Overview
Understanding loan origination fees can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to support you every step of the way. These fees serve a crucial purpose: they cover the costs associated with processing your loan application. Over time, the evolution of these fees has shaped how they impact your overall borrowing costs.
It’s essential to recognize that negotiating these fees can lead to significant savings. We know how challenging this can be, but being informed about your options empowers you to make better financial decisions. Remember, loan origination fees are distinct from points, and understanding this difference can further aid your negotiation strategy.
By approaching this process with knowledge and confidence, you can navigate the complexities of loan origination fees and potentially save money. Take the time to ask questions and explore your options—your financial well-being is worth it.
Introduction
Navigating the mortgage landscape can feel overwhelming, especially when it comes to understanding loan origination fees. These upfront charges, often overlooked, can significantly impact the overall cost of borrowing. We know how challenging this can be, which is why it’s essential for borrowers to grasp the purpose of these fees and recognize their potential for negotiation.
As the financial environment evolves, how can you ensure that you are not only informed but also empowered to save on these fees? This article will delve into the history of loan origination fees, explore effective negotiation strategies, and clarify the critical distinctions between origination fees and points. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge needed to make savvy financial decisions that benefit you and your family.
Define Loan Origination Fees and Their Purpose
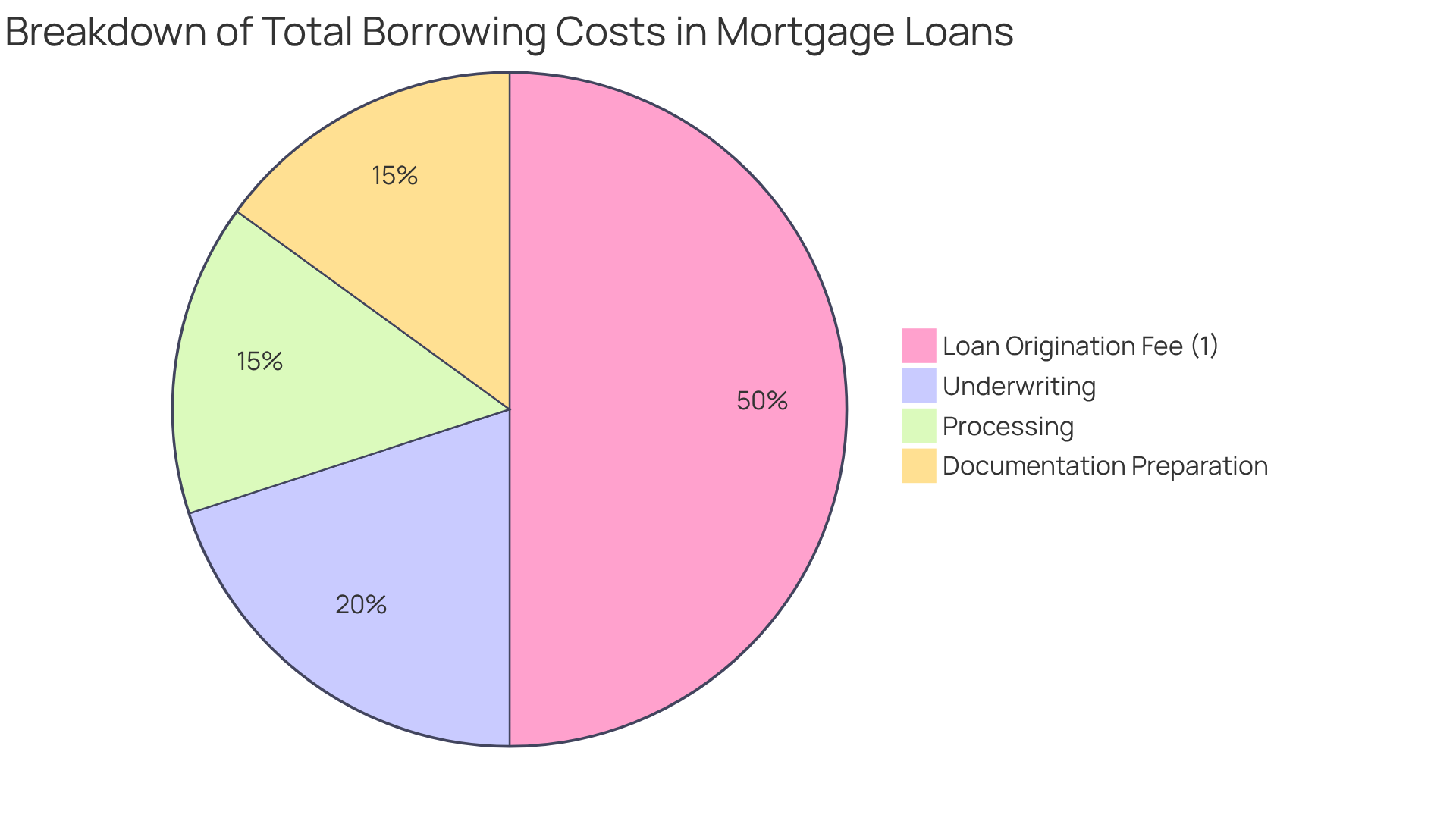
Advance charges are upfront costs that creditors apply to cover the expenses related to handling a new credit request. We know how challenging this can be, and it’s important to . Typically expressed as a percentage of the total loan amount, the loan origination fee compensates the lender for the administrative work involved in evaluating and approving the loan. For instance, if you seek a $200,000 mortgage with a 1% processing fee, you would face an expense of $2,000 at closing. This fee can significantly impact your overall borrowing costs, so it should definitely be included in your budget when considering a mortgage.
The main aim of the loan origination fee is to cover various expenses, including:
- Underwriting
- Processing
- Preparing the necessary documentation for closing
In 2025, the typical borrowing initiation cost is projected to be approximately 1% to 2% of the amount borrowed. This can accumulate rapidly, particularly for first-time home purchasers. Awareness of the loan origination fee is essential, as it is often negotiable and can vary significantly between lenders. Grasping the consequences of the loan origination fee empowers you to make knowledgeable choices and possibly save funds over time. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Explore the History and Evolution of Origination Fees
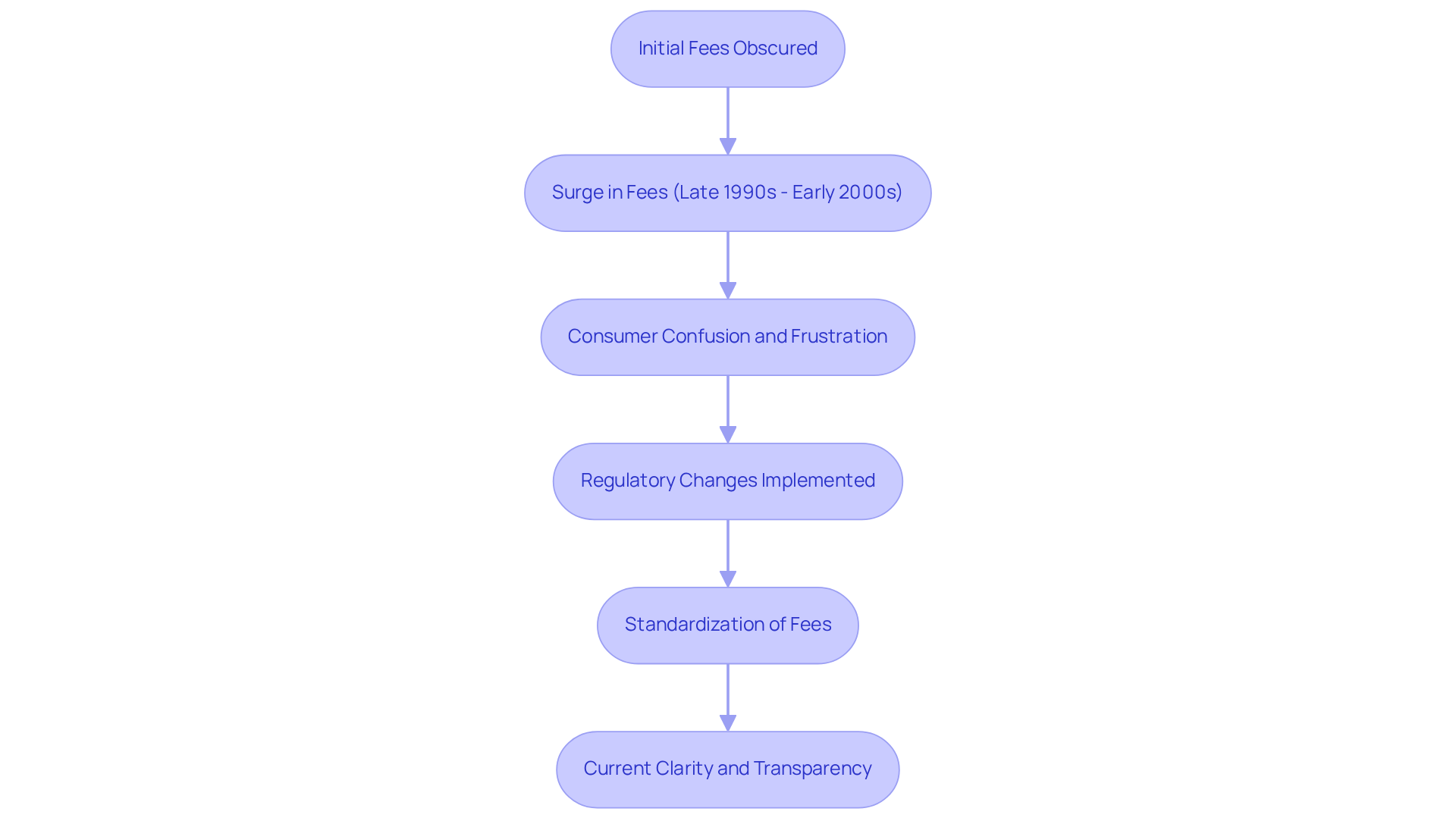
The [loan origination fee](https://debt.org/credit/loans/origination-fees) has long been a part of the mortgage landscape, evolving significantly in response to changing financial regulations and the needs of borrowers like you. Initially, these charges were often obscured within interest rates or bundled with other fees, leaving many borrowers in the dark about what they were truly paying. However, as calls for transparency grew louder, lenders began to clearly outline the loan origination fee, fostering a more open dialogue.
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, the prevalence of the loan origination fee surged, leading to confusion and frustration for many seeking loans. We understand how . In response, regulatory bodies stepped in to establish stricter guidelines, ensuring consumers were fully informed about all [associated costs](https://nasfaa.org/issue_brief_origination_fees). As a result, starting charges, which include the loan origination fee, have become more standardized, typically ranging from 0.5% to 1% of the total loan amount. Yet, it’s important to note that variations in the loan origination fee still exist, depending on the lender and your individual creditworthiness.
For instance, a 1% loan origination fee on a $300,000 mortgage translates to a $3,000 cost, highlighting the significant financial impact this fee can have on your journey toward homeownership. Thankfully, the evolution of regulations has brought about greater clarity, empowering you to evaluate the overall cost of financing more effectively. This includes not just initiation charges, but also interest rates and other related expenses. This shift not only equips you with the knowledge to make informed choices but also fosters a competitive lending environment, where your informed decisions can lead to substantial savings. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Negotiate and Save on Loan Origination Fees
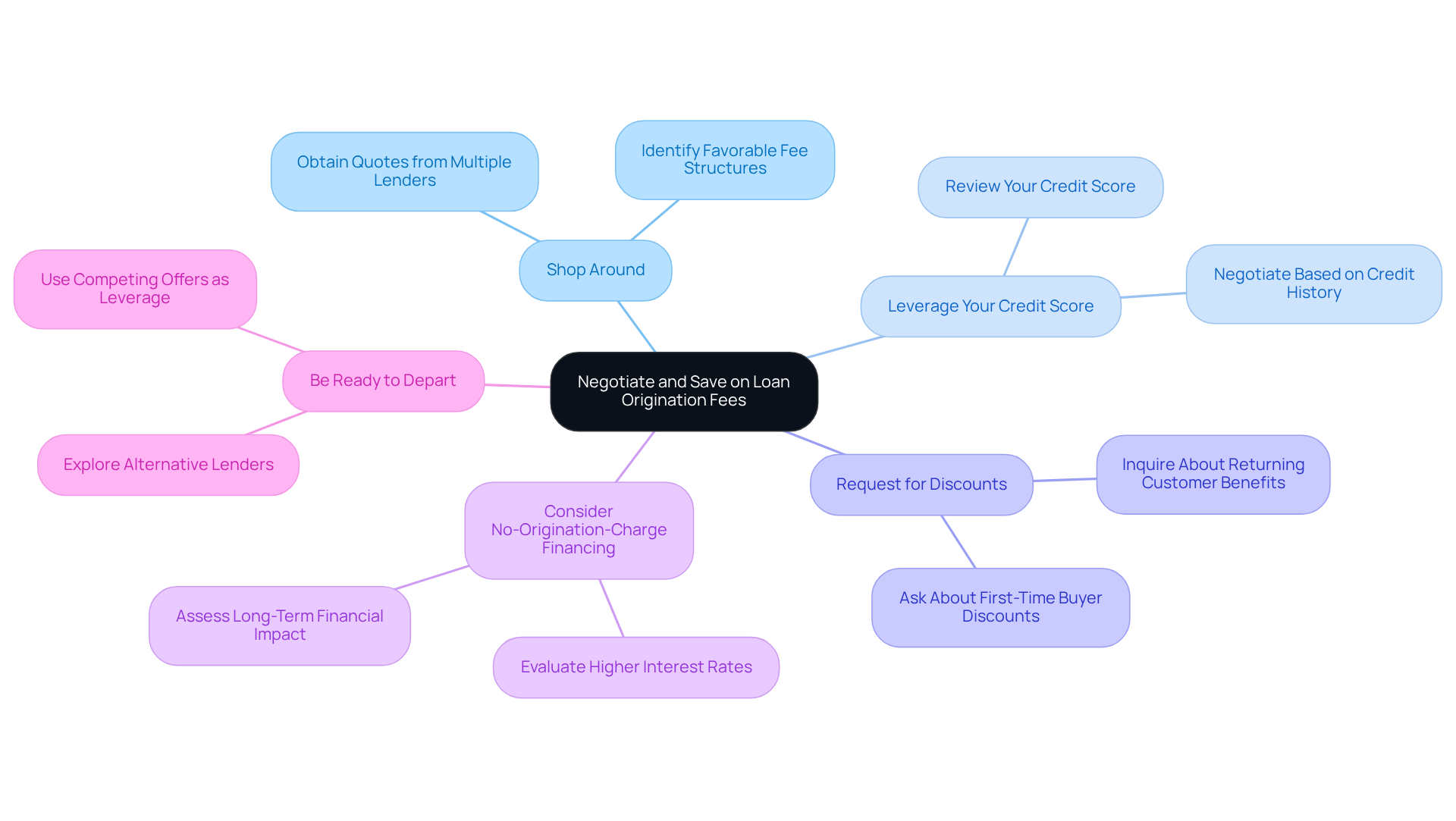
Negotiating the loan origination fee along with other startup costs can lead to significant savings for those seeking funds. We understand how challenging this process can be, so here are some effective strategies to consider:
- Shop Around: Lenders have diverse fee structures, making it crucial to obtain quotes from multiple sources. This allows you to identify lenders with the most , such as the loan origination fee, potentially saving you thousands.
- Leverage Your Credit Score: A strong credit score enhances your negotiating power. Lenders are often more willing to waive or lessen charges for borrowers with outstanding credit histories. It’s beneficial to review your score before applying.
- Request for Discounts: Don’t hesitate to ask about potential reductions in the initiation fee. Many lenders offer discounts for first-time homebuyers or returning customers, which can significantly lower your upfront costs, including the loan origination fee.
- Consider No-Origination-Charge Financing: Some lenders provide financing without origination charges, though they may compensate with a higher interest rate. Evaluate whether this option is more financially beneficial over the duration of the borrowing, including the loan origination fee.
- Be Ready to Depart: If a lender is inflexible on charges, be prepared to explore alternative choices. Indicating that you are considering other options can sometimes prompt lenders to offer better terms to retain your business.
Additionally, it’s important to remember that a maximum debt-to-income (DTI) ratio of 43% is typically required for home loans, which can influence your mortgage rates. By utilizing these strategies, you can effectively navigate the intricacies of loan origination fees and secure more advantageous mortgage conditions. As Karen Axelton notes, “Leverage expert advice to see if you can save thousands of dollars.” Furthermore, F5 Mortgage, with its commitment to transparency and technology-driven service, is here to support you in understanding your DTI ratio and exploring refinancing options tailored to your needs, ensuring a stress-free experience.
Differentiate Between Origination Fees and Points
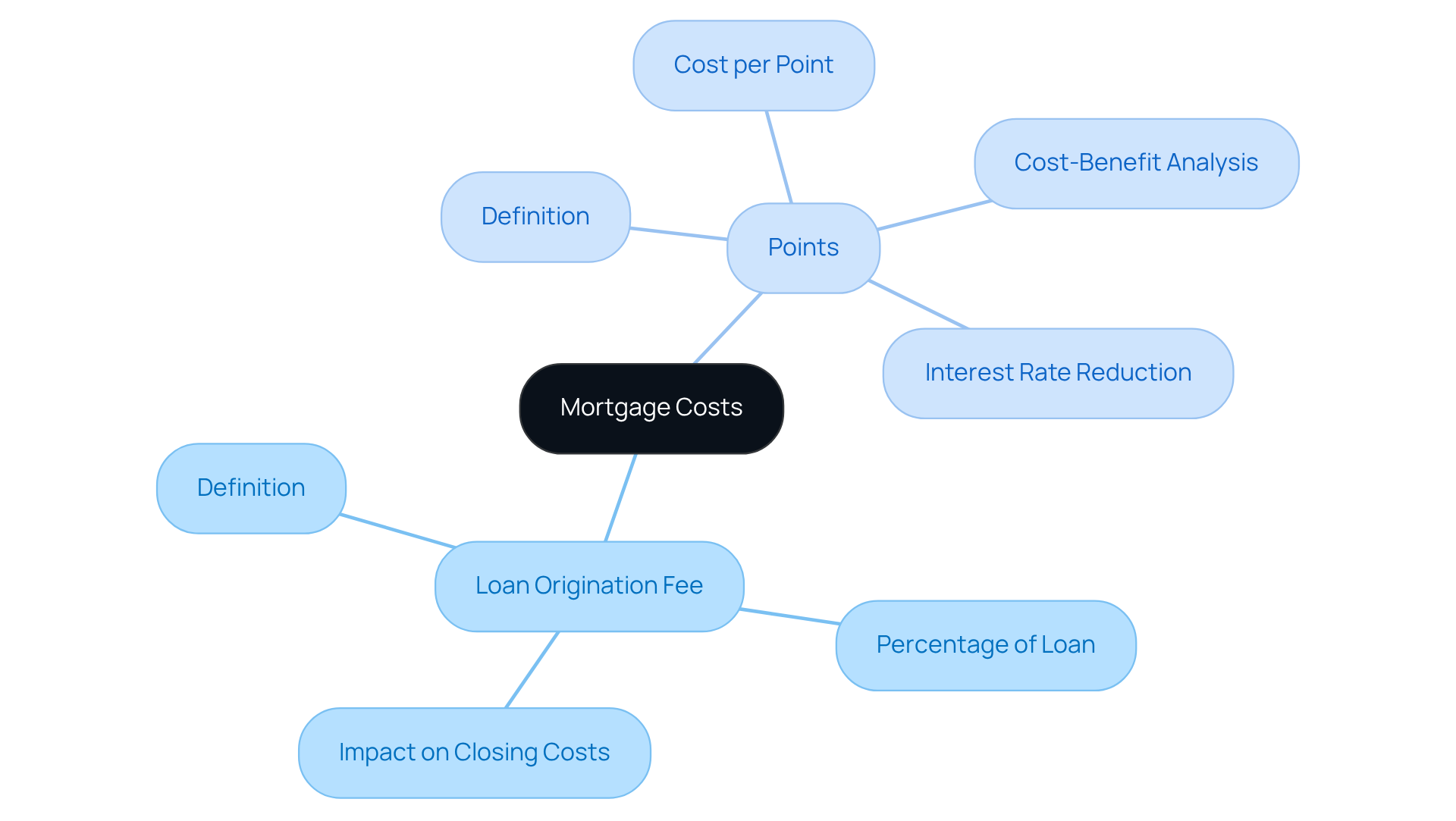
When navigating the mortgage process, understanding the costs involved can feel overwhelming. Two key components to consider are the loan origination fee and points, each serving distinct purposes that can impact your financial journey.
The loan origination fee is an upfront charge imposed by lenders to cover the costs of processing your loan application. Typically expressed as a percentage of the borrowed amount, the loan origination fee is settled at closing and can significantly affect your total closing expenses. We know how challenging it can be to manage these costs, but being informed can help you plan better.
Points: Often referred to as discount points, these optional fees allow you to lower your interest rates. Each point usually costs 1% of the borrowed amount and can reduce the interest rate by approximately 0.25%. For example, paying two points on a $200,000 loan would total $4,000 upfront, potentially leading to lower monthly payments due to the reduced interest rate. This option may seem daunting, but it can offer substantial savings in the long run.
Understanding the difference between the loan origination fee and points is crucial for anyone seeking a mortgage. In 2023, about 58.8% of homebuyers opted to pay points to secure , reflecting a growing trend as rates increased. By grasping these costs, you can develop effective strategies to manage your mortgage expenses.
For instance, calculating the break-even period for points—by dividing the cost of points by the monthly savings—can help you determine if paying points is a sound financial decision. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way as you navigate your mortgage options, empowering you to make informed choices that align with your financial goals.
Conclusion
Understanding loan origination fees is crucial for anyone navigating the mortgage landscape. We know how challenging this can be. These fees, which compensate lenders for the administrative work involved in processing loans, can significantly impact overall borrowing costs. By grasping the nuances of these fees, borrowers can make informed decisions that lead to potential savings and a more manageable financial journey.
The article has explored the history and evolution of loan origination fees, highlighting how regulatory changes have fostered transparency in the lending process. It has also provided practical strategies for negotiating these fees. We emphasize the importance of:
- Shopping around
- Leveraging credit scores
- Understanding the distinction between origination fees and points
Each of these insights equips borrowers with the knowledge necessary to navigate their mortgage options effectively.
Ultimately, being proactive in understanding and negotiating loan origination fees can lead to substantial financial benefits. It is essential for borrowers to take charge of their mortgage experience by asking questions, seeking advice, and exploring all available options. By doing so, they can ensure that they are not only aware of the costs involved but also empowered to make choices that align with their financial goals. This proactive approach paves the way for a successful homeownership journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are loan origination fees?
Loan origination fees are upfront costs charged by creditors to cover expenses related to processing a new credit request. They are typically expressed as a percentage of the total loan amount.
What is the purpose of loan origination fees?
The main purpose of loan origination fees is to compensate lenders for the administrative work involved in evaluating and approving a loan, including underwriting, processing, and preparing necessary documentation for closing.
How much can loan origination fees cost?
In 2025, typical loan origination fees are projected to be approximately 1% to 2% of the amount borrowed. For example, a 1% fee on a $200,000 mortgage would amount to $2,000 at closing.
Are loan origination fees negotiable?
Yes, loan origination fees are often negotiable and can vary significantly between lenders.
Why is it important to understand loan origination fees?
Understanding loan origination fees is essential as they can significantly impact overall borrowing costs. Being aware of these fees empowers borrowers to make informed choices and potentially save money over time.








