Overview
We know how challenging it can be to determine how much house payment you can afford. To navigate this process, it’s essential to evaluate your financial situation. Consider:
- Your income
- Monthly expenses
- Debt obligations
- Savings for a down payment
By calculating key financial ratios, such as the debt-to-income and housing expense ratios, you can create a realistic budget. This will help ensure that your housing costs remain manageable relative to your overall financial health. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
Understanding how much house payment one can afford is a crucial step in the home-buying journey. We know how challenging this can be, and many prospective buyers feel overwhelmed by the complexity of financial calculations and budgeting. This guide offers a comprehensive framework to help you assess your financial situation, calculate key ratios, and ultimately determine an affordable monthly payment.
However, it’s important to recognize that there are various expenses beyond the mortgage itself—such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs. How can you ensure you are truly prepared for homeownership? This article delves into the essential steps and considerations for making informed decisions, empowering you to navigate the housing market with confidence.
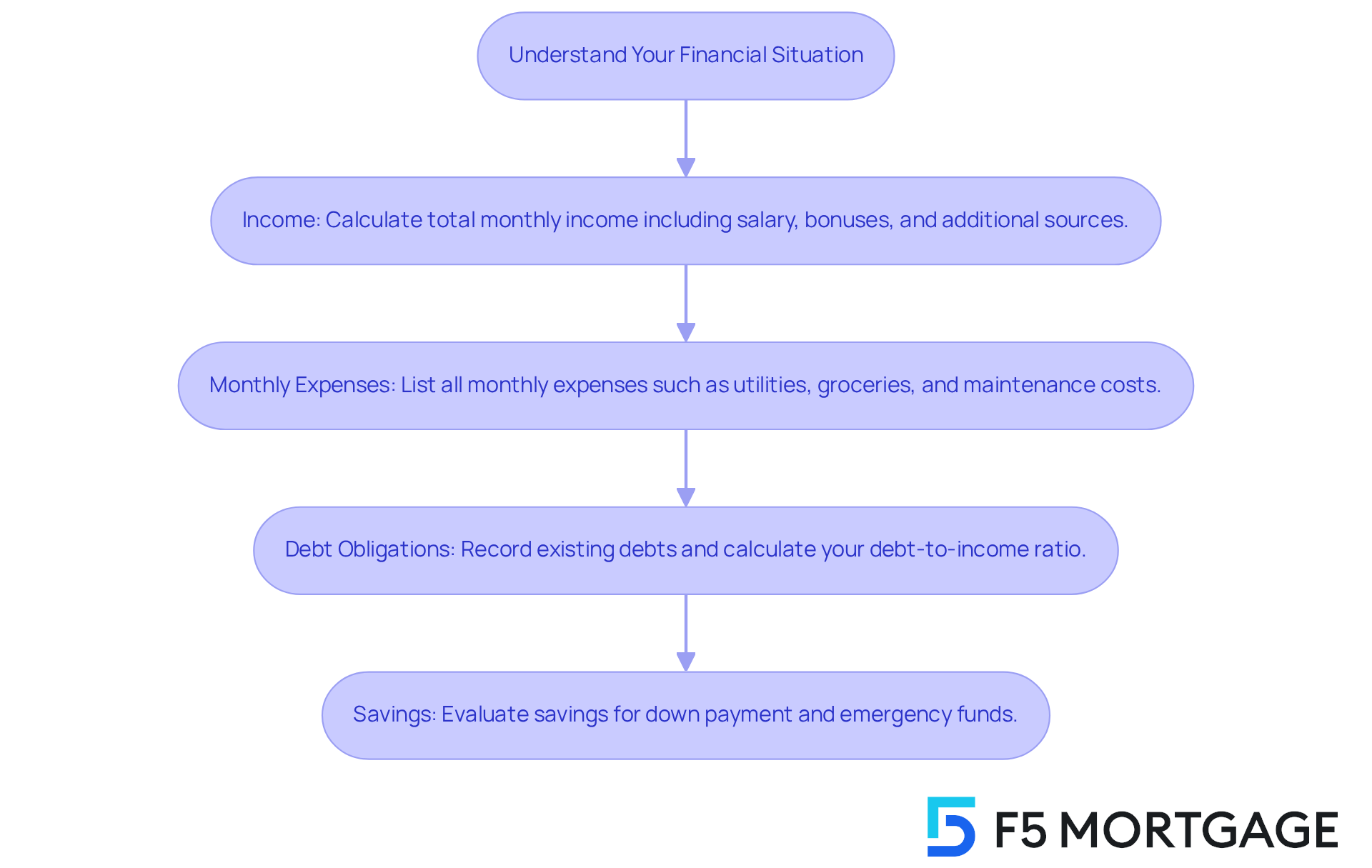
Understand Your Financial Situation
To begin, let’s gather some important information together:
- Income: It’s essential to calculate your total monthly income, including salary, bonuses, and any additional sources. Understanding your income is crucial as it forms the foundation for your budget and helps determine your borrowing capacity.
- Monthly Expenses: Take a moment to list all your monthly expenses, such as utilities, groceries, transportation, and other recurring costs. On average, families in the U.S. spend about $10,000 annually on maintenance, repairs, and improvements, which should be factored into your budget.
- Debt Obligations: Record all your existing debts, including credit card balances, student loans, and car financing. This will help you calculate your debt-to-income ratio, a key metric that lenders use to assess your financial health. A debt-to-income ratio of less than 43% is typically required for home loans, indicating a strong financial position. You can determine this ratio using the formula:
(Total monthly debt expense / gross monthly income) X 100. - Savings: Evaluate your savings for a down payment and emergency funds. Experts suggest setting aside at least 20% to 25% of the property cost for the initial deposit, especially if you are considering FHA loans, which provide low deposit options suitable for first-time homebuyers. Additionally, it’s wise to save for three to four years in advance for a property purchase. A larger down payment can significantly reduce your monthly mortgage payment and may eliminate the need for private mortgage insurance (PMI).
By gathering this information, you will gain a clearer understanding of your financial circumstances. This knowledge empowers you to make informed choices about how much house payment can I afford when investing in a property. We know how challenging this can be, and is essential during the home-buying journey. It allows you to manage expenses effectively and work towards long-term stability. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Calculate Key Financial Ratios
To effectively assess and your financial readiness for a home purchase, calculating key financial ratios is essential. We know how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
-
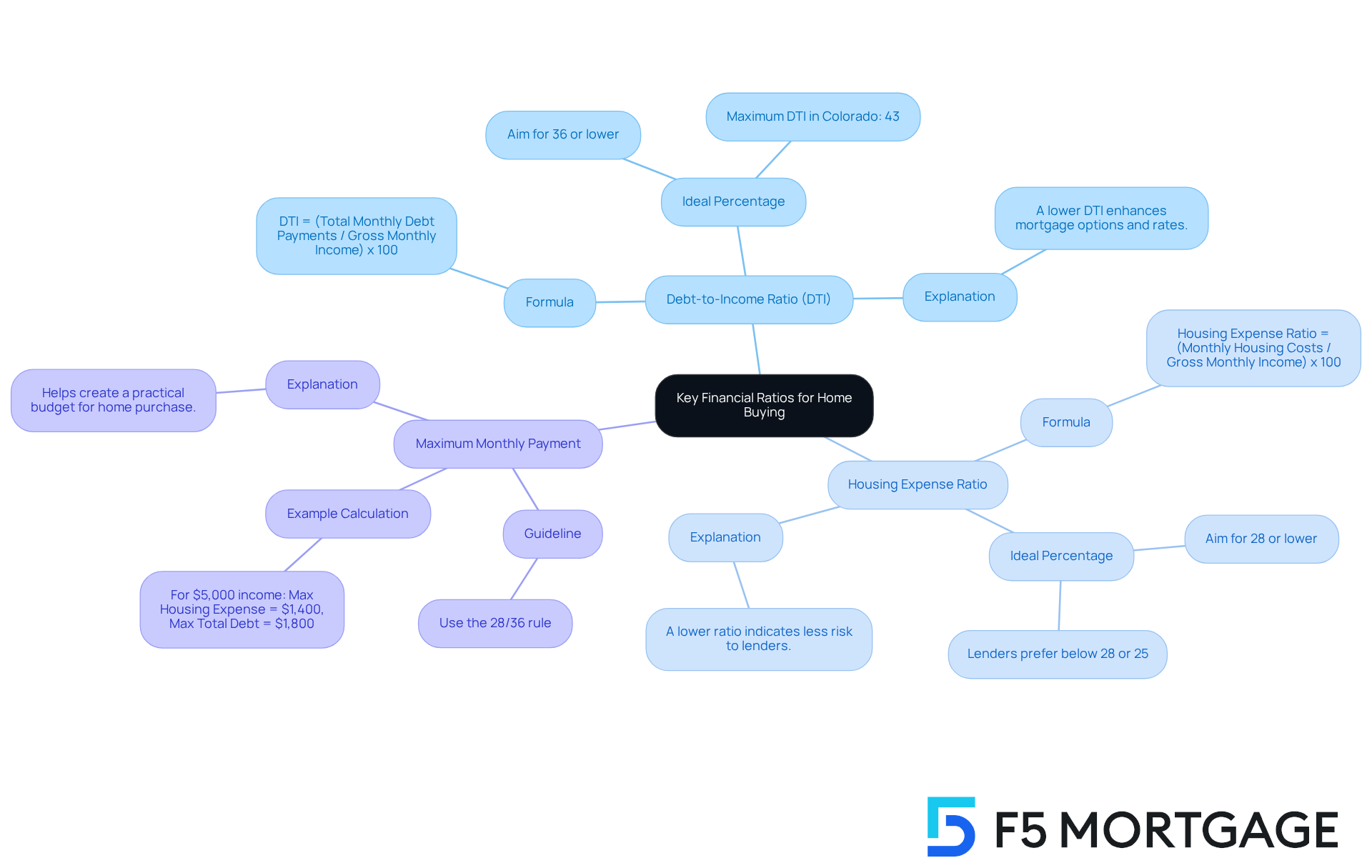
Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI):
- Formula: DTI = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100
- Aim for a DTI of 36% or lower to enhance your mortgage options. A DTI above this threshold may restrict your borrowing ability and result in less favorable credit conditions. In Colorado, a maximum DTI ratio of 43% is typically required for home loans, whether acquiring a traditional mortgage or refinancing an existing one. A better DTI can lead to more competitive mortgage rates. As Dan Silva, Vice President of Marketplace Lending at Own Up, states, “Along with savings and credit score, the debt-to-income ratio is the sole factor lenders utilize to assess if potential borrowers can meet their debt responsibilities each month.”
-
- Formula: Housing Expense Ratio = (Monthly Housing Costs / Gross Monthly Income) x 100
- Ideally, this ratio should be 28% or less, encompassing your mortgage payment, property taxes, and insurance. A lower housing expense ratio indicates less risk to lenders and increases your chances of mortgage approval. Exceeding this ratio can signal financial strain, making it crucial to stay within recommended limits.
-
Calculate Your Maximum Monthly Payment:
- Utilize the 28/36 rule as a guideline. For instance, if your gross monthly income is $5,000, your maximum housing expense should be $1,400 (28% of $5,000), while total debt payments should not exceed $1,800 (36% of $5,000).
By precisely calculating these ratios, you can create a practical budget for your property acquisition, allowing you to assess how much house payment can I afford while ensuring that your housing expenses stay manageable and in line with your overall financial objectives. Additionally, if you’re considering refinancing, F5 Mortgage offers various options tailored to Colorado residents, including conventional loans, FHA loans, and VA loans, which can help you secure better rates and terms based on your DTI. Remember, these calculations are just one part of a broader assessment of your financial readiness for home buying.
Apply Your Calculations to Determine Affordability
Determining how much house payment can I afford can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to guide you through the process with care. Follow these steps to gain clarity and confidence in your home search:
-
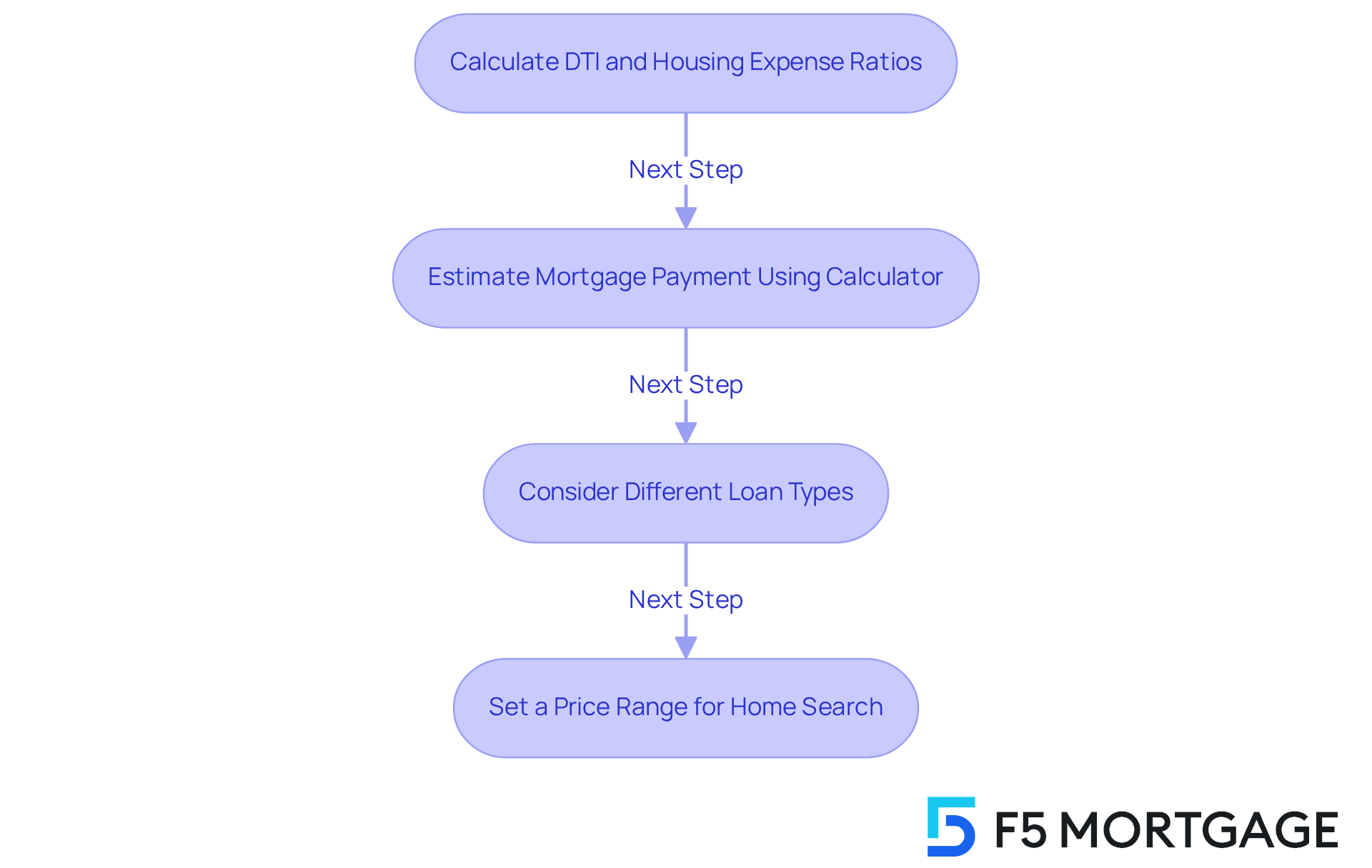
Use Your DTI and Housing Expense Ratios:
- Start by calculating your debt-to-income (DTI) and housing expense ratios. This helps you identify how much house payment can I afford on a monthly basis. Typically, lenders suggest that your housing costs should not exceed 28% of your gross income each month. We know how challenging it can be to balance these figures, but understanding them is crucial.
-
Estimate Your Mortgage Payment:
- Next, utilize a mortgage calculator to estimate your monthly payment based on various home prices, interest rates, and loan terms. For instance, if your budget allows for a $1,400 monthly contribution, enter this amount into the calculator to find the related property price. With around 6.78% for a 30-year fixed mortgage, this could lead to a home price range of roughly $250,000 to $300,000, depending on your initial contribution. Visualizing these numbers can make the process feel more manageable.
-
Consider Loan Types:
- Different loan types, such as FHA, VA, and conventional loans, come with unique requirements and benefits. For example, FHA financing may require a lower down payment, making it appealing for first-time homebuyers, while VA options offer favorable terms for eligible veterans. Assess which loan type aligns best with your financial situation and long-term goals. Remember, each option has its advantages, and we’re here to help you navigate these choices.
-
Set a Price Range:
- Based on your calculations, establish a price range for your home search. If your calculations suggest you can manage a monthly payment of $1,400 at a 4% interest rate on a 30-year mortgage, you should consider how much house payment can I afford for properties priced between $250,000 and $300,000. This approach allows you to focus your search on homes that fit within your financial reach, making the process less daunting.
By applying these calculations and understanding the nuances of different loan options, you can confidently navigate the housing market with a clear grasp of your affordability. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Factor in Additional Homeownership Costs
When budgeting for a home, we know how challenging it can be to navigate additional costs and determine how much house payment can I afford. Understanding these expenses is crucial for your financial planning, especially when considering how much house payment can I afford, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
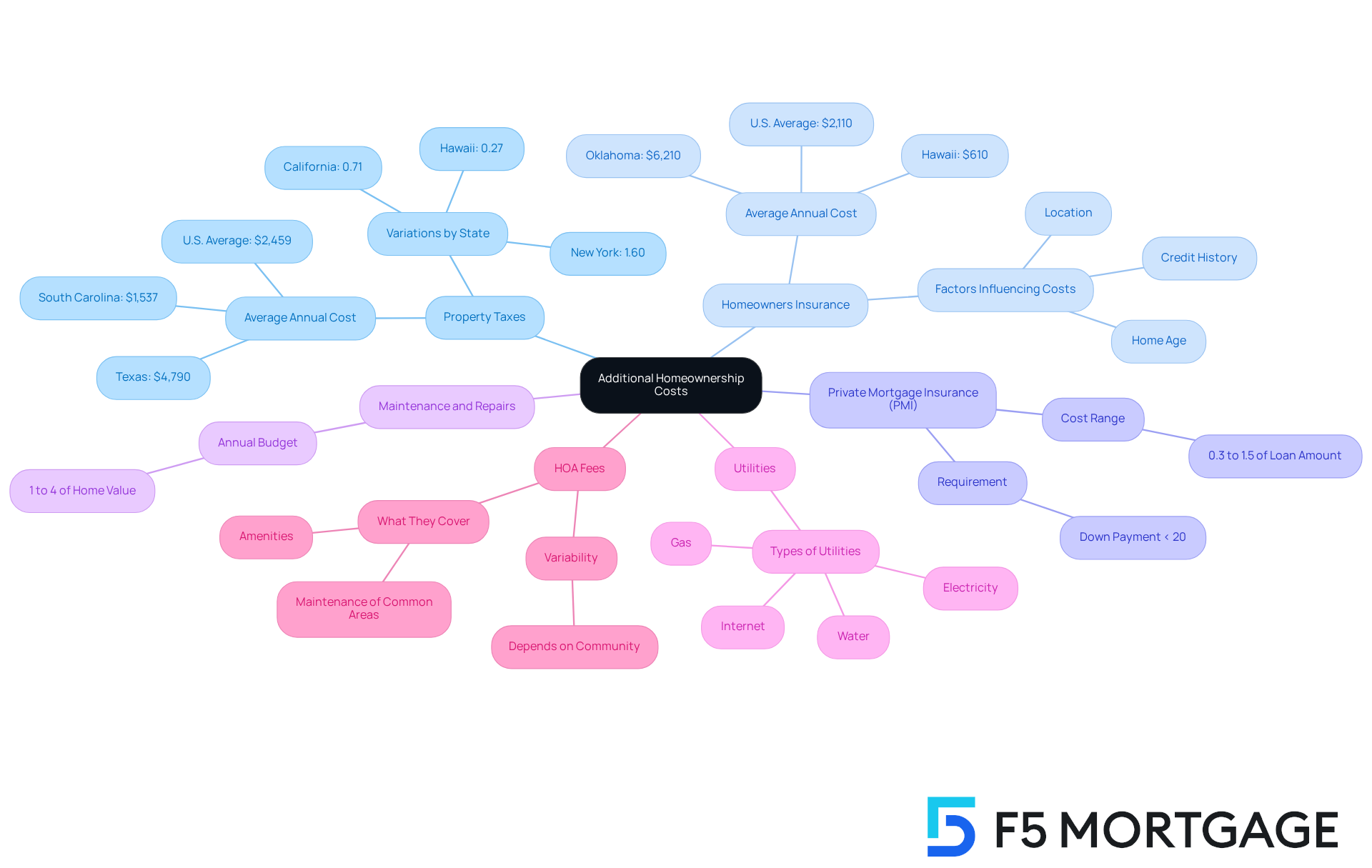
- Property Taxes: Property taxes can vary significantly by location, impacting your overall budget. For instance, the average U.S. household spends about $2,459 annually on property taxes, with rates differing widely across states. In South Carolina, the effective real-estate tax rate is 0.51%, resulting in annual taxes of approximately $1,537 on a property valued at $303,400. In contrast, Texas has an effective tax rate of 1.58%, leading to yearly taxes of approximately $4,790 on the same property value. Investigate the average property tax rate in your area to accurately include this in your budget.
- Homeowners Insurance: This insurance protects your home and belongings from various risks. The average annual cost of homeowners insurance in the U.S. is around $2,110 for a dwelling coverage of $300,000, but this can vary significantly based on location and other factors. For example, homeowners in Oklahoma face the highest average costs at $6,210 annually, while those in Hawaii enjoy the lowest rates at $610. It’s advisable to get quotes from multiple providers to estimate your premium accurately.
- Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): If your down payment is less than 20%, you may need to pay PMI, which can add a significant amount to your monthly costs. This insurance protects the lender in case of default and typically ranges from 0.3% to 1.5% of the original loan amount annually.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Set aside 1% to 4% of your home’s value annually for maintenance and repairs. This budget should cover routine upkeep and unexpected repairs, ensuring your home remains in good condition.
- Utilities: Don’t forget to such as water, electricity, gas, and internet. These costs can add up quickly and should be included in your overall financial planning.
- Homeowners Association (HOA) Fees: If you buy a property in a community with an HOA, include these fees in your budget. HOA fees can vary widely, so it’s essential to understand what they cover and how they fit into your financial plan.
By factoring in these additional costs, you can assess how much house payment can I afford and create a more accurate budget to ensure that you are financially prepared for homeownership.
Conclusion
Understanding how much house payment can be afforded is an essential aspect of the home-buying process. We know how challenging this can be. By carefully evaluating your financial circumstances, you can make informed choices that align with your budget and long-term goals. This guide emphasizes the importance of a thorough assessment of income, expenses, debt obligations, and savings to establish a solid foundation for homeownership.
Key arguments presented throughout the article include the necessity of calculating crucial financial ratios, such as the debt-to-income and housing expense ratios. These ratios help determine what monthly payment is manageable for you. Additionally, we highlight the importance of considering various loan types and additional homeownership costs, such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance. These factors can significantly impact overall affordability. By following these steps, you can confidently navigate your financial readiness for a property purchase.
Ultimately, the journey to homeownership is not just about finding the right property but also about ensuring that your financial decisions are sound and sustainable. By employing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can take proactive steps towards securing your dream home while maintaining financial stability. Embrace the challenge of home buying with a well-informed approach, and remember: thorough financial planning today can lead to a successful and rewarding homeownership experience tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What information should I gather to understand my financial situation?
You should gather information about your total monthly income, monthly expenses, existing debt obligations, and savings for a down payment and emergency funds.
Why is calculating my total monthly income important?
Calculating your total monthly income is crucial as it forms the foundation for your budget and helps determine your borrowing capacity.
What types of monthly expenses should I consider?
You should list all recurring monthly expenses, including utilities, groceries, transportation, and maintenance costs, which average about $10,000 annually for U.S. families.
How do I assess my debt obligations?
Record all existing debts, such as credit card balances, student loans, and car financing, to help calculate your debt-to-income ratio, which lenders use to assess your financial health.
What is a healthy debt-to-income ratio for home loans?
A debt-to-income ratio of less than 43% is typically required for home loans, indicating a strong financial position.
How can I calculate my debt-to-income ratio?
You can calculate it using the formula: (Total monthly debt expense / gross monthly income) X 100.
What savings should I have for a down payment?
It is recommended to set aside at least 20% to 25% of the property’s cost for the initial deposit, especially if considering FHA loans.
How long should I save before purchasing a property?
It’s wise to save for three to four years in advance for a property purchase to ensure you have adequate funds.
What are the benefits of a larger down payment?
A larger down payment can significantly reduce your monthly mortgage payment and may eliminate the need for private mortgage insurance (PMI).
How does understanding my financial situation help in the home-buying process?
Gaining a clearer understanding of your financial circumstances empowers you to make informed choices about how much house payment you can afford and manage expenses effectively for long-term stability.








