Overview
Understanding the key differences between interest rate and APR in mortgages is essential for families navigating this important decision. The interest rate reflects only the cost of borrowing the principal amount, while APR encompasses additional costs such as lender fees and closing expenses. This broader perspective provides a more comprehensive view of total borrowing expenses.
We know how challenging this can be, especially when a lower interest rate might seem appealing. However, it’s crucial to recognize that a lower interest rate doesn’t always mean a better deal. If the APR is significantly higher due to extra fees, families could end up paying more in the long run.
By grasping these distinctions, families can make informed mortgage decisions that align with their financial goals. We’re here to support you every step of the way, ensuring that you choose the best option for your unique situation.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of mortgage costs is vital for families embarking on the journey of homeownership. We know how challenging this can be, and the difference between interest rates and APR can significantly influence your financial decisions. These figures represent more than just numbers—they encapsulate the true expense of borrowing. However, the allure of lower rates is often overshadowed by hidden fees reflected in APR.
How can families ensure they make the most informed choices? This article delves into the key differences between mortgage interest rates and APR, offering insights that empower you to navigate your financial future with confidence.
Define Interest Rate and APR in Mortgages
Understanding borrowing costs is essential for families navigating the mortgage process. The borrowing cost represents the percentage applied to a loan, reflecting the expense of acquiring funds. Typically expressed as an annual figure, it directly impacts your . For instance, if you obtain a $200,000 loan at a 4% charge, you’ll face an annual expense of $8,000, translating to about $667 each month.
However, it’s crucial to consider the , which provides a broader perspective. APR not only includes the percentage charged but also accounts for , such as lender fees, mortgage insurance, and closing expenses. This makes APR a more comprehensive measure of your total borrowing expense. For example, if the same loan has an APR of 4.5%, it indicates that the , including fees, exceeds the charge alone.
We know how challenging this can be. A might seem appealing, but it’s essential to recognize that the comparison of [rate vs APR mortgage](https://f5mortgage.com/10-essential-facts-about-conventional-loans-you-must-know) shows that a higher APR due to additional expenses can make an offer less favorable. When considering , families should first assess their and explore various lenders to find the .
Once you submit a refinancing application, the lender will review your financial documents and property value through an appraisal process. Following this, underwriting occurs, where the lender examines your application and credit history to finalize the approval process. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way as you navigate these important decisions.
Differentiate Between Interest Rate and APR
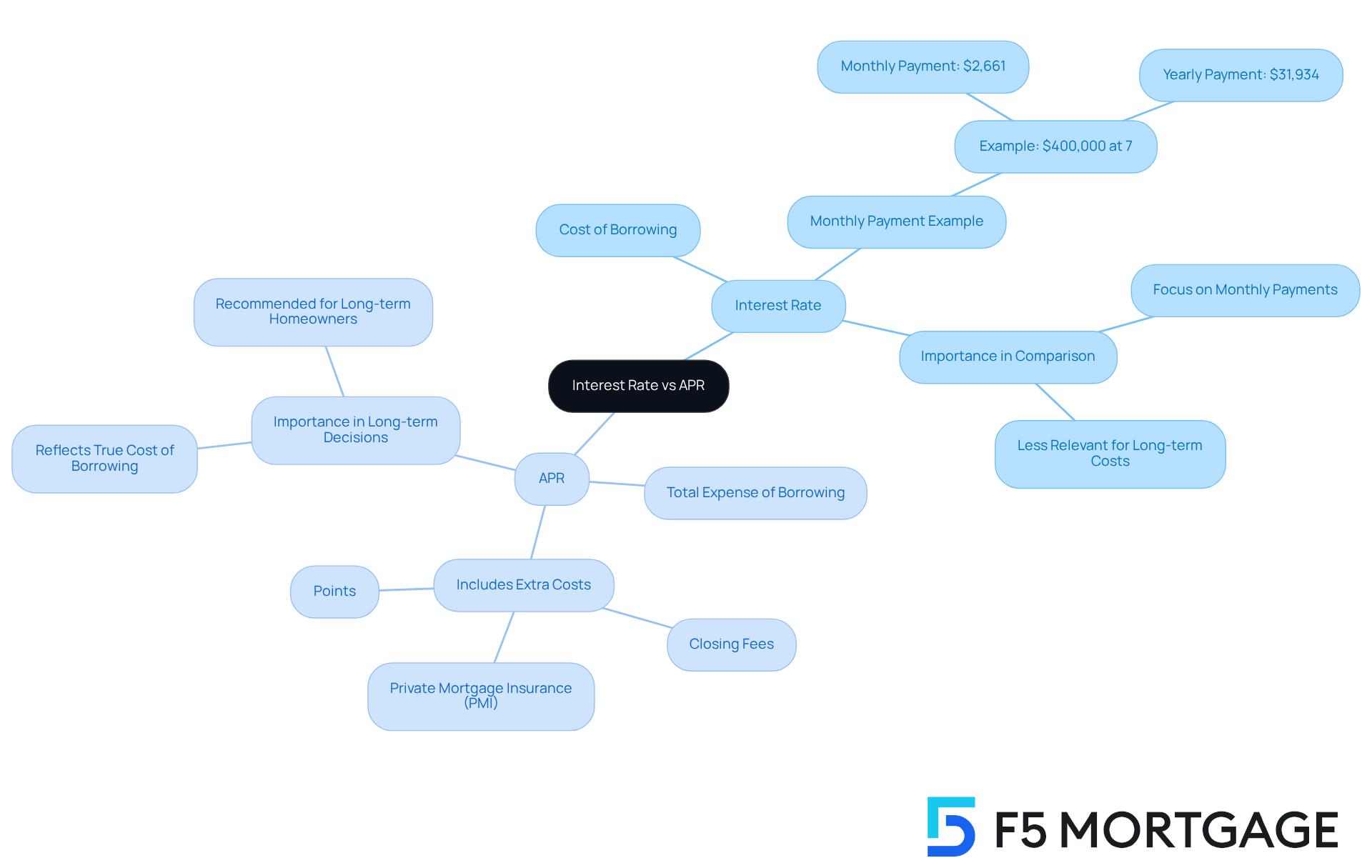
While both the interest rate and the are expressed as percentages, they serve distinct purposes in the mortgage landscape, making it crucial for families to understand these differences as they navigate this process.
Interest Rate: This represents the of the loan, excluding any additional fees or costs. It’s a straightforward figure that many borrowers prioritize when comparing their options. For example, on a $400,000 loan with a 7% interest rate, the monthly payment would be around $2,661, which adds up to approximately $31,934 yearly.
APR (Annual Percentage Rate): In contrast, this figure provides a more comprehensive view of the . It includes the borrowing charge along with extra expenses such as closing fees, private mortgage insurance (PMI), and points. Imagine two loans with the same interest rate but different APRs; the loan with the lower APR generally signifies a more favorable financial option, indicating decreased overall expenses.
We know how challenging it can be to navigate these choices. between the is essential for families to make informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls when selecting a mortgage. , especially for those planning to stay in their homes for an extended period, as it reflects the true cost of borrowing. By contrasting the rate vs apr mortgage, families can and secure the most advantageous conditions.
When seeking lenders, consider , which offers appealing terms and customized assistance tailored to your needs. Furthermore, it is vital to compare APRs of with those of adjustable-rate loans, as the latter can have fluctuating expenses over time. Remember, borrowers generally have less influence over their APR compared to their loan charges, as lenders determine elements such as origination fees and broker costs. Typically, the APR is higher than the interest rate due to the inclusion of these additional expenses. Understanding these nuances can empower families to make more informed choices when evaluating mortgage options.
Analyze the Impact of Interest Rates and APR on Mortgage Payments
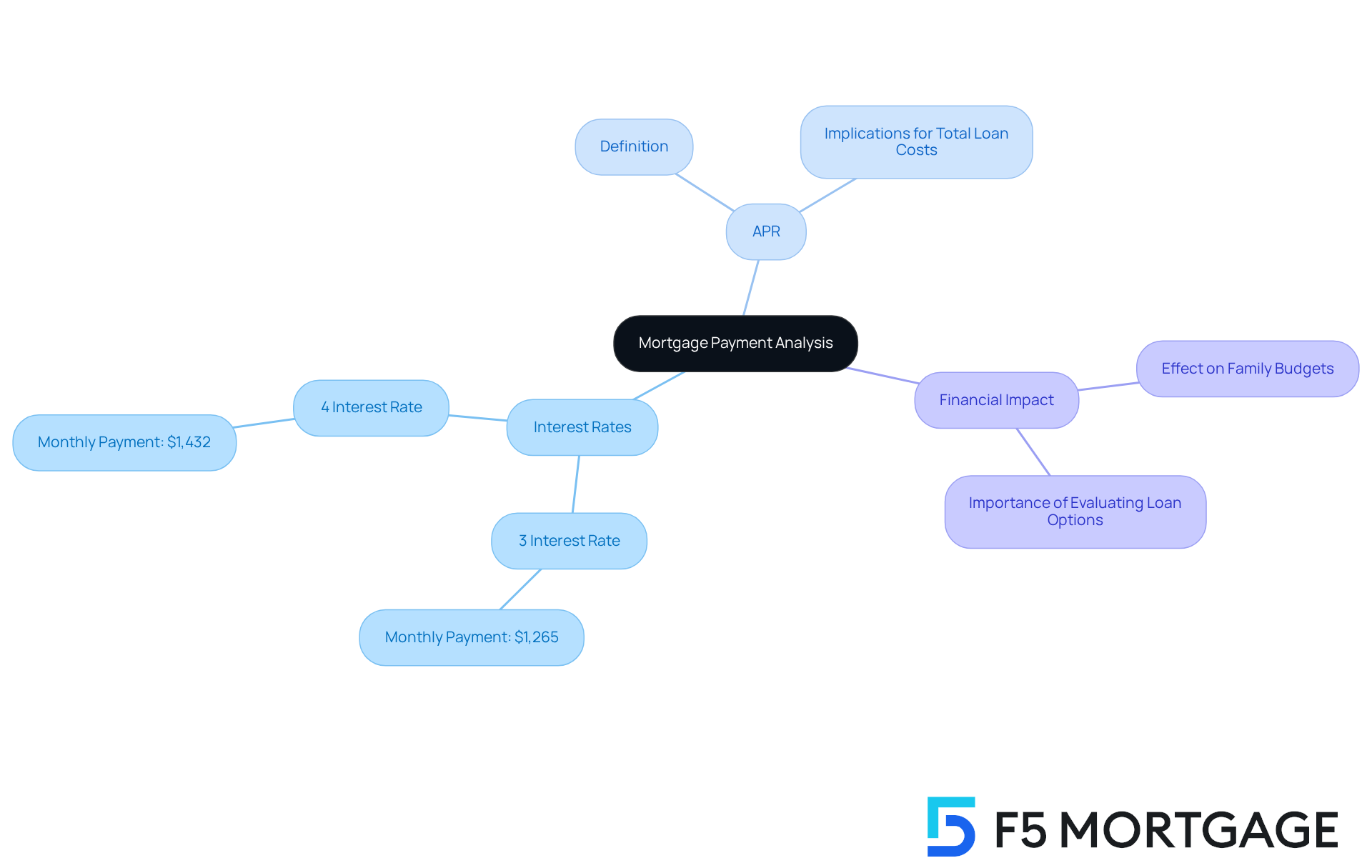
Interest levels and the are crucial factors in shaping mortgage payments, where even small changes can lead to significant monthly expenses. For example, a 1% increase in can raise monthly payments by hundreds of dollars, which can feel overwhelming.
Let’s consider a $300,000 mortgage with a 30-year term: at a 3% interest rate, the monthly payment is around $1,265. However, if borrowing costs rise to 4%, the payment jumps to approximately $1,432, adding an extra $167 each month. This kind of shift can greatly .
The rate vs APR mortgage is equally important, as the APR encompasses not just the borrowing cost but also related fees, which affect the total financing expense. A higher APR, even with a lower initial cost, can lead to a more expensive loan overall. This highlights the need for families to carefully and the rate vs APR mortgage when considering mortgage options.
Experts note that a 1% increase in interest rates can . is essential, especially as the housing market evolves, with those from 2021. Families must remain vigilant about how these changes influence their financial responsibilities.
To effectively compare lenders, , request estimates, and scrutinize the terms, fees, and charges offered by different lenders. can provide families with favorable terms and personalized assistance, ensuring they find the best fit for their financial situation. By monitoring these factors, families can feel empowered to make informed decisions in their home financing journey.
Implement Strategies to Lower Your Interest Rate and APR
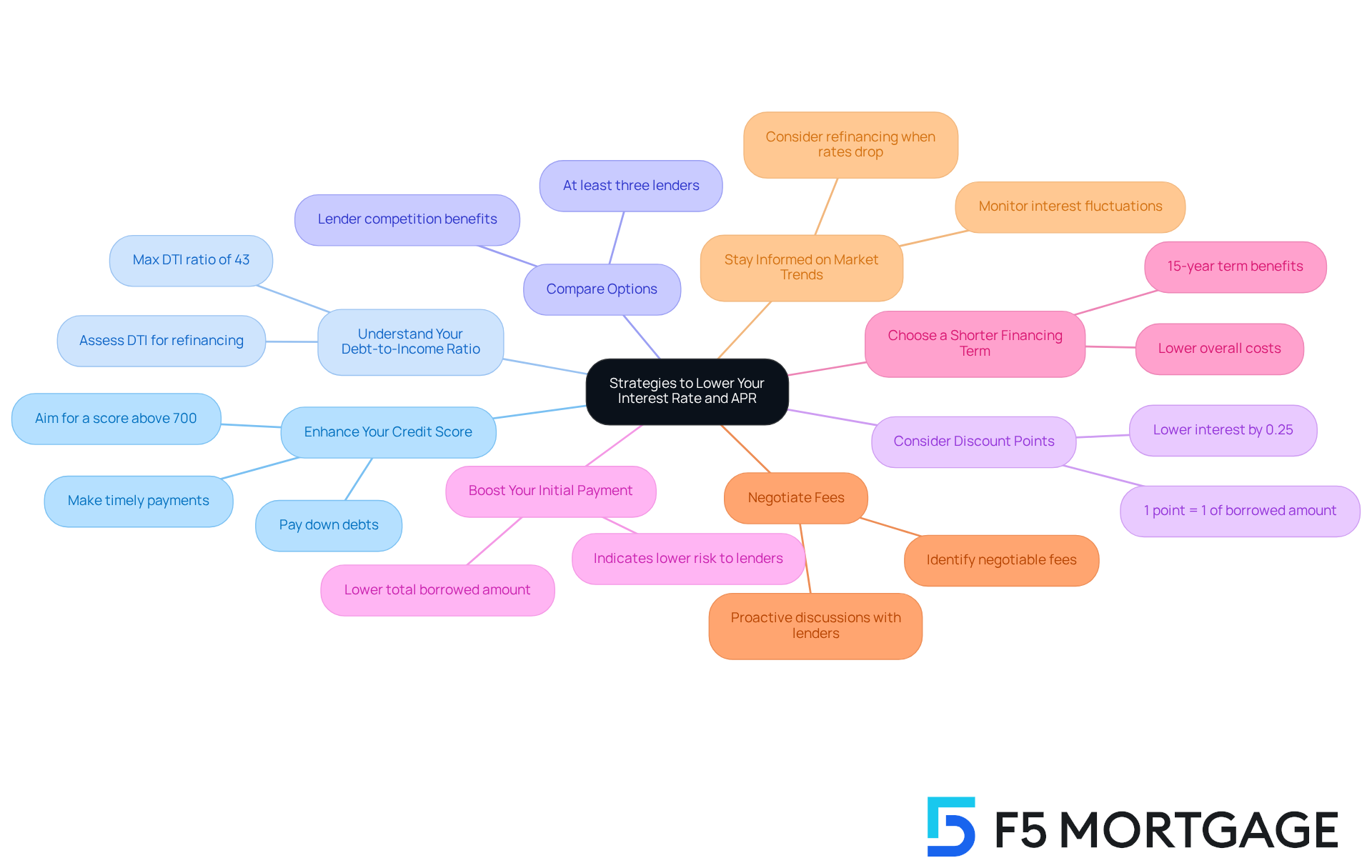
To effectively lower your and APR, consider implementing these supportive strategies:
- Enhance Your Credit Score: We know how challenging it can be to manage finances. A higher credit score is essential for qualifying for a favorable , which results in reduced interest costs. Focus on paying down debts and making timely payments to enhance your score. For instance, improving your credit score from the mid-600s to the mid-700s can result in a decrease in your traditional mortgage cost by several tenths of a percent or more, potentially saving you tens of thousands throughout the duration of the mortgage.
- Understand Your : We understand that navigating finances can be overwhelming. A maximum DTI ratio of 43% is typically required for home loans. An improved DTI can lead to more competitive terms in the context of the rate vs apr mortgage. If you’re considering refinancing, and explore the options available to you.
- : It’s important to know that the rate vs apr mortgage costs can differ greatly among lenders. We recommend from at least three different lenders to secure the best deal. Remember, mortgage lenders are competing for customers, so exploring multiple options can be beneficial.
- : Paying for discount points in advance can effectively reduce your borrowing cost. Generally, each point is valued at 1% of the borrowed amount and can lower your interest by roughly 0.25%. This strategy can be particularly advantageous in a high-rate vs apr mortgage environment, as it offers you some relief.
- Boost Your Initial Payment: We recognize that making a bigger initial payment can feel daunting, but it not only decreases the total borrowed amount but can also result in improved financing terms. Many lenders prefer borrowers who can make substantial down payments, as it indicates lower risk.
- Choose a shorter financing term, like 15 years, as it often leads to reduced costs, which can be important when considering rate vs apr mortgage. While monthly payments might be elevated, the overall cost incurred over the duration of the loan is considerably diminished. This can be a financially prudent decision for many families.
- Negotiate Fees: Don’t hesitate to negotiate lender fees. Some fees may be negotiable, which can help lower your rate vs apr mortgage. Being proactive in discussions with lenders can lead to better overall terms, and we’re here to support you through that process.
- : Monitoring interest fluctuation trends is essential. If rates drop significantly, consider refinancing to take advantage of lower rates, which can lead to substantial savings over time. F5 Mortgage offers various , including FHA and VA loans, which may provide additional benefits depending on your situation. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between the interest rate and APR in mortgages is crucial for families making informed financial decisions. We know how challenging this can be. While the interest rate represents the cost of borrowing the principal amount, the APR provides a more comprehensive view by including additional expenses associated with the loan. Grasping these distinctions empowers families to assess mortgage options effectively and avoid potential pitfalls.
Throughout the article, we highlighted key points that emphasize the importance of evaluating both interest rates and APR when considering mortgage loans. A lower interest rate may initially seem attractive, but a higher APR due to extra fees can lead to a more expensive overall loan. We’re here to support you every step of the way, and strategies for reducing interest rates and APR, such as:
- Improving credit scores
- Understanding debt-to-income ratios
- Comparing offers from multiple lenders
are essential steps in securing favorable mortgage terms.
Ultimately, being well-informed about the rate vs APR mortgage dynamics can significantly impact family finances. It encourages proactive engagement in the mortgage process, allowing families to make choices that align with their long-term financial goals. By prioritizing education on these topics and seeking personalized assistance from professionals, families can navigate the complexities of mortgage financing with confidence and clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of interest rate in mortgages?
The interest rate in mortgages represents the percentage applied to a loan, reflecting the expense of acquiring funds. It is typically expressed as an annual figure and directly impacts monthly mortgage payments.
How does APR differ from the interest rate in mortgages?
APR (Annual Percentage Rate) includes not only the percentage charged on the loan but also additional costs associated with securing financing, such as lender fees, mortgage insurance, and closing expenses. This makes APR a more comprehensive measure of the total borrowing expense.
Why is it important to compare the interest rate and APR when considering a mortgage?
Comparing the interest rate and APR is important because a lower interest rate might seem appealing, but a higher APR due to additional expenses can make an offer less favorable. Understanding both can help borrowers make more informed decisions.
What should families consider when exploring refinancing options?
Families should first assess their financial situation and explore various lenders to find the best terms when considering refinancing options.
What is the process after submitting a refinancing application?
After submitting a refinancing application, the lender will review your financial documents and property value through an appraisal process. Following this, underwriting occurs, where the lender examines your application and credit history to finalize the approval process.








