Overview
Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) can be an attractive option for homebuyers, primarily because of their lower initial interest rates. This feature often results in more manageable monthly payments at the beginning of the mortgage. However, we know how challenging this can be, and it’s essential to understand the potential risks involved. After the initial fixed-rate period, payments may increase, which can create financial strain.
It’s crucial for borrowers to evaluate their financial situations and future plans before committing. By taking the time to assess these factors, families can make informed decisions that align with their long-term goals. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way as you navigate the mortgage process.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) can feel overwhelming for many prospective homebuyers. We understand how challenging this can be. With their appealingly low initial interest rates, ARMs offer a unique opportunity for families aiming to manage their budgets effectively.
However, the potential for fluctuating payments and the intricacies of qualification requirements raise important questions about their long-term viability.
How can you balance immediate affordability with future financial stability when considering an ARM?
We’re here to support you every step of the way as you explore your options.
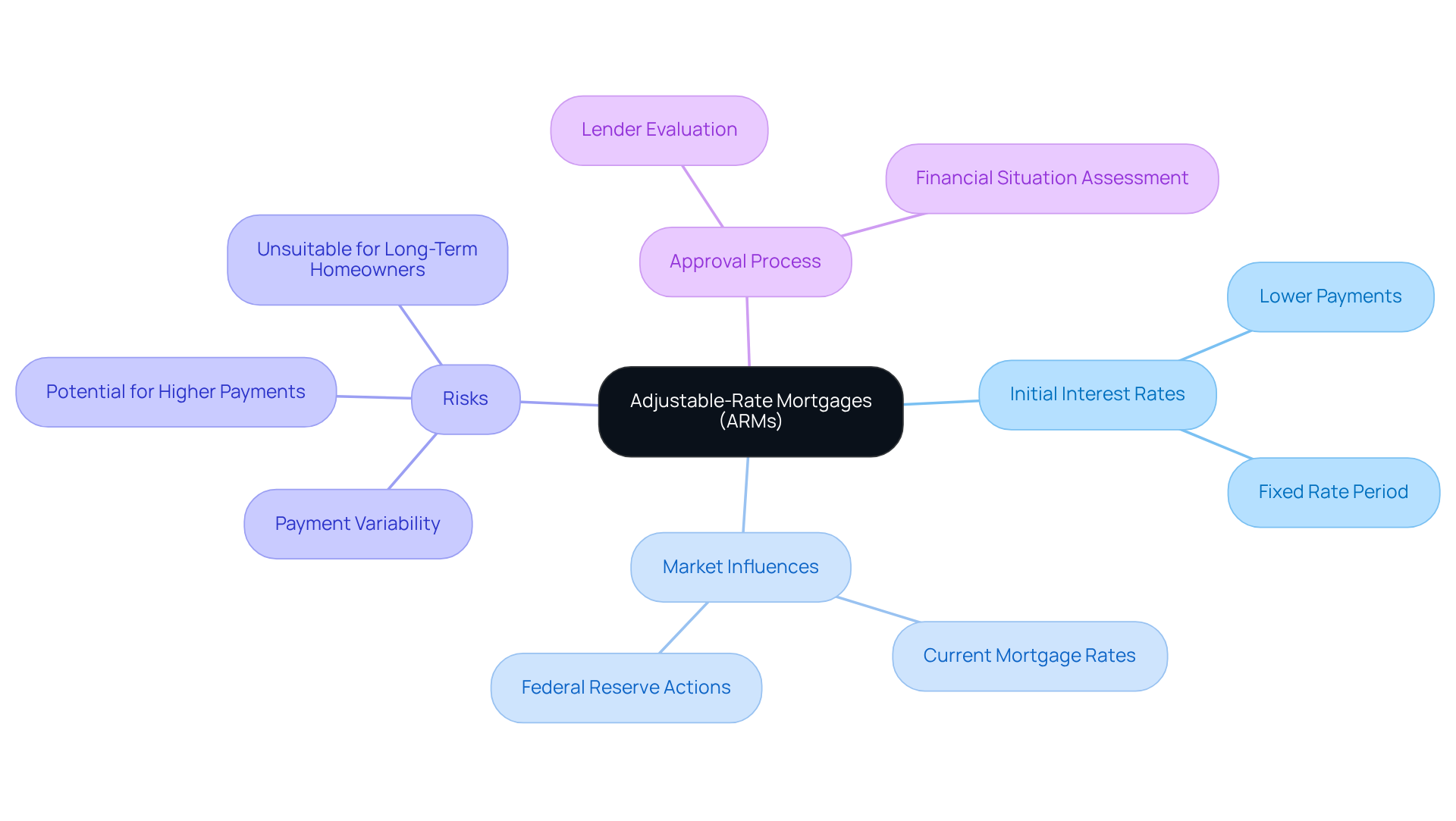
Define Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs)
An arm mortgage can feel a bit overwhelming, but we’re here to help you understand it better. This type of home loan features an interest charge that varies over time, influenced by market conditions. Many families find arm mortgages appealing because they typically start with a lower initial interest rate compared to fixed-rate mortgages, which allows for more manageable monthly payments at the outset.
It’s important to know that the adjustments in fees occur at set intervals, which can vary based on the specific terms of your loan. Understanding this variability is crucial for potential borrowers, as it highlights the potential risks associated with arm mortgages compared to more traditional fixed-rate loans. We know how challenging this can be, and being informed can empower you to make the best decision for your family.
When you’re pursuing an , lenders will take a close look at your financial situation to determine your eligibility. This evaluation can influence the loan amount and interest rate you’ll be offered. By grasping the connection between ARMs and the approval process, you can better navigate your financial planning and homeownership journey. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Explain How ARMs Work
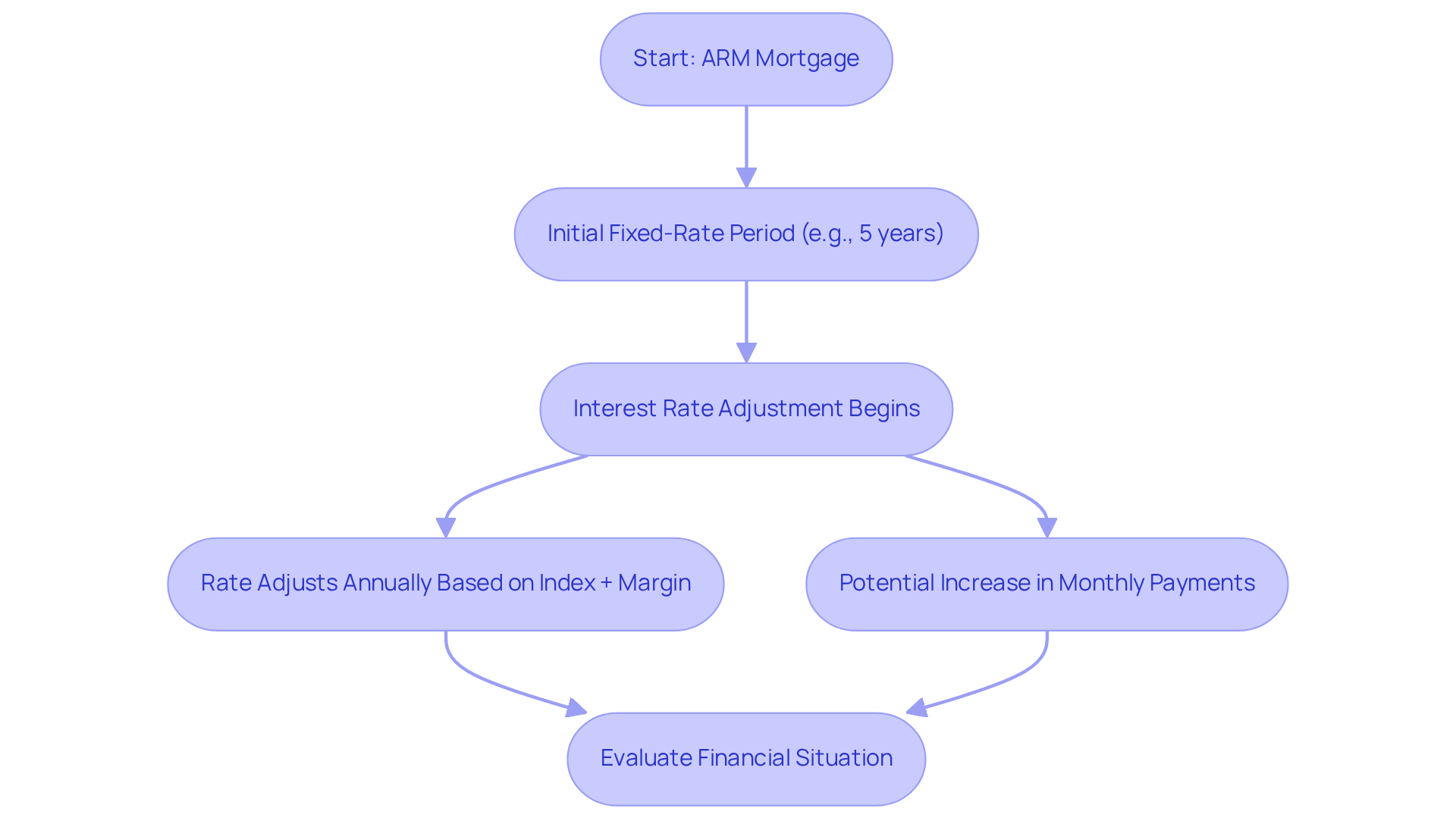
Arm mortgages can be a great option for families looking to manage their finances. They typically feature an initial fixed-rate period, which can range from a few months to several years, with the most common being five, seven, or ten years. For example, a 5/1 ARM maintains a fixed interest rate for the first five years. After that, the rate adjusts annually based on a specific index, like the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), plus a margin determined by the lender. This structure allows families to benefit from reduced initial costs, making arm mortgages particularly appealing in a high-interest-rate environment.
However, we know how challenging it can be to navigate these options. It’s essential for families taking loans to understand how these adjustments work. Once the fixed period ends, the interest rate can vary, which could lead to higher monthly payments. For instance, if a family secures a 5/1 arm mortgage at a 6.20% interest rate, they might enjoy lower costs initially compared to a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage at 6.80%. But when the fixed term concludes, they must be prepared for potential increases in their monthly payments.
Mortgage professionals emphasize the importance of anticipating these changes. As industry experts often remind us, the adjustments depend on economic conditions. Therefore, families should carefully evaluate their financial situations and future plans before committing to an ARM. Understanding the index and margin values, along with the possibility of cost increases, is crucial for making informed decisions about arm mortgage options. We’re here to as you navigate this process.
Evaluate Pros and Cons of ARMs
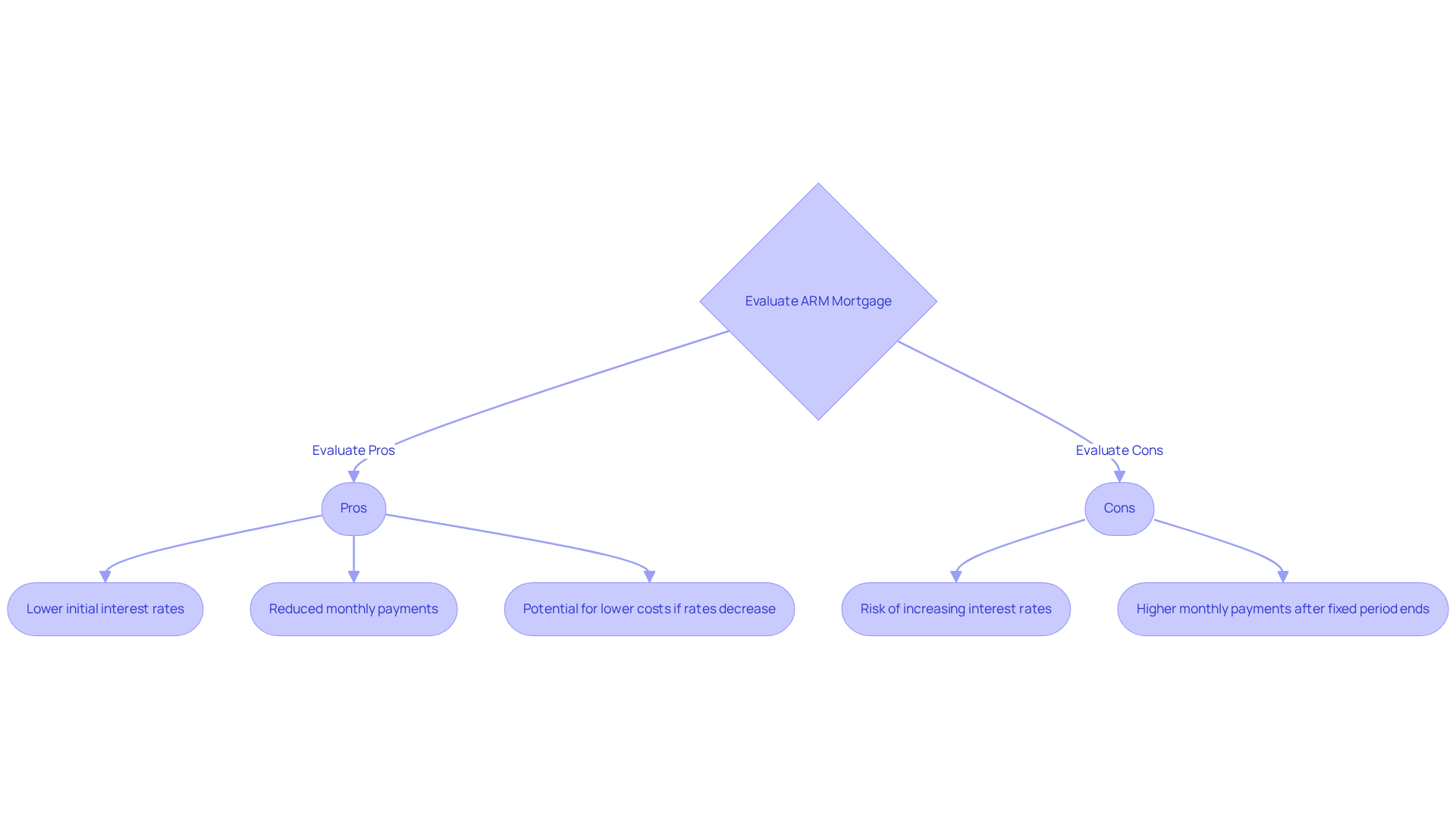
When considering an arm mortgage, it’s important to understand the . One key benefit is the lower initial interest rates, which can lead to reduced monthly payments. This can enhance your buying capacity, making it easier to find a home that meets your family’s needs. Additionally, if interest rates decrease, you could enjoy even lower costs without the need to refinance, providing some financial relief.
However, it’s crucial to also be aware of the potential drawbacks. The risk of increasing interest rates can lead to significantly higher monthly payments once the initial fixed period ends. This uncertainty can make budgeting more challenging, which we know how stressful that can be for families. Understanding both the pros and cons of an arm mortgage is essential for making a choice that aligns with your financial situation.
By weighing these factors carefully, you can make an informed decision that supports your family’s future. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way as you navigate this important process.
Explore Different Types of ARMs
Arm mortgages come in several varieties, each designed to meet the different needs of borrowers. We understand that navigating mortgage options can be overwhelming, so let’s explore some common types that might resonate with your situation.
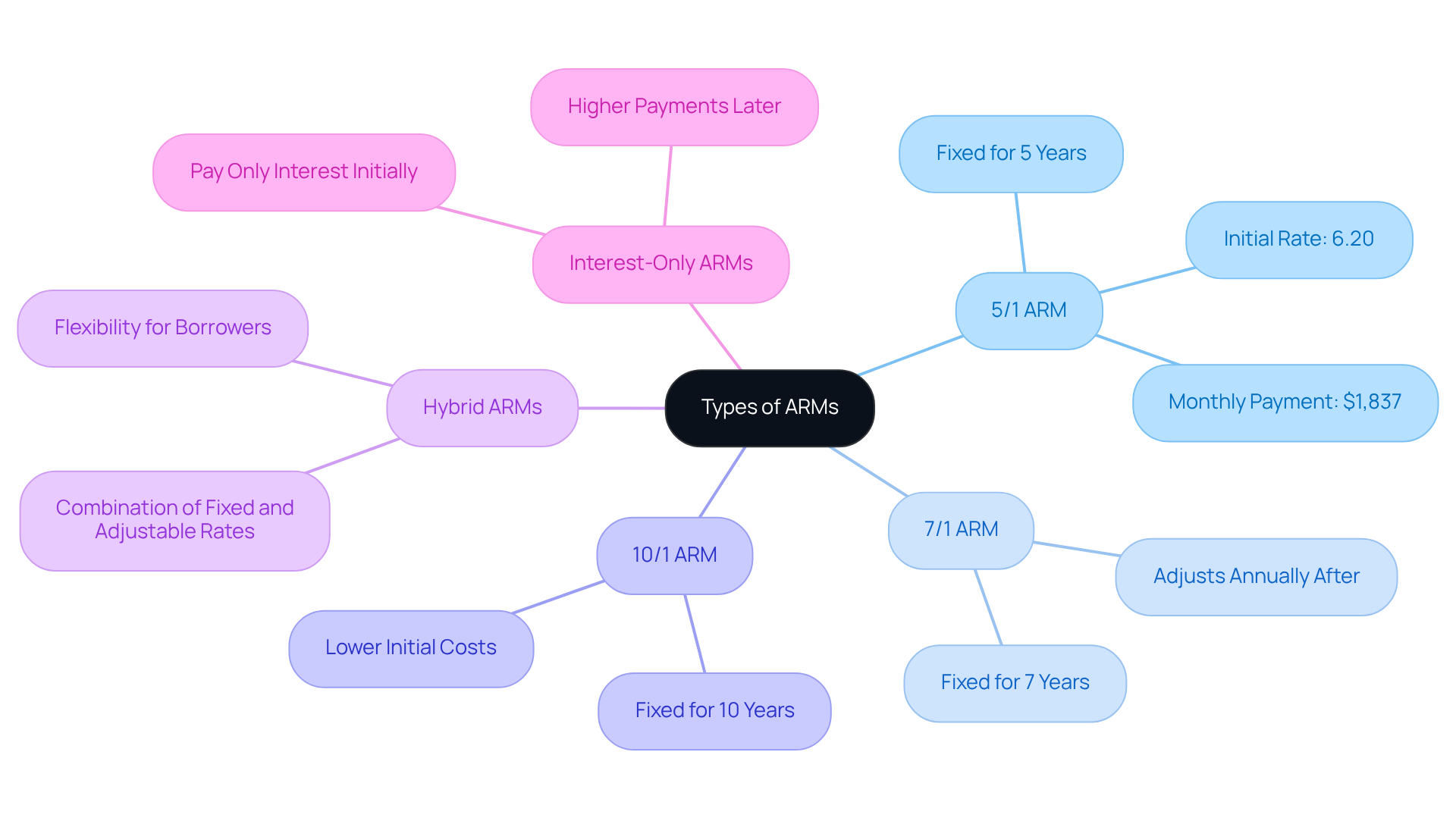
- 5/1 ARM: This mortgage features a fixed interest rate for the first five years, after which the rate adjusts annually based on market conditions. For example, a 5/1 ARM with a starting percentage of 6.20% leads to a monthly expense of roughly $1,837 for a $300,000 loan during the fixed term. This could be a great fit if you plan to stay in your home for a while but want to keep initial costs manageable.
- 7/1 ARM: Comparable to the 5/1 ARM, this option provides a fixed interest for seven years before shifting to yearly modifications. This could be advantageous for those who anticipate moving or refinancing within that timeframe, allowing you to enjoy stability without long-term commitment.
- 10/1 ARM: This type offers a fixed interest for ten years, making it appropriate for individuals who intend to remain in their residences longer but still seek the possibility of lower initial costs. It’s a wonderful choice for families looking to settle down while keeping an eye on their budget.
- Hybrid ARMs: These mortgages blend fixed and adjustable rates, offering a fixed rate for a predetermined period followed by adjustments. This flexibility can appeal to various financial strategies, accommodating different family needs.
- Interest-Only ARMs: These enable individuals to pay solely the interest for a designated timeframe, leading to reduced initial costs. However, we know how challenging it can be when the principal repayment starts, often resulting in considerably larger sums later on.
Understanding these ARM mortgage types is essential for aligning your mortgage choices with your financial objectives and expected duration of homeownership. For example, if you plan to sell before the fixed-rate period ends, ARMs can be particularly beneficial, as they allow you to avoid the risks associated with fluctuating payments. We’re here to as you make these important decisions.
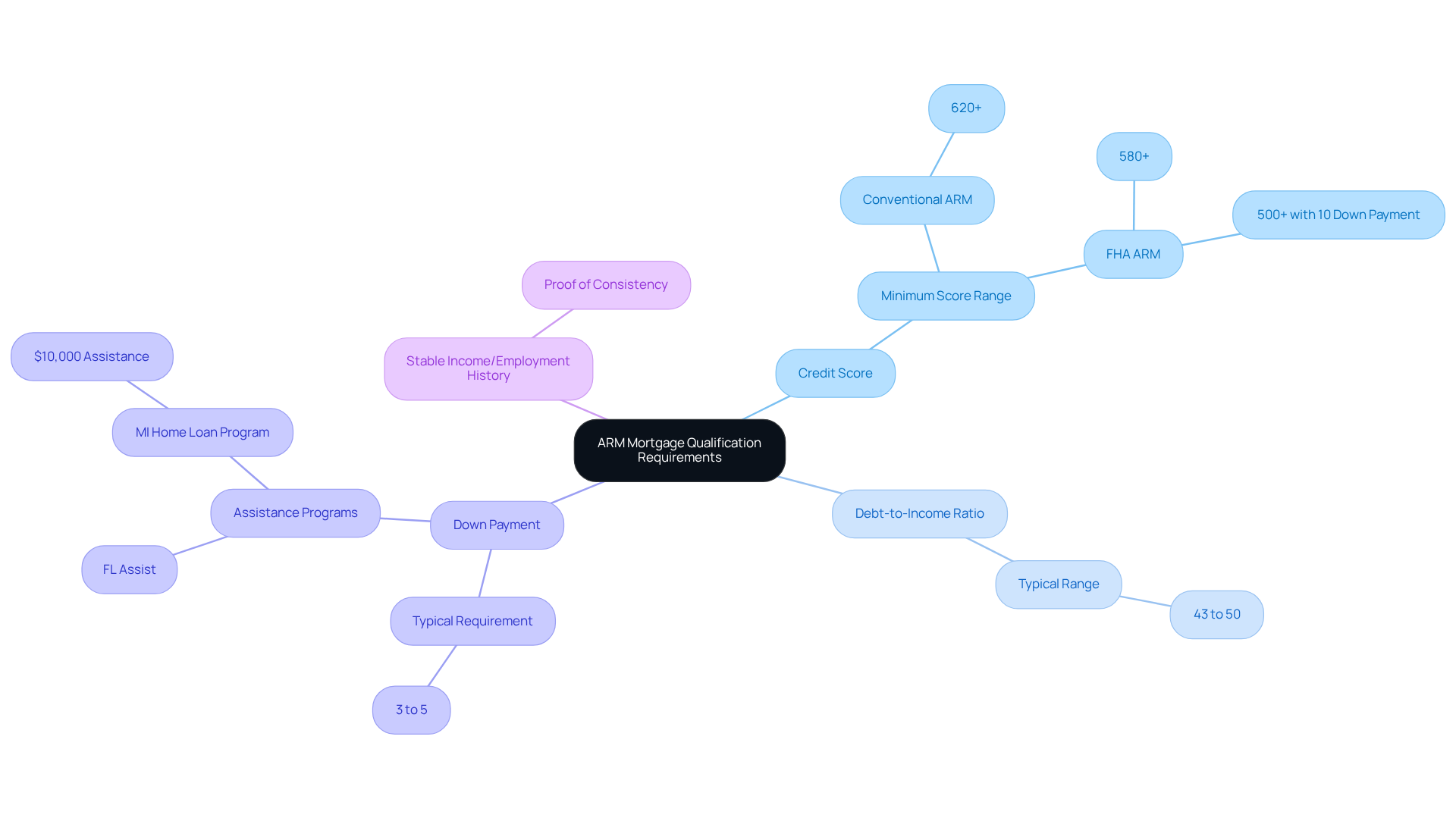
Outline Qualification Requirements for ARMs
Qualifying for an arm mortgage can feel overwhelming, but understanding the specific criteria can help alleviate your concerns. Here are some key requirements that you may encounter:
- Credit Score: Most lenders require a minimum credit score between 580 and 620. This score can significantly impact the interest rates and terms available to you.
- Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio: It’s common for lenders to look for a DTI ratio of 43% to 50%. This ratio is crucial as it reflects your ability to manage monthly payments relative to your income.
- Down Payment: Typically, a down payment of around 3% to 5% of the home’s purchase price is expected. However, programs like FL Assist and can offer up to $10,000 in assistance, making homeownership more attainable for many families.
- : Providing proof of consistent income and a solid employment history is essential to demonstrate your financial stability.
We know how challenging this can be, and comprehending these requirements is vital for prospective applicants to assess their eligibility and prepare for the application process. For instance, an individual with a credit score of 620 and a DTI of 45% may qualify for a competitive arm mortgage, which allows them to benefit from lower initial costs compared to fixed-rate mortgages.
As satisfied clients like Bryce Leonard and Alley Cohen have noted, the support from F5 Mortgage can make this journey smoother and more manageable. Staying informed about these criteria as the market evolves can greatly impact your homebuying experience. Remember, arm mortgages also have limits on increases, providing some protections against significant cost hikes. With F5 Mortgage by your side, you can navigate these options with confidence, knowing we’re here to support you every step of the way.
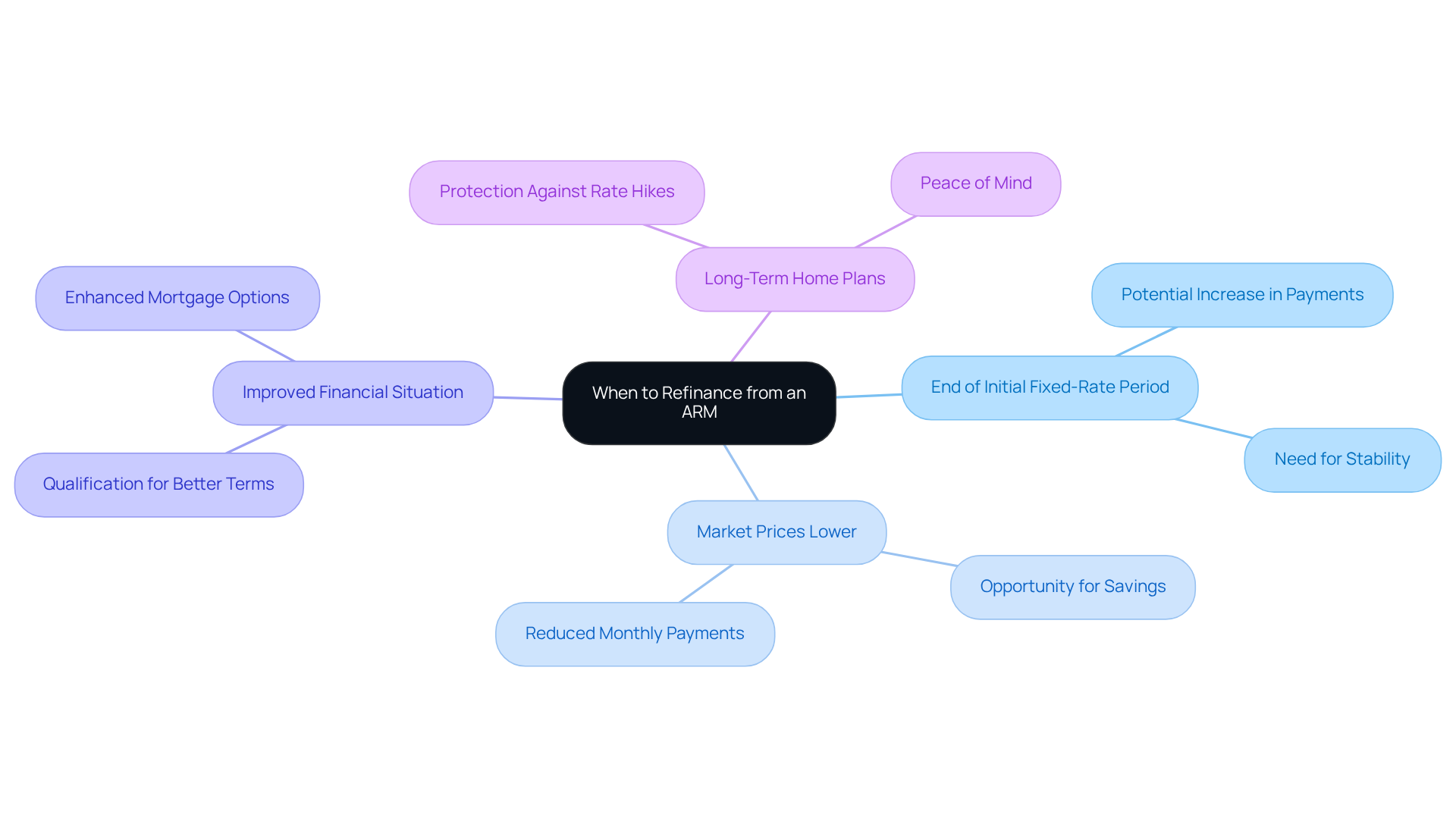
Determine When to Refinance from an ARM
Homeowners, we understand that considering refinancing from an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) can feel overwhelming. However, there are several key circumstances that might make this decision a wise one for you:
- If the initial fixed-rate period is nearing its end, you may face a significant increase in monthly payments. This transition can lead to financial strain, so switching to a fixed-rate mortgage could provide the stability you need.
- Current market prices are lower than your existing ARM figure, presenting a valuable opportunity for potential savings. Refinancing in this scenario can significantly reduce both your monthly payments and overall interest costs.
- An improvement in your financial situation may enable you to qualify for a more favorable loan product, enhancing your mortgage terms.
- If you plan to stay in your home long-term, opting for a fixed-rate mortgage can offer peace of mind against future rate hikes.
Recognizing these signs is crucial. Timely refinancing can lead to . For example, homeowners who transitioned from an ARM mortgage to fixed-rate mortgages in 2025 reported average savings of approximately 15% on their monthly payments. This illustrates the tangible advantages of making informed refinancing decisions.
We’re here to support you every step of the way. Consulting with mortgage professionals can further clarify these strategies, ensuring that you navigate the refinancing process effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) is crucial for homebuyers navigating the complexities of home financing. We know how challenging this can be. These loans present an appealing initial lower interest rate, easing monthly payments at the start. However, the variability in rates over time introduces a level of risk that you must carefully consider. Being informed about how ARMs function, their advantages and disadvantages, and the qualification requirements can empower your family to make decisions that align with your financial goals.
Throughout this article, we explored key insights into ARMs, including:
- How these loans work
- The different types available
- The importance of understanding the approval process
We highlighted the benefits of lower initial rates and the potential for cost savings, while also addressing the risks associated with fluctuating payments once the fixed-rate period ends. Additionally, we provided guidance on when refinancing might be a wise choice, emphasizing the importance of regularly evaluating your personal financial situation.
Ultimately, the decision to pursue an ARM should be based on thorough research and a clear understanding of your individual financial circumstances. We encourage you to weigh the pros and cons carefully and consider seeking professional advice to navigate this process effectively. By doing so, you can ensure that your family makes informed choices that support your long-term financial well-being and homeownership aspirations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM)?
An Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM) is a type of home loan that features an interest charge that varies over time based on market conditions. ARMs typically start with a lower initial interest rate compared to fixed-rate mortgages, allowing for more manageable monthly payments at the beginning.
How do ARMs work?
ARMs usually have an initial fixed-rate period that can last from a few months to several years, commonly five, seven, or ten years. After this period, the interest rate adjusts annually based on a specific index, plus a margin set by the lender. For example, a 5/1 ARM has a fixed interest rate for the first five years, after which it adjusts annually.
What happens after the fixed-rate period of an ARM ends?
After the fixed-rate period ends, the interest rate on an ARM can vary, which may lead to higher monthly payments. Borrowers need to be prepared for potential increases in their payments once the fixed term concludes.
What factors influence the adjustment of ARM interest rates?
The adjustments in ARM interest rates depend on economic conditions and are based on a specific index, such as the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), plus a margin determined by the lender.
How do lenders evaluate eligibility for an ARM?
Lenders evaluate a borrower’s financial situation to determine eligibility for an ARM, which can influence the loan amount and interest rate offered. Understanding this connection can help borrowers navigate their financial planning.
What should families consider before committing to an ARM?
Families should carefully evaluate their financial situations and future plans, understand how the index and margin values work, and anticipate potential cost increases after the fixed-rate period ends before committing to an ARM.








