Overview
When it comes to choosing between a 15-year and a 30-year mortgage, it’s important to understand the key differences that can impact your family’s financial journey. We know how challenging this can be, so let’s explore these options together.
A 15-year mortgage typically involves higher monthly payments, but it also means you’ll pay less overall in interest. This can be a great choice if you’re looking to build equity quickly and save on interest costs in the long run. On the other hand, a 30-year mortgage offers lower monthly payments, which can be more manageable for families juggling various financial responsibilities.
Ultimately, the decision between these two options depends on your individual financial goals and circumstances. We’re here to support you every step of the way as you navigate this important choice. Take a moment to reflect on what works best for your family’s needs.
Introduction
Choosing the right mortgage can significantly impact your financial future, and we know how challenging this can be. With options like the 15-year and 30-year mortgages, it’s essential to understand the key differences between these two paths. A shorter loan term may offer lower interest rates and faster equity building, but it also comes with higher monthly payments that could strain your budget. On the other hand, the allure of lower monthly costs with a 30-year mortgage might lead to a greater overall financial burden due to increased interest payments.
So, which mortgage option aligns best with your financial goals and lifestyle choices? We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Understand the Basics of 15-Year and 30-Year Mortgages
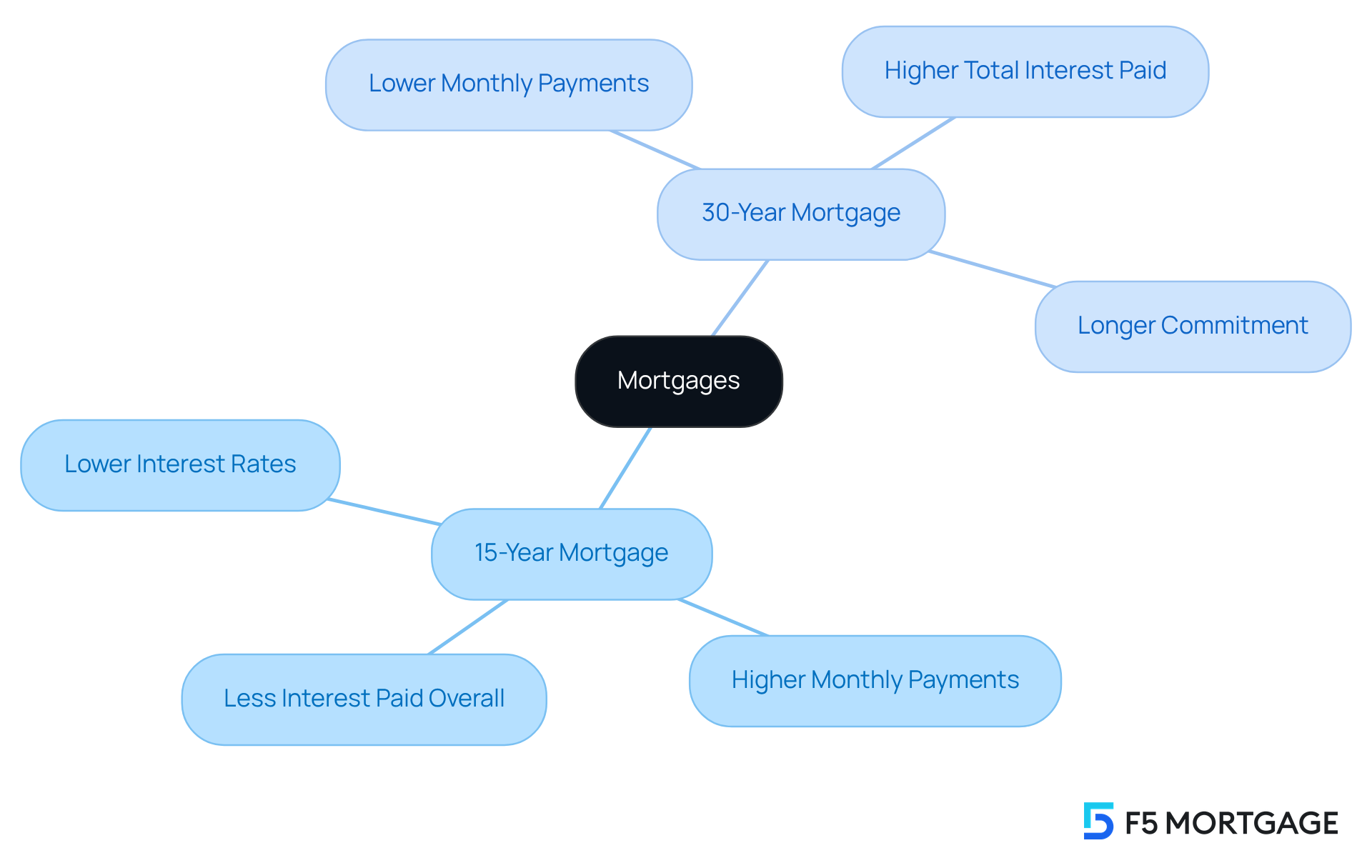
Choosing the right loan is a journey, and understanding your options is crucial. When considering a 15 vs 30 year mortgage, a loan with a 15-year term means you’re committing to a financial obligation that wraps up in just 15 years. On the other hand, a 15 vs 30 year mortgage term stretches that repayment period to 30 years. This shorter duration often comes with a lower interest rate, typically ranging from 0.25% to 1% less than longer-term loans.
While the monthly payments for a 15 vs 30 year mortgage may be higher for the 15-year option, it’s important to recognize that you will pay significantly less in interest over the life of the loan. This can be a great advantage for those who can manage the higher monthly costs. Conversely, when considering a 15 vs 30 year mortgage, a long-term loan offers the benefit of lower monthly payments, making it more manageable for families working with a tighter budget. However, this convenience can lead to higher overall interest charges due to the extended repayment period.
We know how challenging these decisions can be. That’s why it’s essential to understand these basics so you can match your loan choice with your financial goals and capabilities. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way as you navigate this important financial decision.
Compare Financial Costs: Monthly Payments and Total Interest
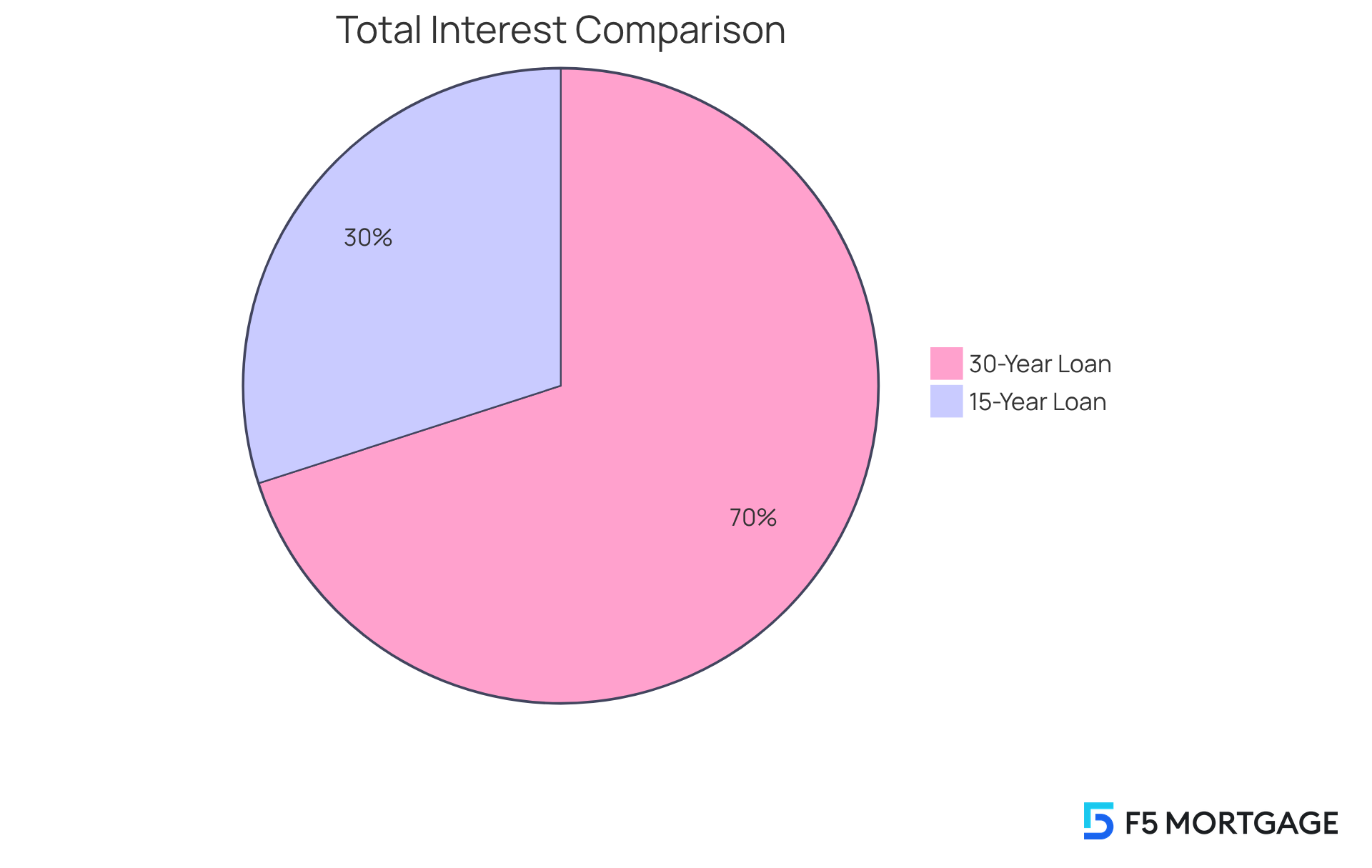
When considering the financial expenses of short-term versus long-term loans, many families face a considerable variation in monthly costs. For instance, on a $300,000 loan with a 6% interest rate, comparing the monthly payment for a 15 vs 30 year mortgage, the payment for the 15-year term would be approximately $2,530. In contrast, the comparison of a 15 vs 30 year mortgage shows that a 30-year term would lower that monthly cost to around $1,800. We know how challenging it can be to navigate these options.
Throughout the duration of the loan, the overall interest paid on the shorter-term loan would be around $92,000. This is significantly less than the roughly $215,000 paid for the longer-term loan. This clear difference highlights an important consideration: while a 15 vs 30 year mortgage long-term loan requires a higher monthly payment, it ultimately saves borrowers a substantial amount in interest.
For those who can manage the higher payments, choosing a long-term loan can be a financially wise option. We’re here to support you every step of the way as you make this important decision.
Evaluate Pros and Cons: Which Mortgage Fits Your Needs?
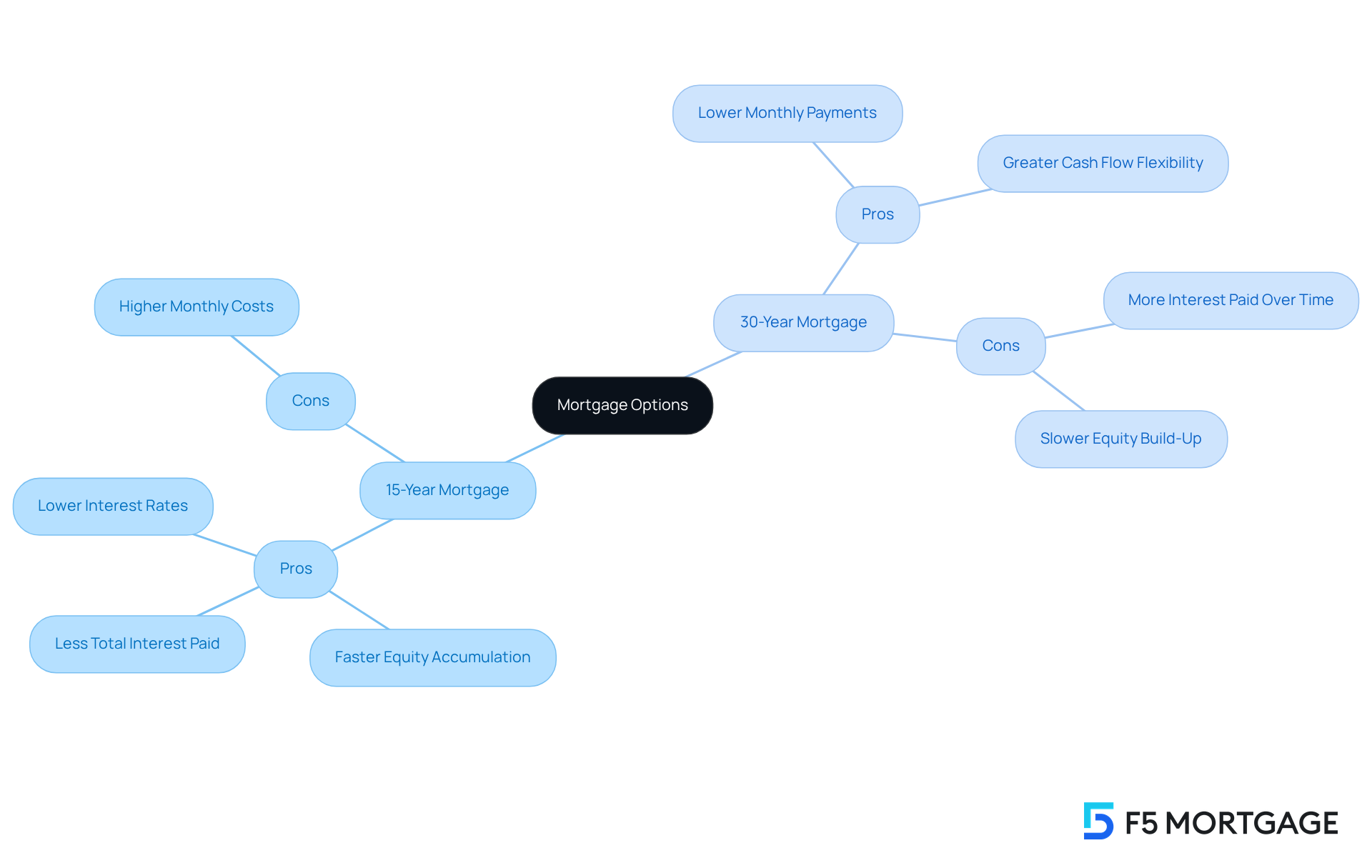
Choosing between a 15 vs 30 year mortgage and a shorter-term option can feel overwhelming, so it’s important to consider your personal financial situation and goals. When comparing a 15 vs 30 year mortgage, the 15-year loan offers some appealing advantages, such as:
- Lower interest rates
- Faster equity accumulation
- Less total interest paid
However, we understand that the higher monthly costs might stretch your budget a bit more than you’d like.
On the other hand, when considering a 15 vs 30 year mortgage, a 30-year loan can ease your monthly expenses, providing greater cash flow flexibility. This can be particularly beneficial for families with additional financial responsibilities. Yet, it’s essential to recognize that borrowers considering a 15 vs 30 year mortgage will end up paying more in interest over time and may take longer to build equity.
Ultimately, your decision should reflect your financial stability, long-term aspirations, and comfort with the monthly payments. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way as you navigate this important choice.
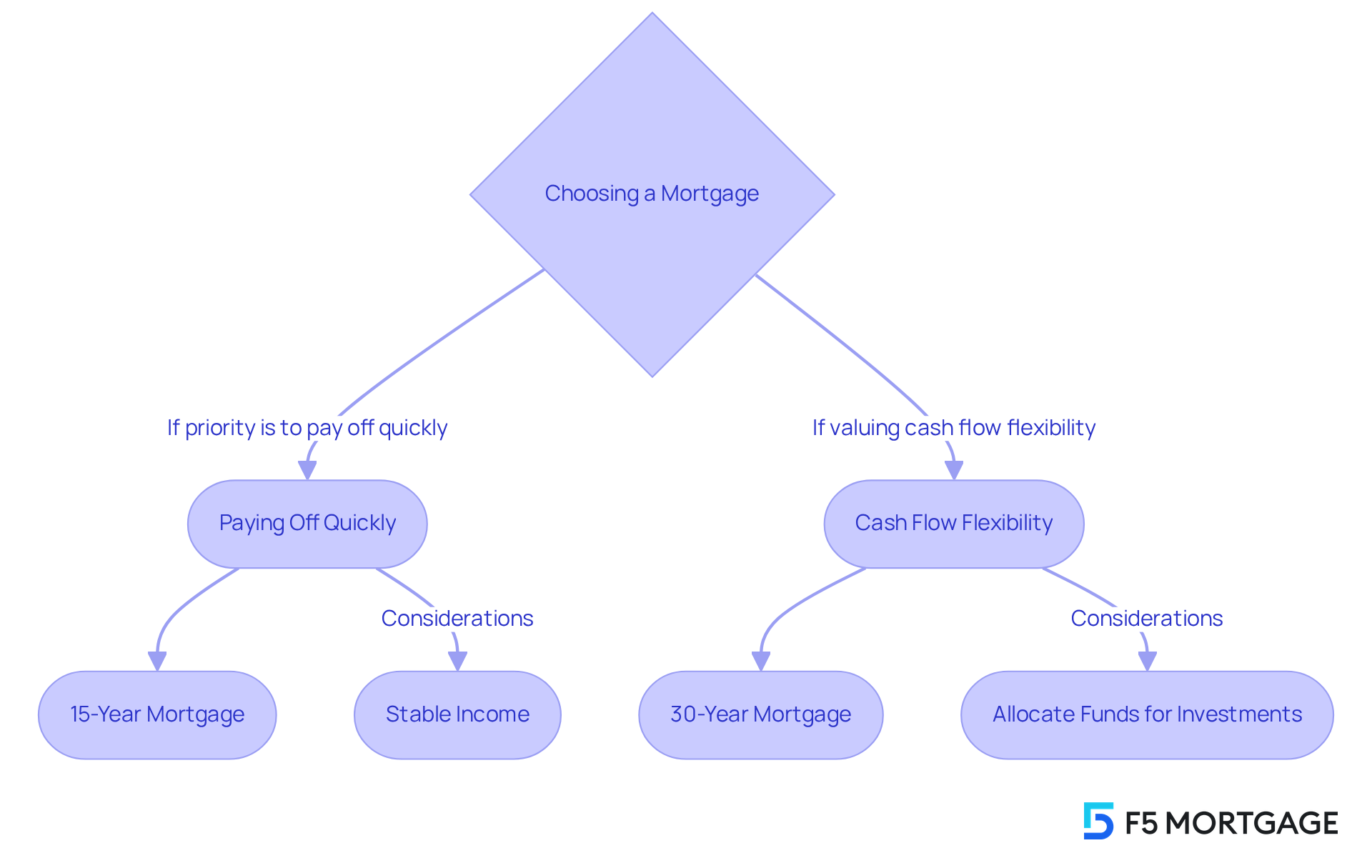
Consider Your Financial Goals and Lifestyle
When choosing between a 15 vs 30 year mortgage and a shorter-term option, we know how challenging this decision can be. It’s essential to reflect on your financial objectives and way of living. If your priority is to pay off your home quickly and save on interest, considering a 15 vs 30 year mortgage may be the best fit for you. This choice is perfect for individuals with stable incomes who can handle larger monthly expenses.
On the other hand, if you value cash flow flexibility and want to allocate funds toward other investments or savings, a 15 vs 30 year mortgage comparison might show that a 30-year mortgage is more suitable. It allows for lower monthly payments, freeing up resources for other financial goals, such as retirement savings or education funds.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your individual circumstances. Consider your income stability, future financial plans, and personal comfort with debt. We’re here to support you every step of the way as you navigate these important decisions.
Conclusion
Choosing between a 15-year and a 30-year mortgage is a significant financial decision that can profoundly impact your future. We understand how challenging this choice can be. The core distinction lies in the repayment term: the 15-year mortgage typically offers lower interest rates and less total interest paid, while the 30-year mortgage provides lower monthly payments, making it more manageable for families with tighter budgets.
In this discussion, we’ve explored key points regarding the financial implications of each mortgage type. A 15-year mortgage results in higher monthly payments, but it ultimately saves you a considerable amount in interest over the life of the loan. On the other hand, a 30-year mortgage may ease your monthly financial strain, but it leads to higher overall interest costs and a slower equity buildup. It’s essential that your choice aligns with your personal financial goals, lifestyle, and comfort with debt.
Reflecting on these considerations, it’s clear that understanding the differences between a 15 vs. 30-year mortgage is crucial for making informed decisions. Whether your priority is to pay off your home quickly or to maintain cash flow flexibility, the right choice hinges on your individual circumstances and future aspirations. We’re here to support you every step of the way as you evaluate these factors, empowering you to select the mortgage that best fits your financial landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a 15-year and a 30-year mortgage?
A 15-year mortgage means you commit to paying off the loan in 15 years, while a 30-year mortgage extends the repayment period to 30 years.
What are the typical interest rates for 15-year and 30-year mortgages?
A 15-year mortgage typically has a lower interest rate, usually ranging from 0.25% to 1% less than that of a 30-year mortgage.
How do monthly payments compare between a 15-year and a 30-year mortgage?
Monthly payments for a 15-year mortgage are generally higher than those for a 30-year mortgage.
What is the advantage of choosing a 15-year mortgage?
The advantage of a 15-year mortgage is that you will pay significantly less in interest over the life of the loan.
What is a potential downside of a 30-year mortgage?
A potential downside of a 30-year mortgage is that, while the monthly payments are lower, you may end up paying more in overall interest due to the extended repayment period.
How should I decide between a 15-year and a 30-year mortgage?
It’s essential to understand your financial goals and capabilities to choose the mortgage that best matches your situation.








