Introduction
Navigating the complexities of a mortgage can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re looking at a significant amount like $350,000. We know how challenging this can be. By understanding the essential terms and factors that influence your monthly payments, you can approach this financial journey with greater confidence.
But what happens when interest rates change or unexpected costs pop up? It’s natural to feel uncertain. This guide is here to support you every step of the way. We’ll break down the process of calculating your mortgage payment into clear, manageable steps. With these insights, you’ll be empowered to make informed decisions about your financial future.
Understand Mortgage Basics and Key Terms
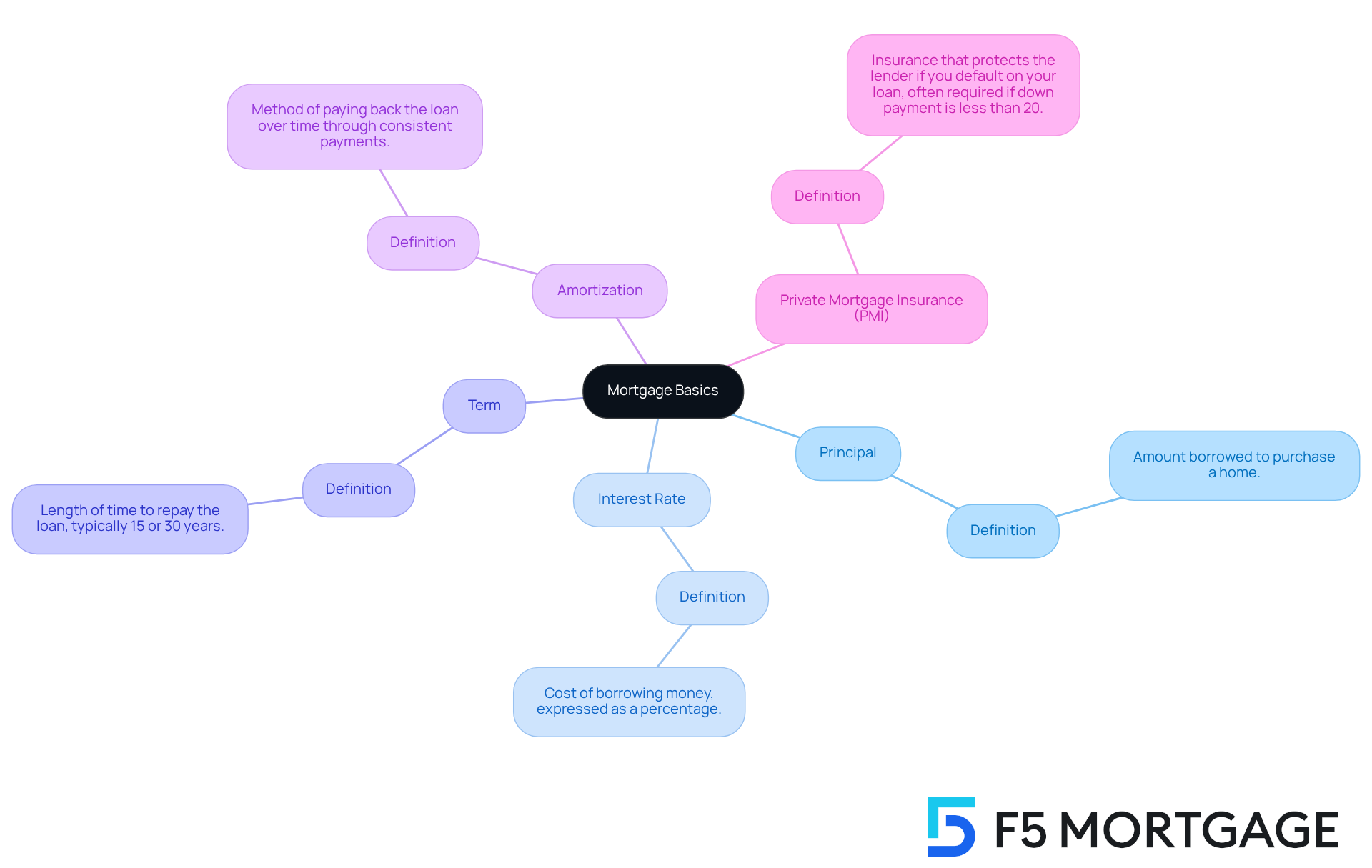
Before you start crunching numbers, let’s take a moment to understand some essential mortgage terms that can make a big difference in your journey:
- Principal: This is the amount of money you borrow to purchase your home.
- Interest Rate: Think of this as the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage.
- Term: This refers to the length of time you have to repay what you’ve borrowed, typically 15 or 30 years.
- Amortization: This is the method of paying back your loan over time through consistent payments.
- Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): This insurance protects the lender if you default on your loan and is often required if your down payment is less than 20%.
We know how challenging this can be, but grasping these concepts will empower you to navigate the financing landscape more effectively. Understanding these terms is a crucial step towards making informed decisions about your mortgage.
Identify Factors Affecting Your Monthly Payment
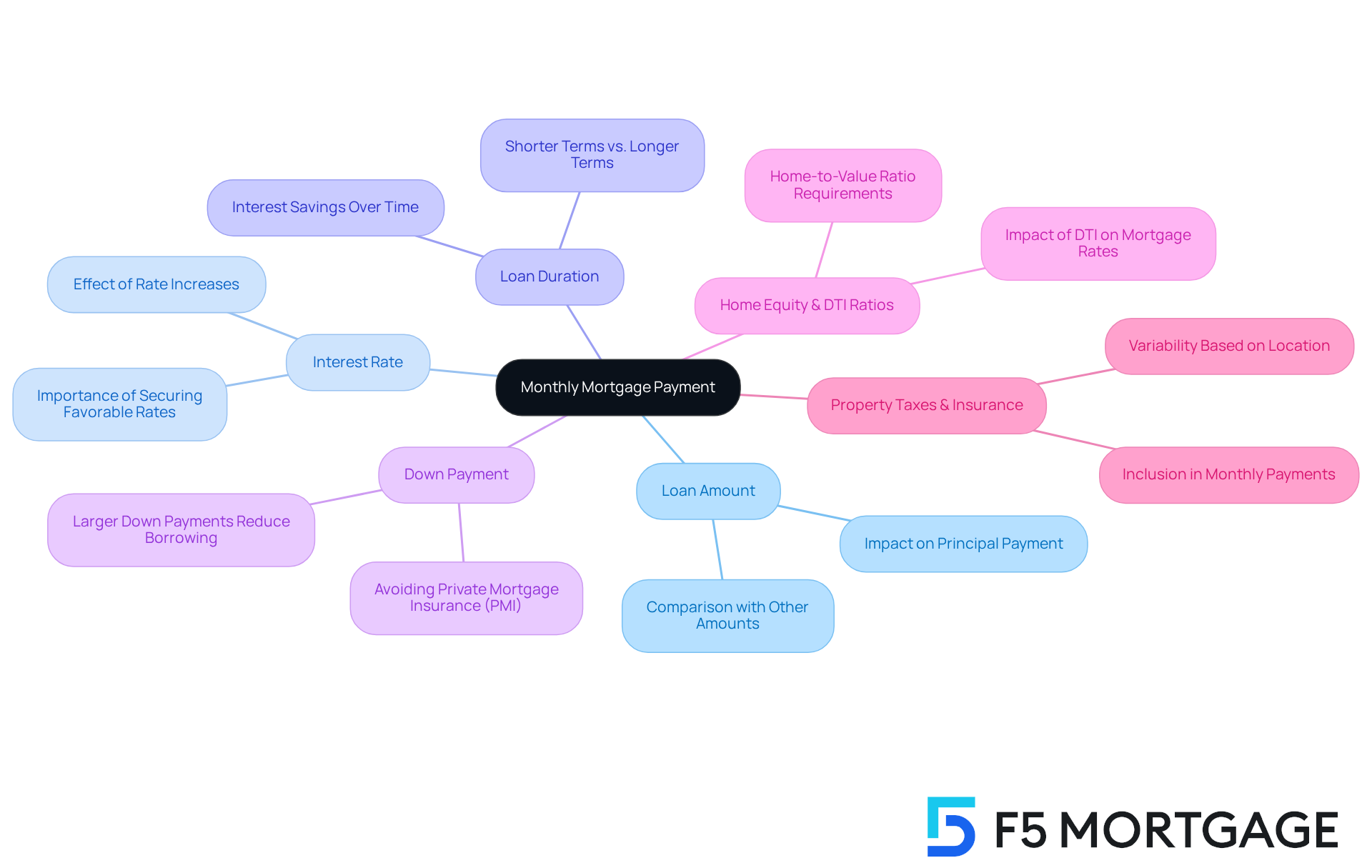
Understanding your 350 000 mortgage monthly payment can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to support you throughout the process. Several key factors play a significant role in shaping what you’ll pay each month:
Loan Amount: The total amount you borrow directly affects the principal part of your payment. For instance, the repayment structure for a 350 000 mortgage monthly payment will differ from that of $250,000 or $600,000. It’s crucial to consider how much you really need.
Interest Rate: A higher interest rate can significantly increase your monthly charges. Imagine this: if your interest rate jumps from 6.5% to 7.5% on a $400,000 loan, your 350 000 mortgage monthly payment could increase by an additional $200. This highlights just how important it is to secure a favorable rate.
Loan Duration: The length of your loan impacts your monthly installments. Shorter terms, like 15 years, typically mean higher payments, but they can save you a lot in interest over time compared to a 30-year loan.
Down Payment: Making a larger down payment can lower the amount you need to borrow, which in turn can reduce your monthly payments. Plus, it might help you avoid private mortgage insurance (PMI), easing your financial burden even more.
Home Equity and DTI Ratios: Many lenders want homeowners to maintain at least an 80% home-to-value ratio, meaning you should have paid down at least 20% of your original loan or your home needs to have appreciated in value. Additionally, a maximum debt-to-income (DTI) ratio of 43% is often required for home loans. A better DTI can lead to more competitive mortgage rates, so understanding these factors is essential for your mortgage options.
Property Taxes and Insurance: These costs are often included in your monthly payment and can vary widely based on where you live and the value of your property. For example, property taxes in high-value areas can add several hundred dollars to your monthly expenses.
By understanding these elements, you can better estimate your potential monthly costs, such as a 350 000 mortgage monthly payment, and make informed choices about your financing options. As interest rates fluctuate, it’s vital to consult with a financing expert who can help you navigate how these factors interact and influence your overall financial situation.
Use a Mortgage Calculator to Determine Payment
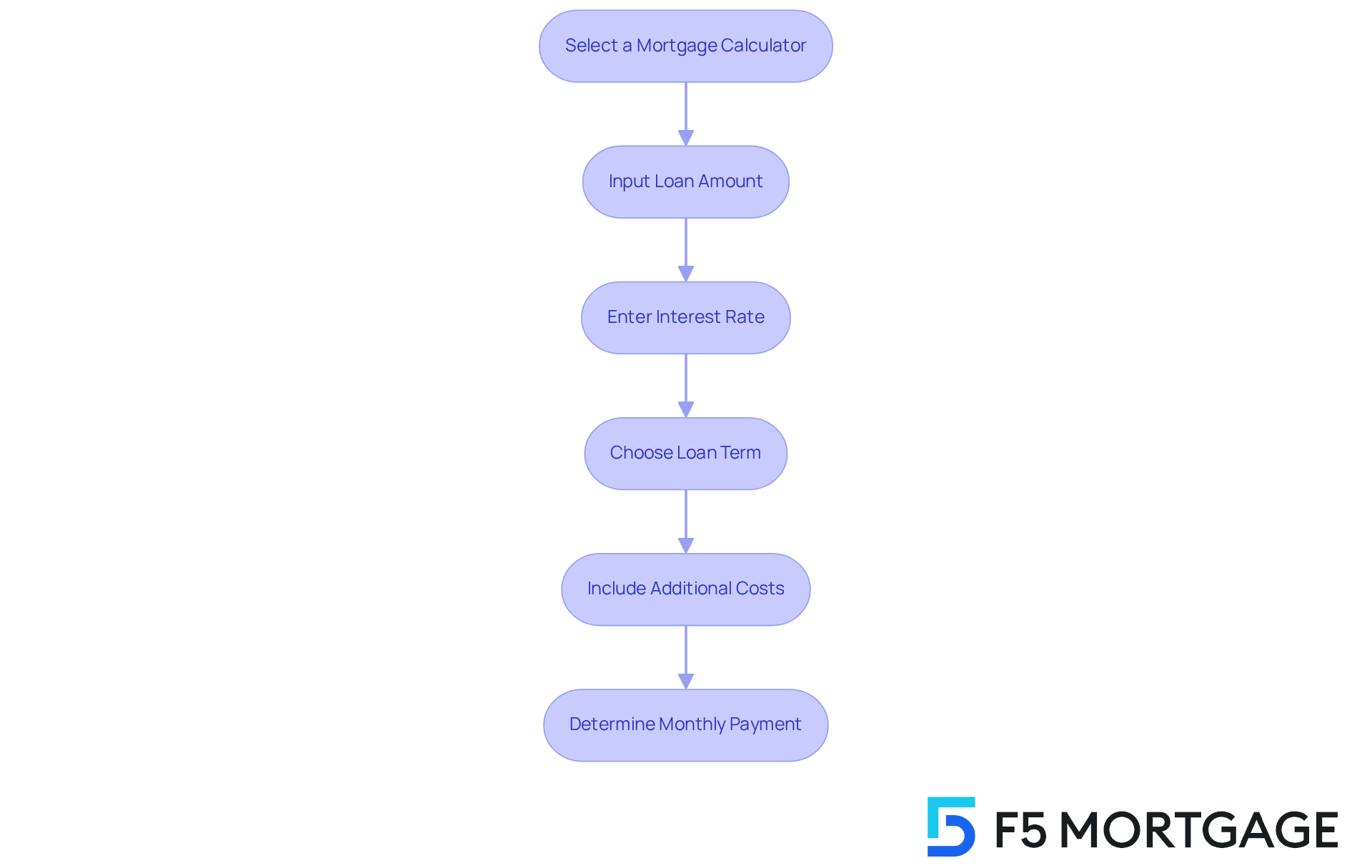
Calculating your 350,000 mortgage monthly payment can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to support you throughout the process. Using a mortgage calculator can simplify this process and provide you with a clearer picture of your financial responsibilities, including your 350,000 mortgage monthly payment. Here’s how to get started:
- Select a Mortgage Calculator: Choose a reputable online calculator, like those from Bankrate or Zillow, to ensure accuracy.
- Input Loan Amount: Enter the amount you plan to borrow – let’s say it’s $350,000.
- Enter Interest Rate: Input the current interest rate you expect to receive. This can significantly impact your payment.
- Choose Loan Term: Decide on the loan term that works for you, such as 30 years.
- Include Additional Costs: If applicable, add estimates for property taxes, insurance, and PMI. These costs can add up, so it’s important to factor them in.
- Determine: Finally, click the calculate button to view your estimated monthly payment.
By utilizing a loan calculator, you can save time and gain a clearer understanding of the 350,000 mortgage monthly payment you can expect. We know how challenging this can be, but taking these steps can empower you to make informed decisions.
Adjust Loan Parameters for Accurate Calculations
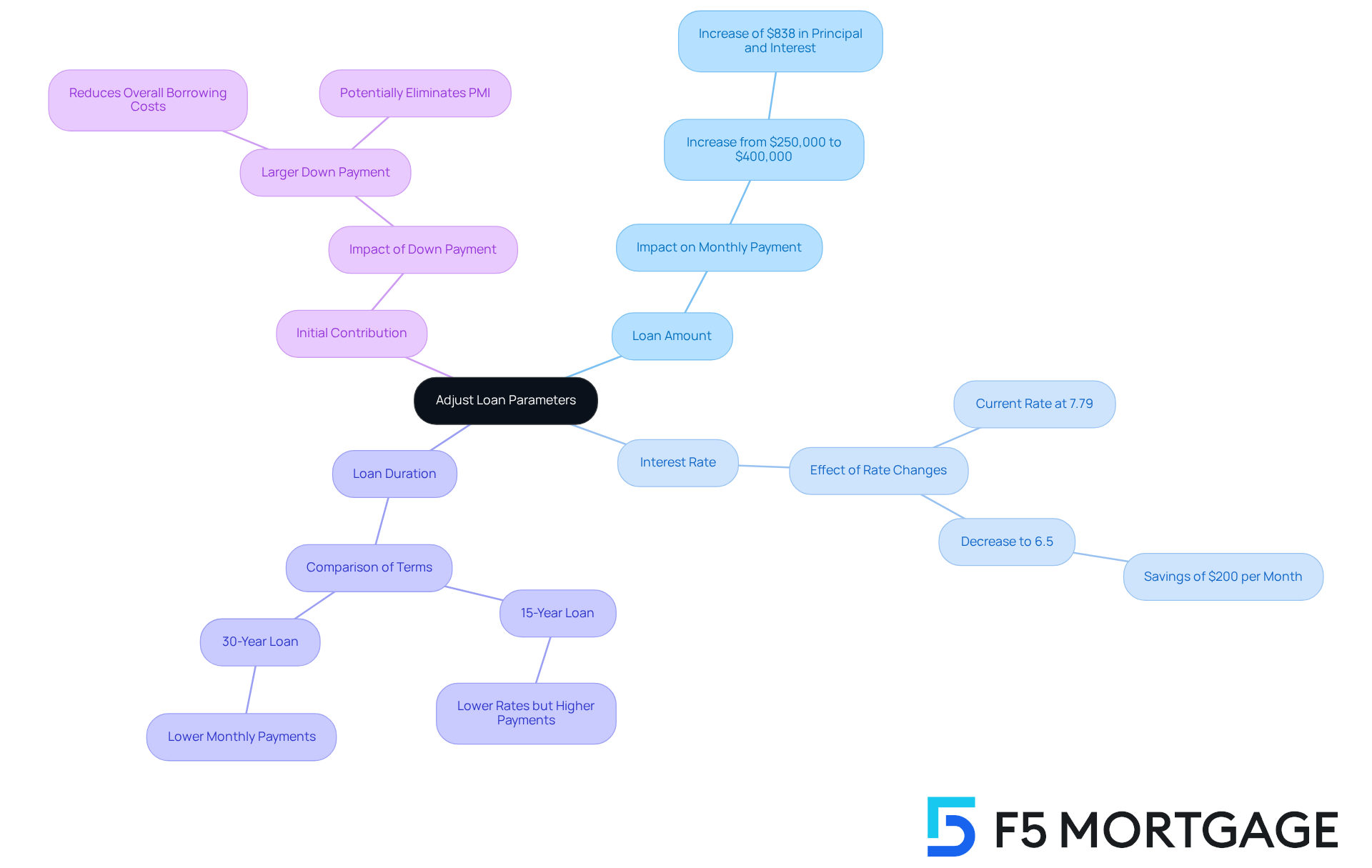
Refining your estimate for the 350 000 mortgage monthly payment can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to support you every step of the way. By adjusting a few key parameters, you can discover a loan structure that accommodates a 350 000 mortgage monthly payment while aligning with your budget and financial goals.
Loan Amount: Experimenting with different amounts can make a big difference in your monthly payment. For instance, if you raise your borrowing amount from $250,000 to $400,000, your principal and interest costs could increase by about $838. Understanding how the size of your loan impacts the affordability of a 350 000 mortgage monthly payment is crucial.
Interest Rate: Inputting various rates helps you see potential changes in your costs. With interest rates hitting 7.79% in late 2023, even a small decrease to 6.5% could save you around $200 each month, impacting your 350,000 mortgage monthly payment on a $400,000 mortgage. Keeping an eye on rate fluctuations is essential for making informed decisions.
Loan Duration: Comparing 15-year versus 30-year terms can reveal how the length of your financing impacts your regular expenses. A 15-year loan often comes with lower rates but higher monthly payments, while a 30-year term spreads costs over a longer period, making it more manageable.
Initial Contribution: Adjusting your initial contribution can show you how it affects your total loan and private mortgage insurance (PMI). Making a larger down payment can reduce your overall borrowing costs and might even eliminate PMI, which can significantly lower your 350 000 mortgage monthly payment.
By thoughtfully adjusting these parameters, you can navigate the mortgage process with confidence, ensuring that your decisions align with your family’s needs.
Evaluate Your Results and Plan Accordingly
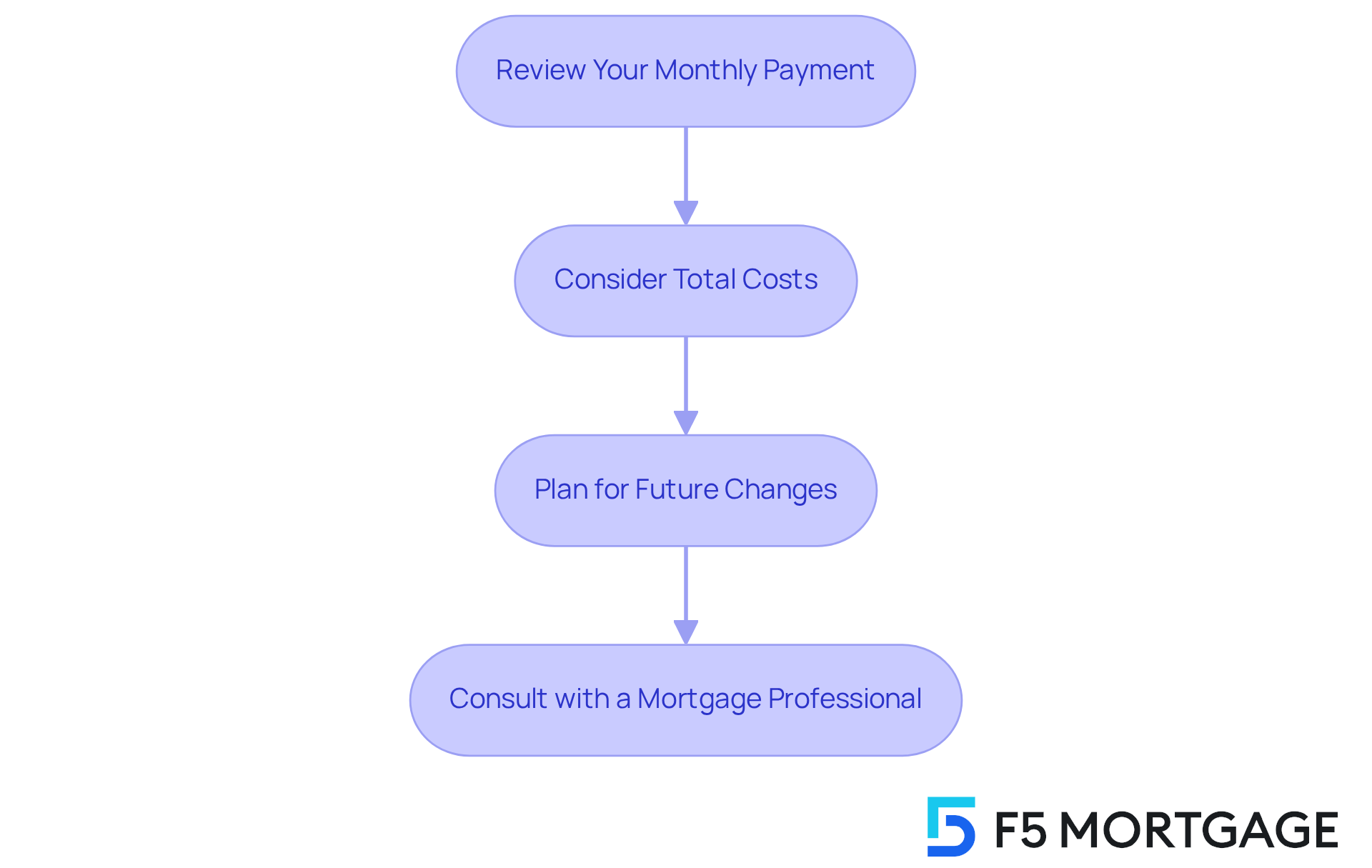
After calculating the 350,000 mortgage monthly payment, let’s take a moment to evaluate your results effectively. We know how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Review Your Monthly Payment: First, confirm that your payment aligns with your budget and financial objectives. A thoughtfully designed budget should consider all elements of homeownership, ensuring that your loan fits comfortably within your overall financial picture.
Consider Total Costs: Next, it’s crucial to factor in additional expenses like property taxes, homeowners insurance, and private mortgage insurance (PMI). These costs can significantly influence your overall financial obligation each month. For instance, property taxes can vary widely by location, averaging around 1.1% of the home’s value annually, while homeowners insurance typically costs between $800 and $1,200 per year.
Plan for Future Changes: It’s also wise to anticipate how fluctuations in interest rates or property taxes may influence your costs over time. With loan rates expected to average around 6.7% in 2025, understanding potential rises in your 350,000 mortgage monthly payment is essential for long-term financial planning.
Consult with a Mortgage Professional: If you have questions or need tailored advice, consider reaching out to a mortgage broker. Their expertise can help clarify your financial obligations and guide you in making informed decisions.
By thoroughly evaluating your results and planning for the future, you can approach homeownership with greater confidence and financial security.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of calculating a $350,000 mortgage monthly payment can feel overwhelming. We know how challenging this can be, but this guide is here to help you navigate through it with confidence. By breaking down the essential components that influence your monthly payments – from key mortgage terms to effective use of calculators – you can approach the mortgage landscape with clarity.
Key factors like the loan amount, interest rate, loan duration, down payment, and additional costs such as property taxes and insurance significantly impact your monthly mortgage payments. Adjusting these parameters can lead to more favorable outcomes, ensuring your mortgage aligns with your financial goals and budget. Remember, evaluating results and planning for future changes are crucial steps in maintaining your financial security.
As you embark on your journey toward homeownership, staying informed about the evolving mortgage landscape is vital. Engaging with mortgage professionals and utilizing reliable calculators can empower you to make well-informed decisions. By taking control of the mortgage process, you can secure a stable financial future while enjoying the many benefits of homeownership. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the principal in a mortgage?
The principal is the amount of money you borrow to purchase your home.
How is the interest rate defined in the context of a mortgage?
The interest rate is the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage.
What does the term of a mortgage refer to?
The term refers to the length of time you have to repay what you’ve borrowed, typically 15 or 30 years.
What is amortization in relation to mortgages?
Amortization is the method of paying back your loan over time through consistent payments.
What is Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)?
PMI is insurance that protects the lender if you default on your loan, often required if your down payment is less than 20%.
What factors affect my monthly mortgage payment?
Key factors include the loan amount, interest rate, loan duration, down payment, home equity, debt-to-income ratios, and property taxes and insurance.
How does the loan amount influence my mortgage payment?
The total amount you borrow directly affects the principal part of your payment; higher loan amounts result in higher monthly payments.
How does the interest rate impact my monthly mortgage payment?
A higher interest rate can significantly increase your monthly payments; for example, a jump from 6.5% to 7.5% on a $400,000 loan could raise your payment by an additional $200.
What is the effect of loan duration on monthly payments?
Shorter loan terms, like 15 years, typically result in higher monthly payments, but can save you money in interest over time compared to longer terms like 30 years.
How can a larger down payment affect my mortgage?
A larger down payment can lower the amount you need to borrow, reducing monthly payments and potentially helping you avoid PMI.
What are home equity and debt-to-income (DTI) ratios?
Home equity refers to the portion of your home that you own outright, while DTI ratios measure the percentage of your income that goes toward debt payments, with a maximum of 43% often required for home loans.
How do property taxes and insurance affect my monthly mortgage payment?
Property taxes and insurance costs are often included in your monthly payment and can vary widely based on location and property value, potentially adding significant amounts to your expenses.








