Overview
Understanding how to calculate your mortgage on a $300,000 house can feel overwhelming. We know how challenging this can be, but we’re here to support you every step of the way. Key terms such as principal, interest rate, and loan term are essential to grasp, and applying a specific formula can help estimate your monthly payments.
This article will guide you through these elements with empathy, providing a step-by-step example that illustrates how different factors—like your down payment, interest rate, and loan duration—can significantly impact your financial obligations over time. By recognizing these variables, you can make informed decisions that align with your family’s needs.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of home financing can feel overwhelming, especially when considering a significant investment like a $300,000 house. We understand how challenging this can be. That’s why grasping the intricacies of mortgage calculations is essential for prospective homeowners. It not only impacts monthly budgets but also shapes long-term financial health.
What factors should you consider to make informed decisions? How can you effectively calculate mortgage payments to avoid costly mistakes? This guide is here to support you every step of the way. We’ll demystify the mortgage process, offering a step-by-step approach to calculating payments and understanding key terms. Ultimately, we aim to empower you to take confident strides toward homeownership.
Understand Mortgage Basics and Key Terms
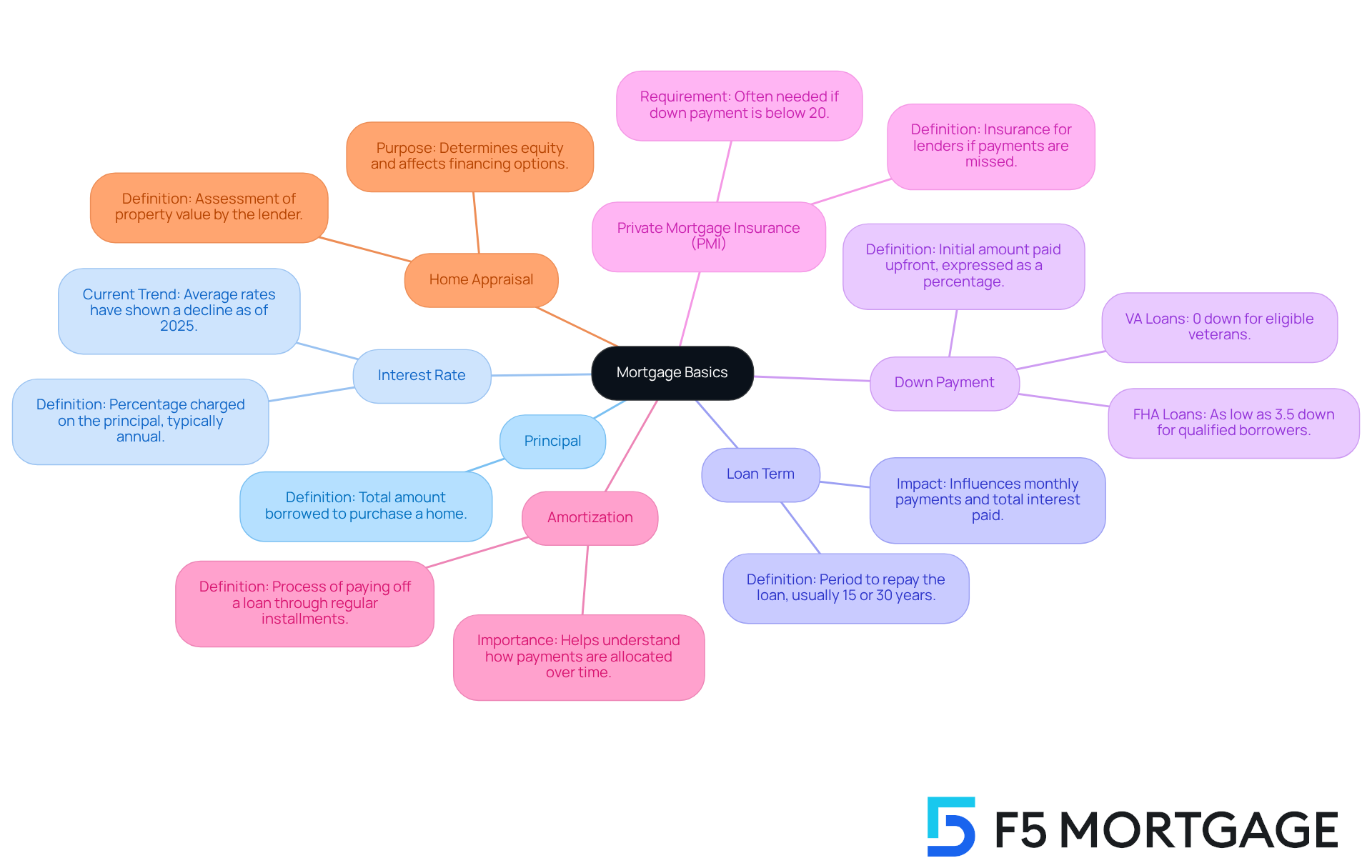
Before diving into calculations, we know how challenging it can be to navigate the . Familiarizing yourself with key mortgage terms is essential to shape your understanding and empower your journey:
- Principal: This is the total amount of money you borrow to purchase your home. The principal for a would typically be close to this amount, depending on your .
- : This is the percentage of the principal that lenders charge for borrowing money, usually expressed as an annual rate. As of 2025, average interest rates for fixed-rate mortgages have shown a decline, making it a favorable time for potential buyers.
- : This pertains to the period during which you agree to repay the amount borrowed, typically established at 15 or 30 years. Choosing the right borrowing period can significantly influence your monthly payments and total interest paid over the duration of the debt.
- Down Payment: This is the initial amount you pay upfront when purchasing a home, typically expressed as a percentage of the home’s purchase price. For FHA mortgages, qualified borrowers can obtain a home with as little as 3.5% down, while VA financing may permit 0% down for eligible veterans, making them an appealing choice for many purchasers.
- : This insurance safeguards the lender if you fail to meet your payment obligations. PMI is frequently necessary if your initial contribution is below 20%, increasing your monthly expenses.
- Amortization: This is the process of gradually settling your loan through regular installments that cover both principal and interest. Understanding can help you observe how your contributions are distributed over time.
- : The lender will order a home appraisal to determine the current market value of your property. This will identify how much equity you have, which will affect your rates and overall financing options.
Understanding these terms is essential for comprehending how your loan installment is organized and the elements that affect it. We’re here to support you every step of the way, and understanding these terminologies can enable you to make during your home purchasing journey.
Apply the Mortgage Payment Formula
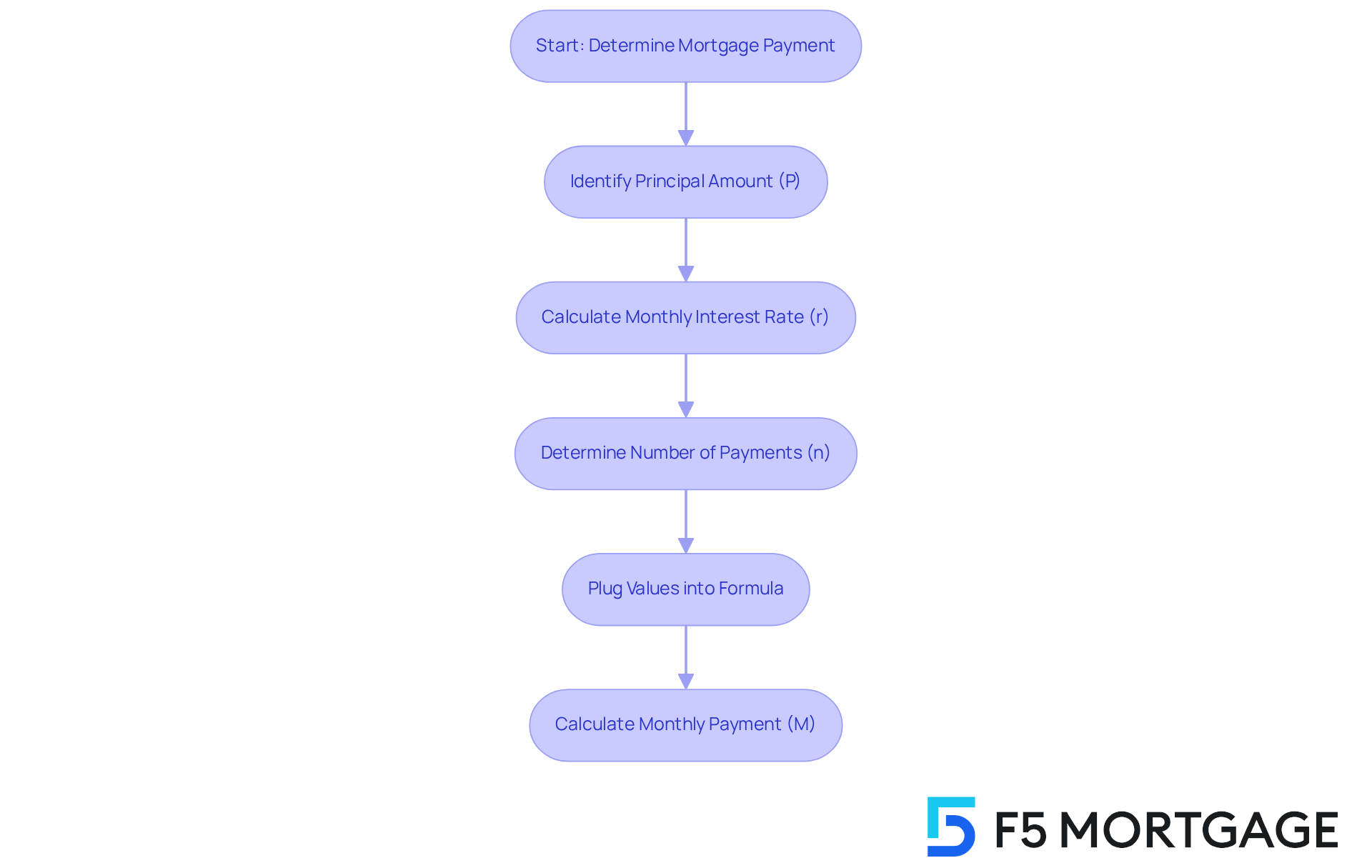
Calculating your can seem daunting, but we’re here to help you through it. You can use the following formula to find your payment:
M = P * (r(1 + r)^n) / ((1 + r)^n - 1)
Where:
- M = Total monthly mortgage payment
- P = Principal loan amount (the amount borrowed)
- r = Monthly interest rate (annual interest rate divided by 12)
- n = Number of payments (loan term in years multiplied by 12)
Let’s walk through an example together. Imagine you have a at a 6.72% annual interest rate with a 30-year term. First, you would transform the yearly interest rate into a monthly rate: 6.72% / 100 / 12 = 0.0056. Then, calculate the total number of contributions: 30 years * 12 months = 360 contributions. Now, plug these values into the formula:
M = 300000 * (0.0056(1 + 0.0056)^{360}) / ((1 + 0.0056)^{360} - 1)
Finally, determine M to find your recurring charge.
By applying this formula, you can estimate your regular installment based on your . As of August 2025, the is around 6.72%. This can significantly impact your monthly payment. For instance, a mortgage on a 300k house at this rate would result in a monthly payment of about $1,948. Over the life of the loan, you might pay approximately $347,514.57 in interest.
If you’re considering refinancing, it’s important to . This means looking at your , determining your , and dividing the total costs by your monthly savings. For example, if your refinancing expenses are $4,000 and your savings each month are $100, your break-even point would be 40 months ($4,000 / $100 = 40 months). This calculation can help you decide if based on how long you plan to stay in your home.
Understanding loan term lengths and your is also crucial when evaluating refinancing. Longer terms might lower your monthly payments but could lead to higher overall interest costs. Conversely, shorter terms may reduce interest but increase monthly payments. Evaluating your can assist you in determining how much loan you can comfortably afford, ensuring you make informed choices about your financing options. Remember, we know how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Consider Factors Affecting Your Monthly Payments
Several factors significantly influence your monthly mortgage payments, and .
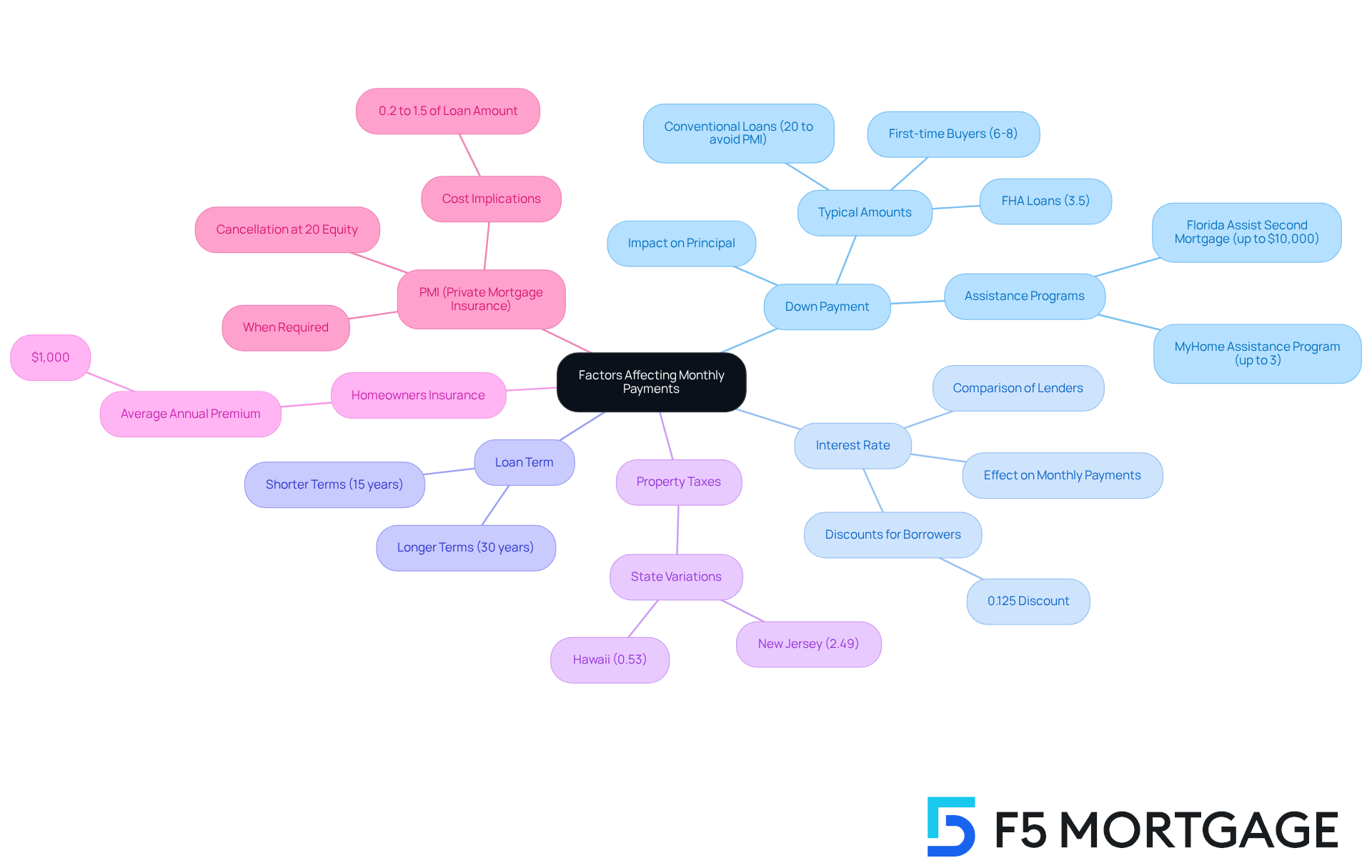
- : A larger down payment reduces the principal amount borrowed, leading to lower monthly payments. For example, a 20% deposit on a mortgage on a 300k house totals $60,000, which can significantly reduce your monthly financial responsibility. We know how challenging this can be; the typical initial contribution for is merely 6%, and FHA mortgages necessitate a minimum initial contribution of 3.5% with a credit rating of no less than 580. Furthermore, , including the MyHome Assistance Program in California, which offers up to 3% of the home’s purchase price, and the My Choice Texas Home program, providing up to 5% for down support and closing assistance. In Florida, programs like the Florida Assist Second Mortgage Program can provide up to $10,000 for upfront costs, making homeownership more accessible.
- : The interest rate directly influences the overall expense of borrowing. Elevated rates lead to greater interest costs throughout the duration of the loan, thus increasing your regular charge. For instance, a 1% rise in interest can contribute hundreds of dollars to your regular payment. We’re here to support you every step of the way, and working with F5 Mortgage can help you secure tailored to your financial situation. It’s crucial to compare lenders to find the best deal.
- Loan Term: The length of the loan term also plays a crucial role. Shorter durations, such as 15 years, usually lead to increased installments but reduced interest paid in total, while longer durations, like 30 years, distribute the costs, resulting in lower installments but higher interest over time.
- : These taxes are frequently incorporated in your regular charge and can differ considerably by state. For instance, typical property tax percentages vary from 0.53% in Hawaii to 2.49% in New Jersey, influencing your total cost each month.
- Homeowners Insurance: Required by lenders, this insurance safeguards your home and increases your ongoing expenses. The average annual premium can vary widely, but budgeting around $1,000 annually is common.
- PMI (Private Mortgage Insurance): If your down payment is below 20%, you might be obligated to pay PMI, which can add an extra 0.2% to 1.5% of the borrowed amount to your recurring charge. For a mortgage on a 300k house, this could mean an extra $600 to $4,500 annually. PMI can be canceled once you reach 20% equity in your home.
Comprehending these elements, along with the , will aid you in more accurately assessing your overall expenses and planning accordingly. By understanding these factors, you can feel more equipped and confident as you embark on the journey of homeownership.
Utilize Mortgage Calculators and Resources
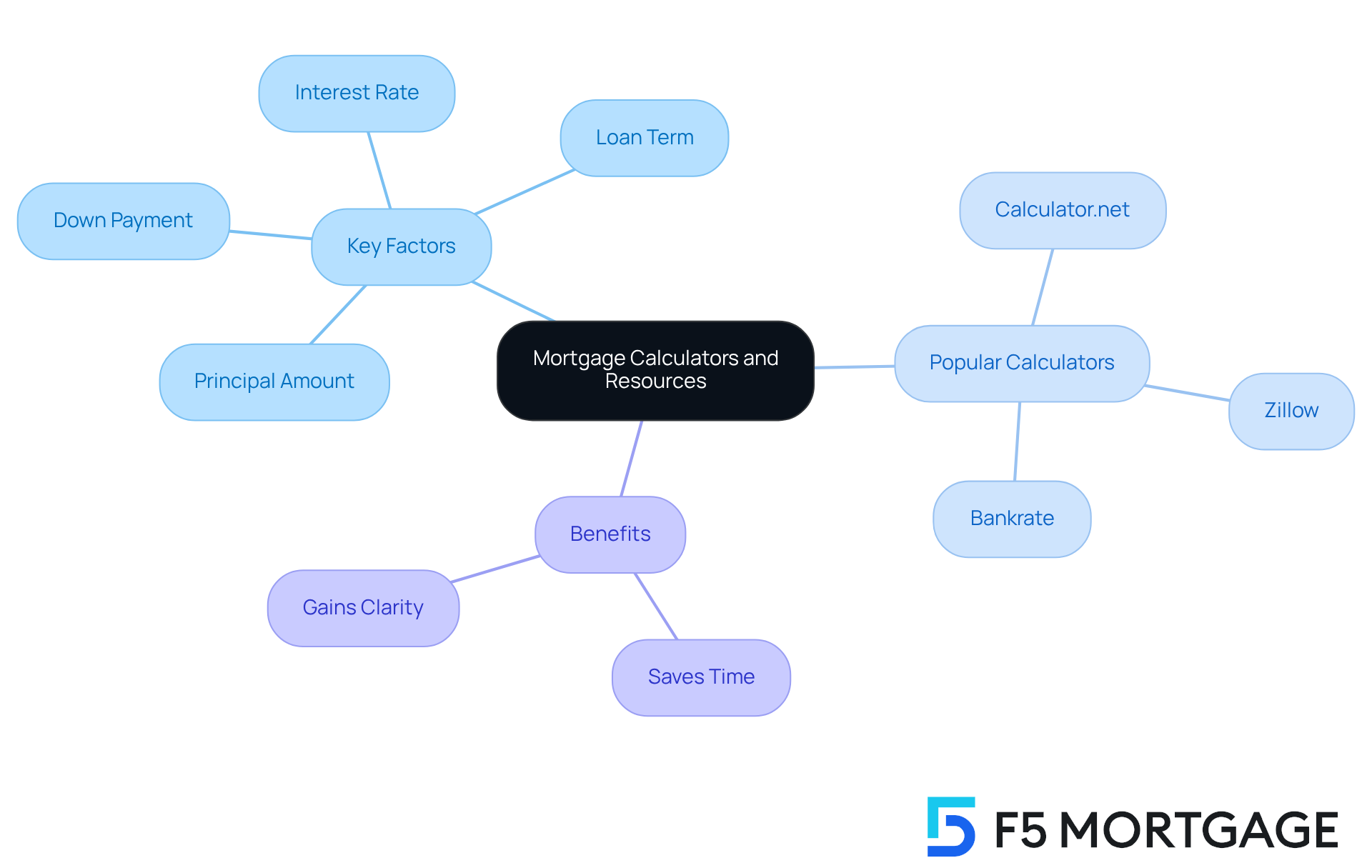
To simplify your loan calculations, we understand how beneficial can be. These helpful tools allow you to estimate your by inputting several key factors:
- Principal Amount: Enter the total you intend to borrow.
- Interest Rate: Input the anticipated interest rate for your mortgage.
- Loan Term: Choose the duration of your loan, typically 15 or 30 years.
- Down Payment: Specify the you plan to make.
Popular loan calculators among homebuyers in 2025 include tools from Calculator.net, Zillow, and Bankrate. These platforms not only provide quick estimates but also offer , including property taxes and insurance. For example, the Calculator.net Mortgage Calculator features a comprehensive interface for entering various factors, while ensures a swift estimation process.
Financial advisors emphasize the benefits of these online calculators, highlighting how they empower homebuyers to visualize their clearly. By utilizing these resources, you can save time and gain a clearer understanding of your financial obligations, ultimately assisting you in making informed choices throughout your .
To , ensure that you have accurate estimates for your inputs. This approach will give you a clearer picture of your potential monthly payments and help you set a realistic budget for your home search. Remember, we know how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of mortgage calculations is essential for anyone considering purchasing a home, especially when dealing with a significant investment like a $300,000 house. We know how challenging this can be, and this guide aims to illuminate the key terms and concepts that form the foundation of mortgage financing. By doing so, we empower potential homeowners to navigate their financial journey with confidence.
In this article, we delved into important mortgage components, including:
- Principal
- Interest rates
- Loan terms
- The impact of down payments
We provided a clear formula for calculating monthly payments and highlighted various factors that can influence these costs, such as property taxes and insurance. Additionally, we emphasized the utility of online mortgage calculators, which can simplify the process of estimating monthly obligations and help buyers make informed financial decisions.
Ultimately, being well-informed about mortgage basics and utilizing available resources can significantly enhance the home-buying experience. As your journey toward homeownership unfolds, we encourage you to leverage the insights gained from this guide to explore your options thoroughly. This ensures that you make choices that align with your financial goals. Taking proactive steps today can lead to a more secure and fulfilling investment in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the principal in a mortgage?
The principal is the total amount of money you borrow to purchase your home. For a mortgage on a $300,000 house, the principal would typically be close to this amount, depending on your down payment.
What is an interest rate in the context of mortgages?
The interest rate is the percentage of the principal that lenders charge for borrowing money, usually expressed as an annual rate. As of 2025, average interest rates for fixed-rate mortgages have shown a decline.
What does loan term refer to in a mortgage?
The loan term refers to the period during which you agree to repay the borrowed amount, typically established at 15 or 30 years. This choice can significantly influence your monthly payments and total interest paid.
What is a down payment?
A down payment is the initial amount you pay upfront when purchasing a home, typically expressed as a percentage of the home’s purchase price. For FHA mortgages, qualified borrowers can obtain a home with as little as 3.5% down, while VA financing may permit 0% down for eligible veterans.
What is Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)?
PMI is insurance that protects the lender if you fail to meet your payment obligations. It is often required if your down payment is below 20%, which can increase your monthly expenses.
What does amortization mean in relation to mortgages?
Amortization is the process of gradually repaying your loan through regular installments that cover both principal and interest. Understanding amortization schedules helps you see how your payments are distributed over time.
What is a home appraisal?
A home appraisal is an assessment ordered by the lender to determine the current market value of your property. This appraisal helps identify how much equity you have, which can affect your rates and overall financing options.








