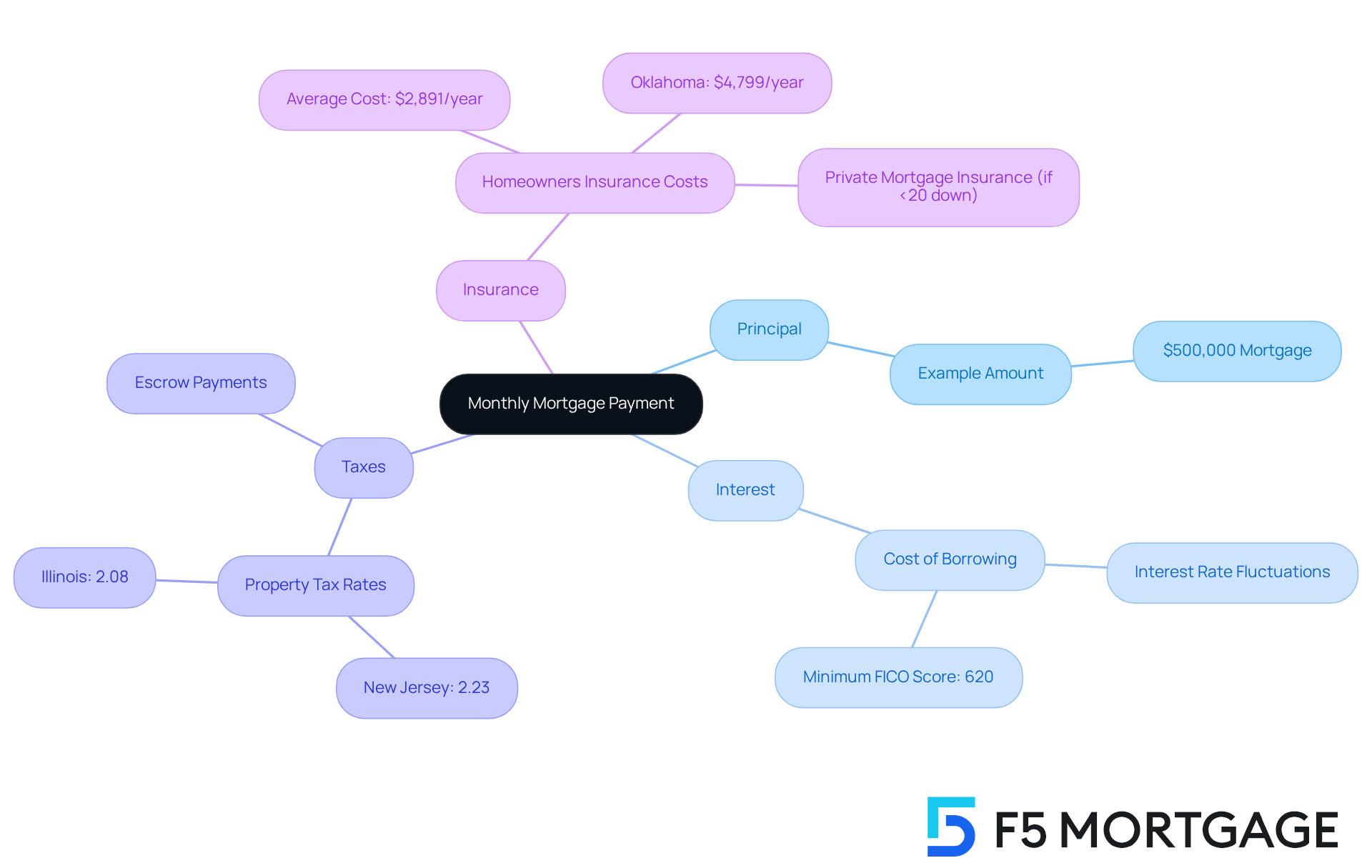
Understanding your monthly housing loan payment can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. A typical payment consists of four essential elements, commonly referred to as PITI: Principal, Interest, Taxes, and Insurance. Let’s break these down together.
- Principal: This is the total amount you borrow from the lender. For instance, if you take out a 500,000 mortgage payment, that amount represents your principal.
- Interest: This represents the cost of borrowing that principal amount, expressed as a percentage. Interest rates can fluctuate based on market conditions and your personal creditworthiness. Often, a minimum FICO credit score of 620 is required for loans, which can add to the stress of the process.
- Taxes: Property taxes, assessed by local governments, can vary significantly based on where you live. For example, New Jersey has the highest effective property tax rate at 2.23%, closely followed by Illinois at 2.08%. These taxes are typically included in your monthly payment and held in escrow to ensure they are paid on time, alleviating some of the burden.
- Insurance: Homeowner’s insurance is crucial for protecting your property from potential damages and is usually a requirement from lenders. The for a $500,000 home is around $2,891 annually, but this can vary based on factors like location and coverage limits. Notably, Oklahoma has the highest average home insurance rates at $4,799 per year. If your down payment is less than 20%, you may also need to pay for private mortgage insurance, adding to your monthly costs.
We know how challenging this can be, but grasping these elements is essential for predicting your overall expenses and organizing your budget effectively. For example, if you calculate your PITI for a $500,000 mortgage with a 4% interest rate, property taxes of $6,000 annually, and homeowners insurance costing $2,891 per year, your monthly payment would break down as follows:
- Principal and Interest: Approximately $2,387
- Taxes: $500
- Insurance: $241
This results in a total monthly payment of around $3,128.
By understanding the complexities of PITI, you can better manage your loan responsibilities and make informed financial choices. As Weaver suggests, “Keep track of your real estate tax bill and your insurance bill” to prevent unforeseen rises in your loan payments. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Analyze Factors Affecting Mortgage Rates and Payments
Several factors significantly influence mortgage rates and, consequently, the amount of your 500,000 mortgage payment. Understanding these can help ease the stress of navigating the process of a 500,000 mortgage payment.
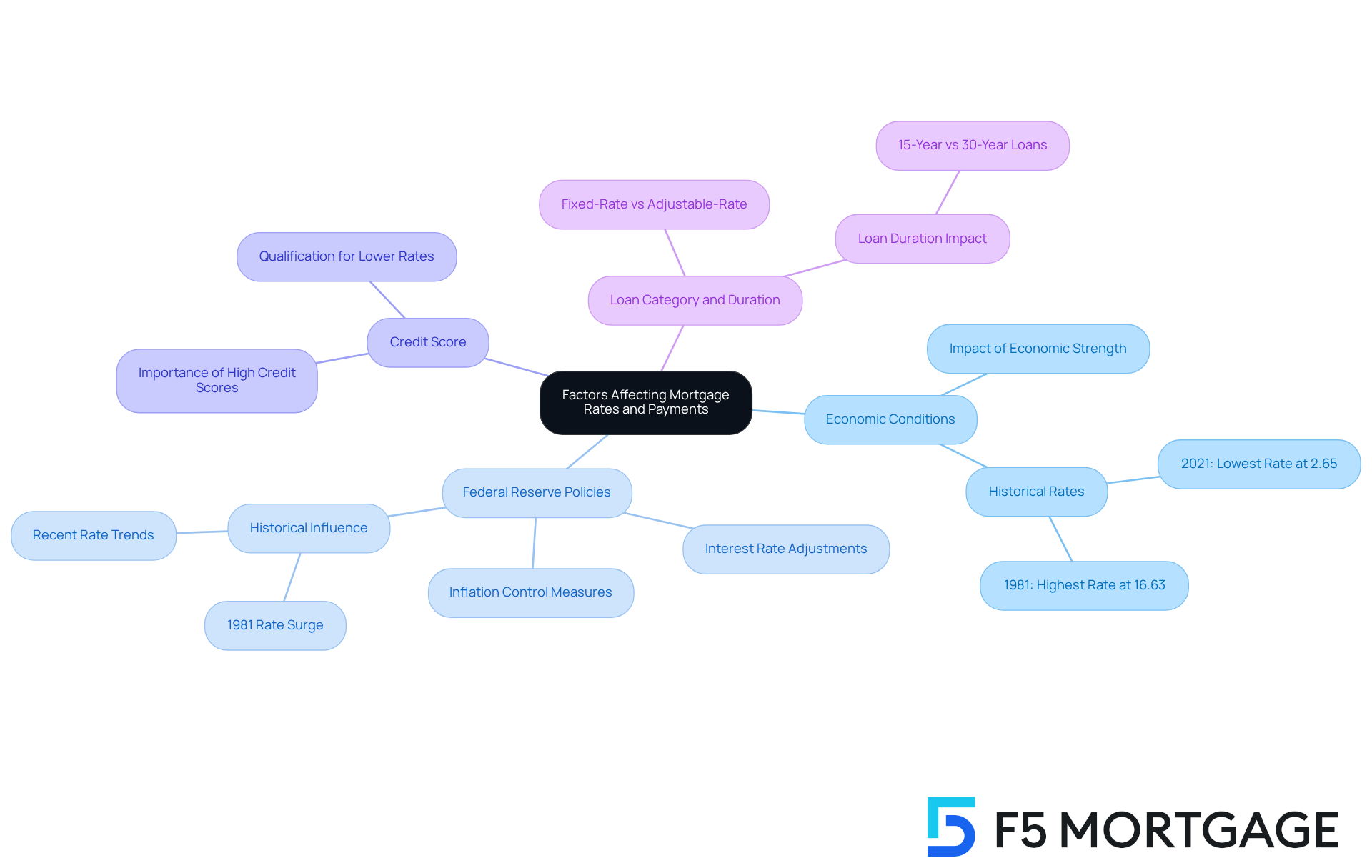
- Economic Conditions: The overall well-being of the economy plays a crucial role in determining interest levels. In a strong economy, heightened demand for loans can lead to increased costs. Conversely, during economic recessions, rates may decrease as a strategy to encourage borrowing and spending. For instance, in 2021, the lowest 30-year loan costs were recorded at 2.65%, providing a historical reference for current figures.
- Federal Reserve Policies: The choices made by the Federal Reserve regarding benchmark interest rates directly affect loan costs. When the Fed raises interest rates, borrowing expenses typically follow suit. Recently, the Fed has aimed to maintain elevated levels to combat inflation, which has exceeded the target of 2% for some time. In 1981, average loan interest soared to 16.63%, largely due to the Fed’s actions, highlighting the substantial impact of these policies on borrowing costs.
- Credit Score: Your is a vital factor in determining the interest rate for which you qualify. Generally, higher credit scores lead to lower fees, making it essential for borrowers to maintain strong credit health to secure favorable loan terms. As Peter G. Miller points out, elevated interest rates can reduce home affordability, emphasizing the significance of credit scores in securing a 500,000 mortgage payment.
- Loan Category and Duration: The type of financing—such as fixed-rate versus adjustable-rate—and the loan duration—like 15 years versus 30 years—also influence interest costs. Fixed-interest loans offer stability, while adjustable-rate loans may present lower initial costs but can increase over time. Understanding these differences can help borrowers choose the right loan product and timing, potentially saving thousands over the life of the loan.
Real-world examples illustrate these dynamics: In 2016, the average loan interest fell to a historic low of 3.65%, resulting in a monthly payment of $915 for a $200,000 loan, which is much lower than a 500,000 mortgage payment, making homeownership more attainable. In contrast, in 1981, the average interest surged to 16.63%, leading to an astonishing payment of $2,800 on a 500,000 mortgage payment for the same loan amount, emphasizing how economic conditions and Federal Reserve strategies can dramatically affect borrowing costs. Furthermore, the consumer price index rose by 0.3% in June, resulting in an annual inflation rate of 2.7%, further demonstrating how inflation impacts home loan costs. As the economy continues to evolve, it’s vital for prospective homebuyers to monitor these factors closely. We know how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Calculate Your Monthly Payment: A Step-by-Step Guide
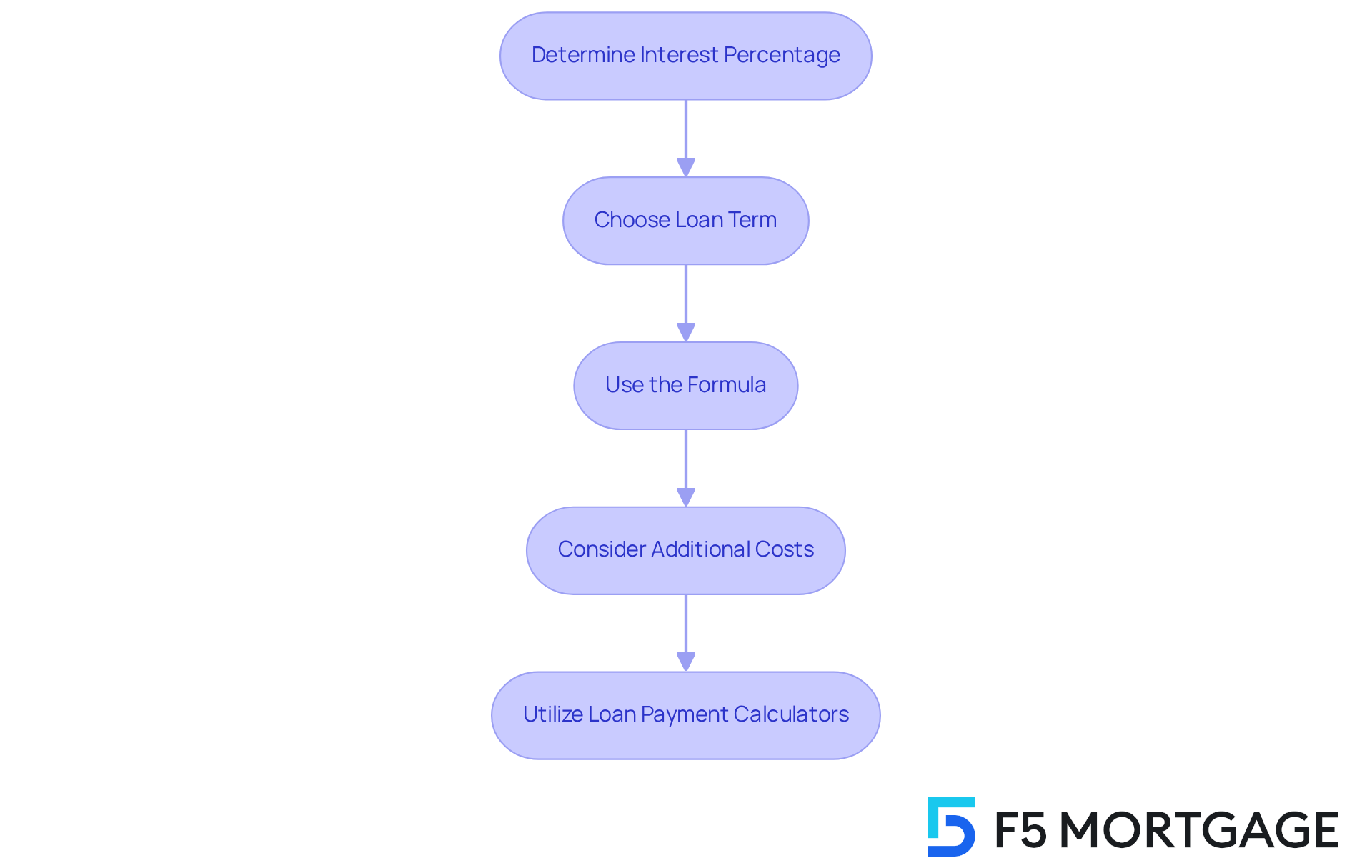
Calculating your monthly mortgage payment for a $500,000 mortgage can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. Let’s break it down into manageable steps together:
-
Determine Your Interest Percentage: For our example, we’ll use an interest percentage of 6%. This is a common rate, and we know how important it is to find the best option for your family.
-
Choose Your Loan Term: We’ll consider a 30-year term for this calculation. This longer term can often make monthly payments more manageable, giving you peace of mind.
-
Use the Formula: The formula for calculating your monthly payment (M) is:
M = P × (r(1 + r)^n) / ((1 + r)^n - 1)Where:
- P = principal loan amount ($500,000)
- r = monthly interest rate (annual rate / 12 months)
- n = number of payments (loan term in months)
For a 6% interest rate:
- r = 0.06 / 12 = 0.005
- n = 30 × 12 = 360
Plugging in these numbers:
M = 500,000 × (0.005(1 + 0.005)^360) / ((1 + 0.005)^360 - 1)After performing the calculation, your monthly payment would be approximately $3,000. This figure can help you budget effectively, ensuring you’re prepared for your financial commitment.
-
Consider Additional Costs: Remember to factor in property taxes, homeowner’s insurance, and any applicable PMI. This comprehensive approach will provide a clearer picture of your total monthly financial commitment. We understand how these additional costs can add up, so being aware of them is crucial.
Utilizing present loan payment calculators can further simplify this process. These tools allow you to modify variables like interest rates and loan terms, helping you see their impact on your payments. With the right tools and understanding, you can confidently . Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of a $500,000 mortgage payment is essential for prospective homeowners. We know how challenging this can be, and this article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the various factors that influence monthly payments. By grasping the components such as principal, interest, taxes, and insurance, individuals can better prepare for the financial responsibilities that come with homeownership.
Key insights reveal how interest rates, loan duration, and economic conditions significantly impact mortgage payments. For instance:
- A 30-year loan at a 7% interest rate results in a monthly payment of approximately $3,327.
- A 15-year loan at the same rate increases the monthly obligation to about $4,494.
Additionally, understanding the effects of property taxes and homeowners insurance can help in budgeting more effectively, ensuring that all aspects of home financing are accounted for.
Ultimately, navigating the mortgage process requires careful consideration of multiple factors. As interest rates fluctuate and economic conditions evolve, staying informed is crucial for making sound financial decisions. We’re here to support you every step of the way. Prospective homeowners are encouraged to utilize available tools and resources to calculate their mortgage payments accurately and to seek guidance throughout their journey to homeownership. Taking these steps can lead to a more confident and informed approach to managing a significant financial commitment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors influence the monthly mortgage payment on a $500,000 loan?
The monthly mortgage payment is influenced by the interest rate, loan duration, and initial deposit. Additionally, payments typically include principal and interest, and may also encompass property taxes and insurance.
How much would a $500,000 mortgage payment be for a 30-year fixed-rate loan at 7.00% interest?
For a 30-year fixed-rate loan at 7.00% interest, the monthly payment would be approximately $3,327, not including property taxes and insurance.
What would the monthly payment be for a 15-year mortgage at the same interest rate?
For a 15-year mortgage at 7.00% interest, the monthly payment would be about $4,494. This option significantly reduces the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Why is it important to understand mortgage payments when considering homeownership?
Understanding mortgage payments is crucial as it helps prepare for the financial responsibilities of homeownership, including how interest rates can fluctuate and impact overall affordability.
How can interest rates affect mortgage payments in the future?
Interest rates can fluctuate, which can greatly influence your monthly obligations and long-term financial planning. Tracking these rates is vital as you prepare for homeownership.