Overview
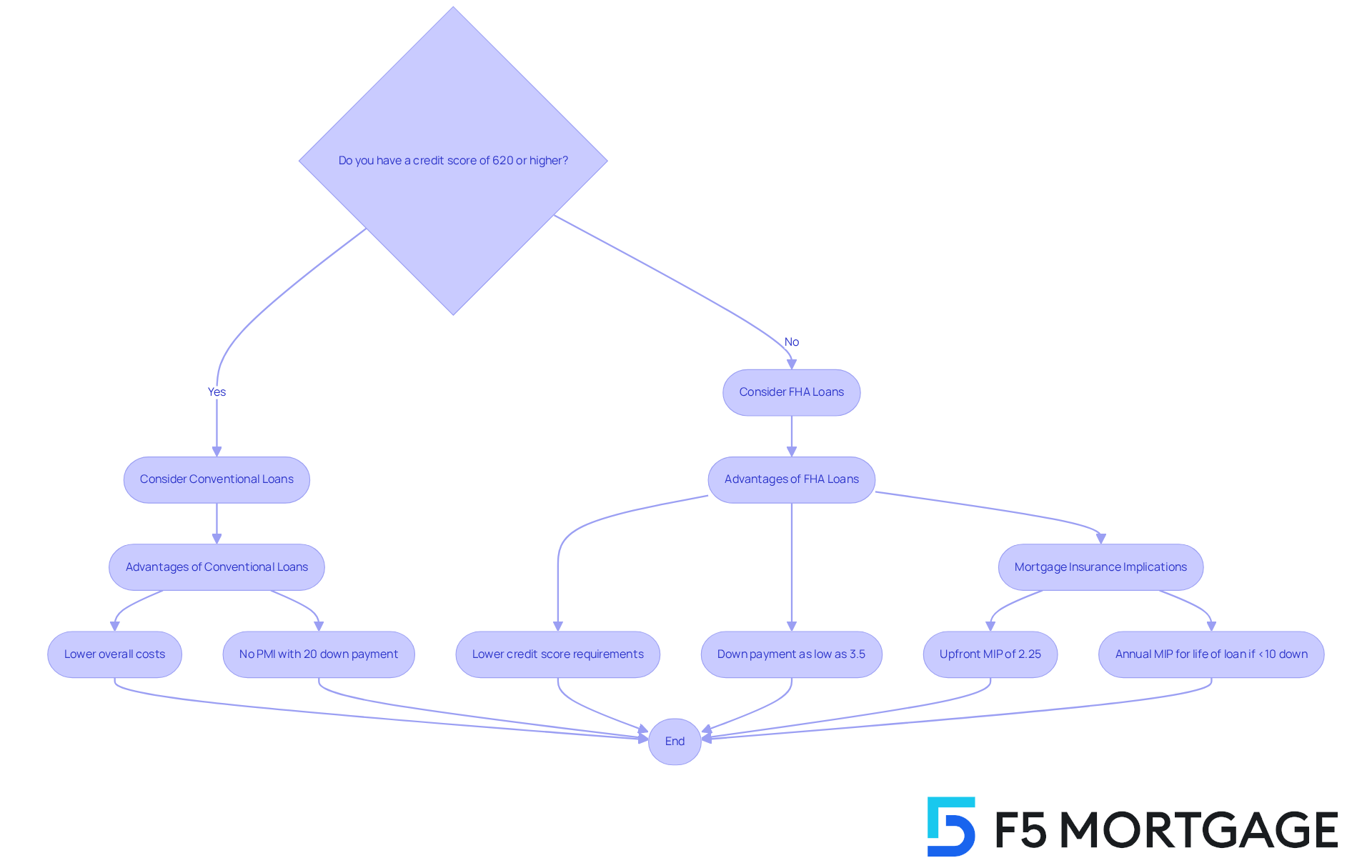
Navigating the world of home loans can feel overwhelming, especially for first-time buyers or those facing financial hurdles. Understanding the main difference between FHA and conventional loans can be a crucial step in your journey. FHA loans are designed with accessibility in mind, allowing for lower credit scores and down payments. This makes them a more suitable option for individuals who may be experiencing financial challenges.
For instance, FHA loans require a minimum credit score of just 580 for a down payment of 3.5%. In contrast, conventional loans typically demand a credit score of at least 620 and often require larger down payments. By illustrating these differences, we see how each loan type caters to various financial situations, ensuring that there is a path forward for everyone.
We know how challenging this can be, but we’re here to support you every step of the way. As you consider your options, remember that understanding these distinctions can empower you to make informed decisions about your future home.
Introduction
Understanding the landscape of mortgage options is crucial for anyone embarking on the journey to homeownership. We know how challenging this can be, especially when faced with choices like FHA and conventional loans. These options present distinct paths that cater to varying financial situations and credit histories.
This article delves into the nuances of these two loan types, exploring their unique features and requirements. As you consider your options, we’re here to support you every step of the way. The implications of each choice are significant, and as you weigh them, the question remains: which loan structure will best support your aspirations while navigating the complexities of home financing?
Define FHA and Conventional Loans
FHA mortgages, or Federal Housing Administration mortgages, are here to help. We know how challenging it can be for low-income and first-time homebuyers to secure funding for a home. These government-supported financing options are designed specifically to assist you in this journey. The difference between FHA and conventional mortgages is that FHA loans typically require lower credit scores and down payments, making them more accessible.
On the other hand, traditional financing is not backed by the government. This means they usually demand higher credit scores and down payments, which can be daunting. Traditional loans can fall into two categories:
- Conforming loans, which adhere to guidelines set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac
- Non-conforming loans, which do not meet these standards
Understanding the difference between FHA and conventional loans is crucial as you navigate your home-buying journey. We’re here to support you every step of the way, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your needs and circumstances.
Examine FHA Loan Requirements and Features
FHA loans are designed to be accessible, requiring a minimum credit score of 580 for a down payment of just 3.5%. If your credit score falls between 500 and 579, a 10% down payment is necessary. Beyond credit scores, it’s important for applicants to show stable income and maintain a debt-to-income ratio (DTI) of 43% or less. Additionally, these financial products come with mortgage insurance premiums (MIP), which include both an upfront premium and ongoing monthly payments.
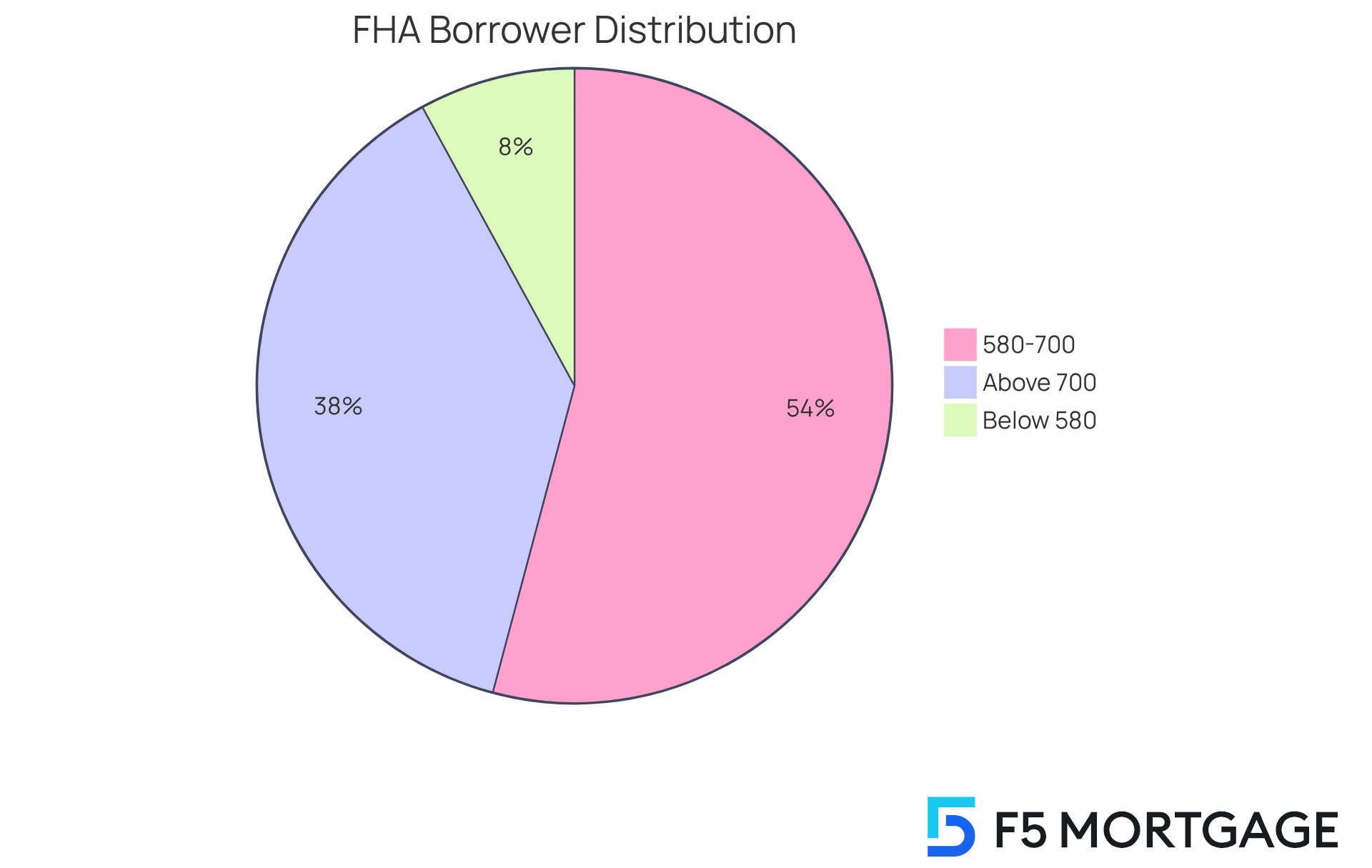
The benefits of FHA financing shine particularly for first-time homebuyers, as they help lower financial barriers and offer flexible underwriting criteria. For instance, in 2020, half of all FHA mortgages were secured by borrowers with credit scores between 600 and 700. This highlights how appealing this program is for those with less-than-perfect credit histories. Moreover, 35% of FHA borrowers had scores of 700 or higher, indicating that even those with strong financial backgrounds are taking advantage of these favorable terms.
Real-life stories showcase how FHA financing can effectively support individuals with low credit ratings. Borrowers with scores as low as 500 have successfully obtained mortgages, albeit with a higher down payment requirement. This flexibility opens the door to homeownership for many families who might otherwise feel excluded from traditional financing options. Additionally, FHA mortgages are particularly beneficial for those looking to improve their homes, offering a pathway to funding that accommodates various financial situations.
In summary, FHA financing stands as a vital resource for first-time homebuyers and those with lower credit ratings. It provides a blend of accessibility and support, empowering individuals to navigate the home buying process with confidence. We understand how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Explore Conventional Loan Criteria and Characteristics
We know how challenging navigating the mortgage process can be. Traditional financing typically requires a minimum credit rating of 620, though many providers prefer ratings of 740 or higher to offer the best terms. While the down payment can be as low as 3%, it’s important to note that if you put down less than 20%, you’ll need to pay private mortgage insurance (PMI).
At F5 Mortgage, we’re here to support you every step of the way. We understand the importance of flexibility, which is why we offer competitive rates and personalized assistance to help families achieve their dream of homeownership. Traditional financing provides greater flexibility in terms of loan amounts and property categories, often resulting in lower overall costs compared to FHA options, illustrating the difference between FHA and conventional financing, especially for those with strong financial backgrounds.
With our fast and efficient pre-qualification process, you can take the first step towards homeownership in just 10 minutes. Let us help you turn your dreams into reality, because we believe everyone deserves a place to call home.
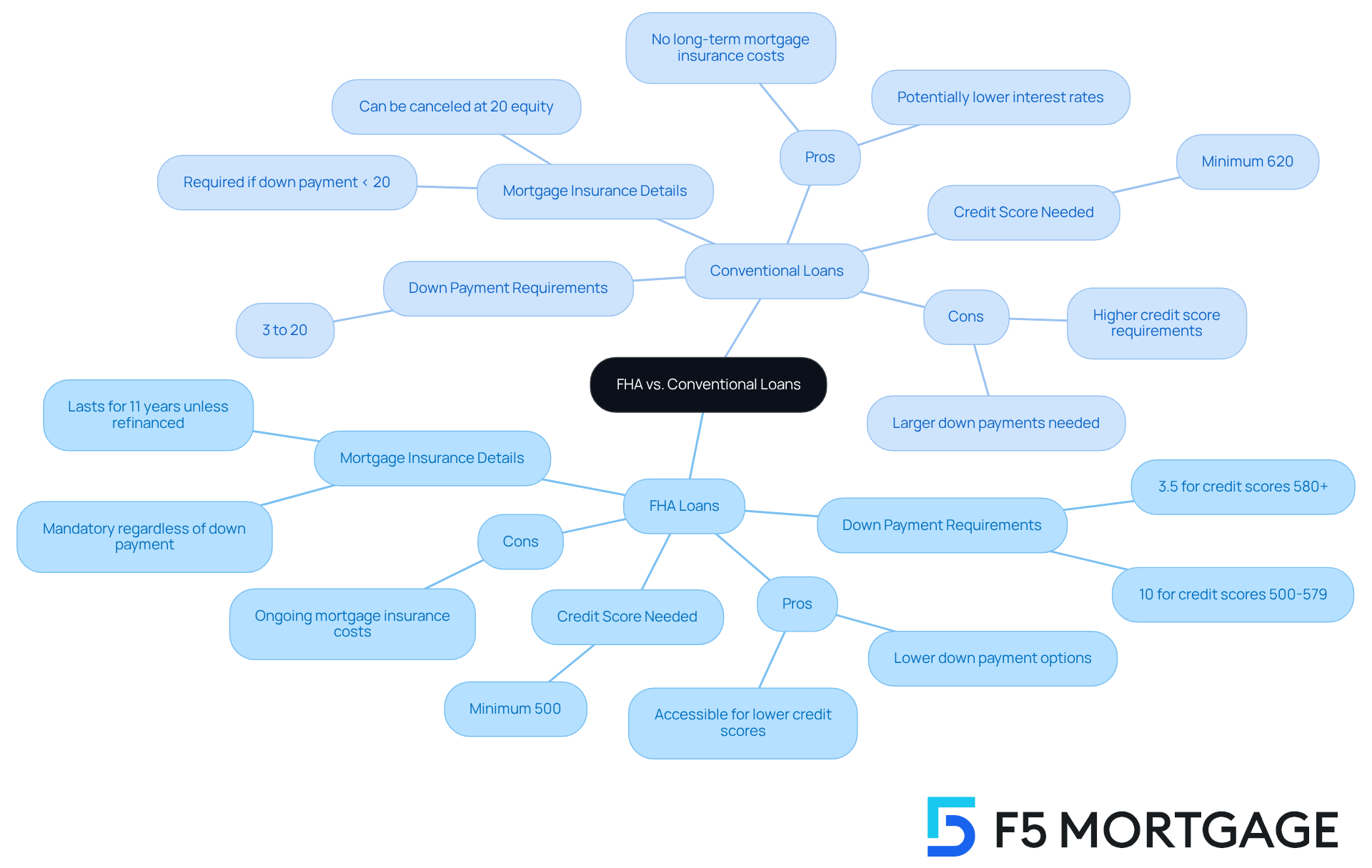
Compare Pros and Cons of FHA vs. Conventional Loans
FHA mortgages can be a wonderful option for first-time homebuyers, especially because they offer reduced down payment requirements. For individuals with credit scores of 580 or higher, the down payment can be as low as 3.5%. We understand that this accessibility is crucial, as even those with credit scores as low as 500 may qualify, although they would need to make a higher down payment of at least 10%. However, it’s important to note that FHA mortgages require mandatory mortgage insurance, which can significantly increase the overall cost over time. For instance, even with a 10% down payment, mortgage insurance remains in effect for 11 years unless the loan is refinanced.
On the other hand, traditional financing typically requires higher credit scores—usually at least 620—and down payments ranging from 3% to 20%. While these options may come with lower interest rates, borrowers who put down less than 20% will need to pay for private mortgage insurance (PMI), which can be canceled once they achieve 20% equity in their home. This flexibility can lead to significant savings for those who can manage the higher initial costs.
Real-life scenarios highlight these differences: families with lower credit scores often find FHA financing to be a viable option, allowing them to enter the housing market sooner. Conversely, families with stronger financial profiles may prefer traditional financing to avoid the long-term costs associated with mortgage insurance.
When weighing the pros and cons, FHA financing provides a pathway to homeownership for individuals facing financial challenges, but the ongoing mortgage insurance can be a drawback. Traditional financing options, while requiring stronger financial standing and larger down payments, can ultimately save money in the long run for those who qualify. The difference between FHA and conventional financing hinges on personal financial situations and long-term homeownership goals. It’s essential for borrowers to thoroughly assess their unique circumstances, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Guide to Choosing Between FHA and Conventional Loans
Choosing between financing options requires understanding the difference between FHA and conventional loans, and it can feel overwhelming, but it’s essential to carefully consider important elements like your financial history, down payment ability, and long-term financial goals. FHA mortgages are often a great option for those with lower credit scores or limited savings, as they allow a minimum score of 500 and down payments as low as 3.5%. This accessibility makes them particularly appealing for first-time homebuyers or anyone facing financial challenges.
On the other hand, if you have a strong credit profile—usually a score of 620 or higher—and can manage a larger down payment, it is important to consider the difference between FHA and conventional mortgages, as a conventional mortgage might be more advantageous. These loans typically come with lower overall costs, especially when you factor in private mortgage insurance (PMI), which can be completely avoided with a down payment of 20% or more. Additionally, traditional financing options often provide greater flexibility regarding limits and property types, making them suitable for buyers in competitive markets.
It’s also important to consider the total cost of mortgage insurance and your plans for the property. FHA loans require an upfront mortgage insurance premium (MIP) of 2.25% and an annual MIP that lasts for the life of the loan if your down payment is below 10%. In contrast, PMI for conventional loans can be canceled once you reach 80% equity in your home, potentially leading to significant savings over time.
Real-life stories highlight these points: families with lower credit scores have successfully used FHA loans to purchase their first homes, while others with higher credit scores have enjoyed the cost savings that illustrate the difference between FHA and conventional loans. Ultimately, your decision should reflect your unique financial situation and homeownership aspirations, ensuring you select the mortgage type that best supports your journey. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between FHA and conventional loans is vital for prospective homebuyers as they navigate the often complex landscape of mortgage options. We know how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
FHA loans, backed by the government, provide a more accessible pathway for individuals with lower credit scores and limited savings. This can be a lifeline for many first-time buyers and those facing financial challenges. On the other hand, conventional loans cater to those with stronger financial profiles, offering potentially lower overall costs.
Throughout this article, we’ve discussed key points, including the specific requirements and features of both loan types. FHA loans typically require lower credit scores and down payments, making them an attractive choice for many. Conversely, conventional loans demand higher credit ratings and down payments, but they can lead to significant savings over time, especially for borrowers who can avoid private mortgage insurance.
Ultimately, the choice between FHA and conventional loans should align with your individual financial situation and homeownership goals. It’s essential to consider factors such as your credit history, down payment capacity, and long-term financial implications. By thoroughly assessing these elements, you can make informed decisions that best support your journey toward homeownership.
Remember, seeking guidance from mortgage professionals can provide invaluable assistance in navigating this important financial milestone. You don’t have to do this alone; there are resources and people ready to help you achieve your dream of owning a home.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are FHA loans and how do they differ from conventional loans?
FHA loans, or Federal Housing Administration mortgages, are government-supported financing options designed to assist low-income and first-time homebuyers. They typically require lower credit scores and down payments compared to conventional loans, which are not backed by the government and usually demand higher credit scores and down payments.
What are the types of conventional loans?
Conventional loans can be categorized into two types: conforming loans, which adhere to guidelines set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, and non-conforming loans, which do not meet these standards.
What are the credit score requirements for FHA loans?
FHA loans require a minimum credit score of 580 for a down payment of 3.5%. If the credit score is between 500 and 579, a 10% down payment is necessary.
What other financial criteria must FHA loan applicants meet?
FHA loan applicants must show stable income and maintain a debt-to-income ratio (DTI) of 43% or less.
What are mortgage insurance premiums (MIP) associated with FHA loans?
FHA loans come with mortgage insurance premiums (MIP), which include both an upfront premium and ongoing monthly payments.
Who benefits the most from FHA financing?
FHA financing is particularly beneficial for first-time homebuyers and individuals with lower credit ratings, as it helps lower financial barriers and offers flexible underwriting criteria.
How have FHA loans been utilized by borrowers with varying credit scores?
In 2020, half of all FHA mortgages were secured by borrowers with credit scores between 600 and 700, while 35% of FHA borrowers had scores of 700 or higher, indicating that even those with strong financial backgrounds are taking advantage of these favorable terms.
Can individuals with low credit scores obtain FHA loans?
Yes, individuals with credit scores as low as 500 have successfully obtained FHA loans, although they are required to make a higher down payment. This flexibility opens the door to homeownership for many families who might otherwise feel excluded from traditional financing options.








