Overview
Choosing between a 15-year and a 30-year mortgage can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to support you every step of the way. This article compares these two options to help families like yours determine which one aligns best with your financial needs.
- A 15-year mortgage typically offers lower interest rates and allows you to build equity faster. However, it does come with higher monthly payments, which can strain your budget.
- On the other hand, a 30-year mortgage provides lower monthly payments, giving you greater financial flexibility. Yet, it’s important to note that this option results in higher total interest costs over time.
We know how challenging this decision can be. By understanding the pros and cons of each mortgage type, you can make informed choices that fit your budget and long-term goals. Take a moment to reflect on what matters most to your family, and remember that the right mortgage can pave the way for a secure financial future.
Introduction
Choosing the right mortgage is a pivotal decision that can significantly shape your family’s financial future. We understand how challenging this can be, especially when you’re torn between the allure of lower monthly payments with a 30-year mortgage and the long-term savings of a 15-year option. This decision goes beyond mere numbers; it requires a thoughtful understanding of how each choice impacts your budgeting, equity accumulation, and overall financial health.
As you navigate this complex landscape, you might wonder:
- Which mortgage term truly aligns with your family’s needs and aspirations?
- How can you balance immediate affordability with long-term financial goals?
We’re here to support you every step of the way, guiding you to make informed choices that reflect your unique circumstances.
Understand Mortgage Terms and Amortization
Mortgage terms define the duration over which a borrower commits to repaying a loan, often comparing a . Amortization refers to the organized method of settling a loan through regular contributions that include both principal and interest. A 15-year loan, for example, allows homeowners to settle their debt in a shorter period. While this leads to increased regular costs, it considerably throughout the loan’s duration. In contrast, a 30-year loan lengthens the repayment period, resulting in lower installment amounts but higher total interest costs.
We know how challenging it can be to choose the right mortgage option. Recent trends suggest that around 90% of home purchasers opt for a , indicating a preference for affordable installments amid rising home costs, which averaged $503,800 in early 2025. This choice is particularly relevant for families striving to balance their budgets while investing in their homes. Financial consultants emphasize the , as they directly impact a family’s and long-term goals.
For instance, consider a family purchasing a house for $400,000 with a comparison of a 15 year vs 30 year mortgage at an average interest rate of 6.9%. They would face monthly payments of about $2,632, which is significantly lower compared to roughly $3,500 for a 15 year vs 30 year mortgage at the same rate. This difference highlights the need for families to navigate their financial capabilities carefully when selecting a loan option.
Additionally, families should explore (ARMs) as an alternative. ARMs typically offer lower introductory rates, making them suitable for those who plan to pay off their mortgage quickly or refinance in a few years. However, it’s essential to understand the risks associated with variable rates, including the importance of interest adjustment caps that protect borrowers from significant rate increases.
To calculate your break-even point for refinancing, follow these steps:
- Determine , including all closing fees and expenses associated with refinancing.
- Calculate your from your current payment.
- Divide your refinancing expenses by your regular savings to find out how many months it will take to break even. For instance, if your refinancing costs are $4,000 and your monthly savings are $100, your break-even point would be 40 months.
As families consider their options, the decision between a 15 year vs 30 year mortgage, or even an ARM, should align with their financial situation, lifestyle, and future aspirations. Understanding the nuances of loan terms and amortization, as well as calculating the break-even point for refinancing, is crucial for making informed decisions that support their homeownership journey. Testimonials from satisfied clients highlight the in assisting families with these choices, ensuring they find the optimal financing option for their needs.
Compare 15-Year and 30-Year Mortgages: Costs and Benefits
When evaluating options, we know how challenging this decision can be. Several critical factors emerge that can significantly impact your financial future:
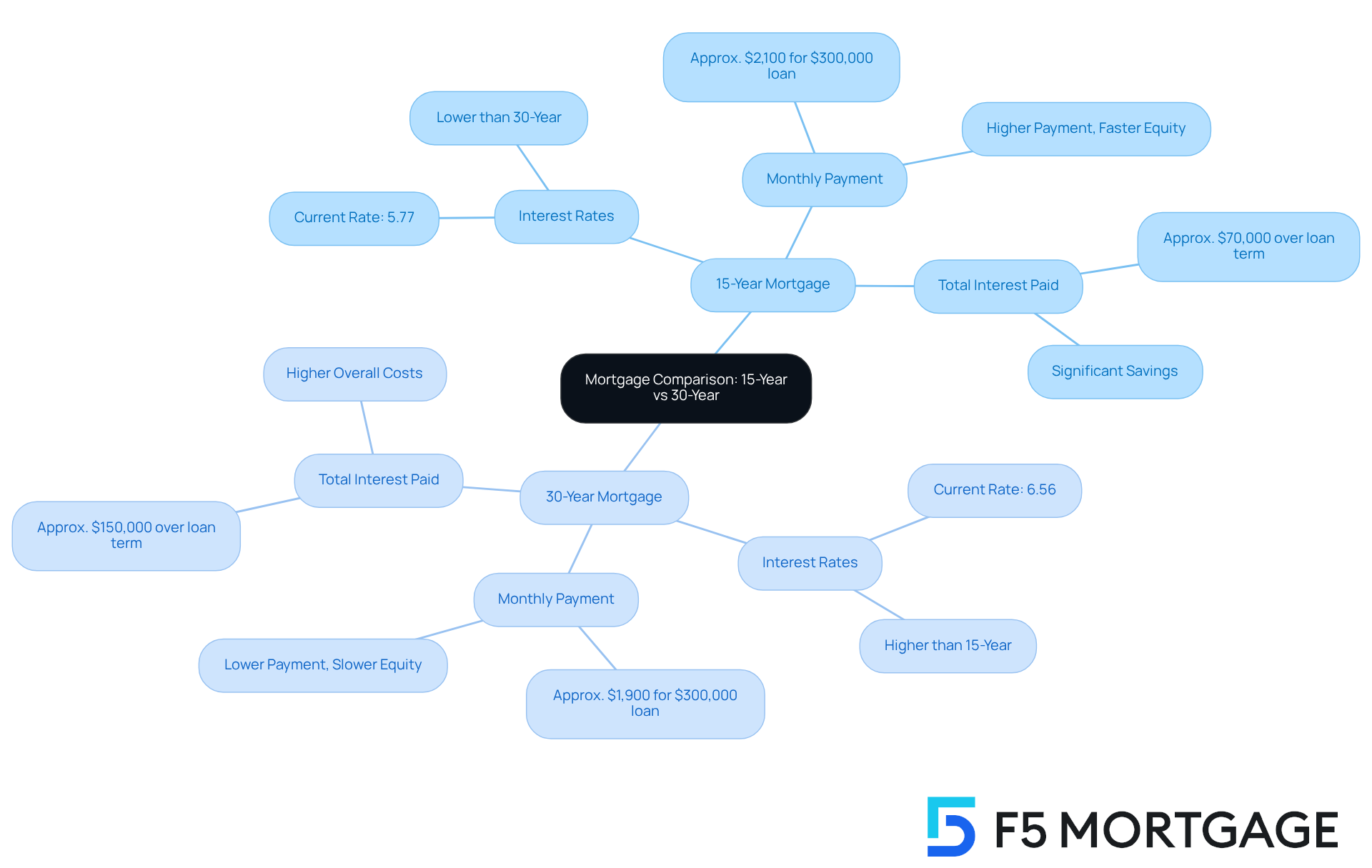
- Interest Rates: Generally, compared to their 30-year counterparts. At present, the typical rate for a decade and a half loan is roughly 5.77%, whereas the remains around 6.56%. This difference can greatly affect your overall borrowing costs.
- Regular Installments: The regular installments for a long-term loan can feel daunting. For example, on a $300,000 loan, the monthly payment for a 15-year term would be around $2,100, while a 30-year term loan would require roughly $1,900. While this higher payment can strain your monthly budget, it leads to quicker equity accumulation, which can be a comforting thought.
- Total Interest Paid: Over the duration of the loan, a long-term home loan can lead to . For the same $300,000 loan, borrowers might pay around $70,000 in interest with a shorter loan term, compared to over $150,000 with a longer loan term. This illustrates the of the [15 year vs 30 year mortgage](https://f5mortgage.com/?p=10572), empowering you to make a well-informed decision.
These comparisons highlight the , allowing families to make informed choices based on their budgetary limitations and long-term financial goals. We’re here to support you every step of the way in this important journey.
Evaluate Pros and Cons of 15-Year vs 30-Year Mortgages
Evaluate Pros and Cons of 15-Year vs 30-Year Mortgages
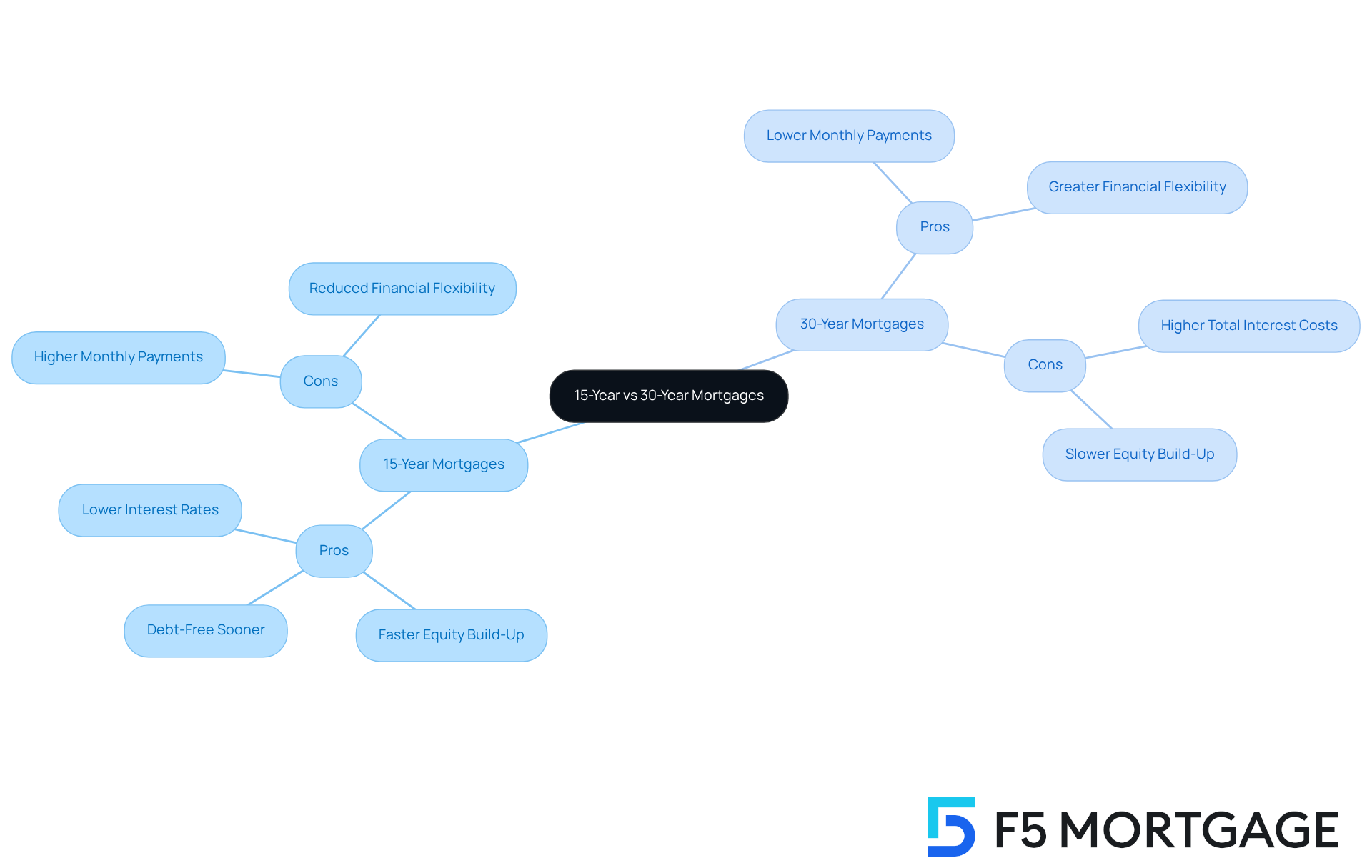
Pros and Cons of 15-Year Mortgages:
Pros:
- : We understand how important savings are for your family. Typically, when comparing a 15 year vs 30 year mortgage, the 15-year mortgages offer , leading to substantial savings over the loan’s lifespan.
- : Building equity more rapidly can be a significant advantage, especially if you choose to sell or refinance in the future.
- : Imagine settling your mortgage obligations in just 15 years. This enables families to attain financial freedom earlier, offering peace of mind.
Cons:
- Higher Monthly Payments: However, it’s important to note that the monthly payments are considerably higher. This can strain a family’s budget and limit discretionary spending.
- Reduced Financial Flexibility: With increased expenses, you may find it challenging to save or invest in other financial opportunities.
Pros and Cons of 30-Year Mortgages:
Pros:
- : On the other hand, 30-year mortgages come with lower monthly payments. This can facilitate easier budgeting for families, making it more manageable.
- : With reduced payments, you can free up disposable income. This allows families to allocate funds toward savings or investments, which is crucial for future planning.
Cons:
- : It’s essential to consider that over the duration of the loan, borrowers will incur significantly more interest compared to a 15-year mortgage. This can impact your overall financial health.
- Slower Equity Build-Up: Additionally, building equity takes longer with a 30-year mortgage. This can be a disadvantage if you need to sell or refinance quickly.
This thorough assessment aims to provide families with essential insights. By understanding the pros and cons of each option, you can match your loan selection with your financial situation, ensuring you make informed choices that align with your long-term objectives. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Select the Right Mortgage Term for Your Financial Goals
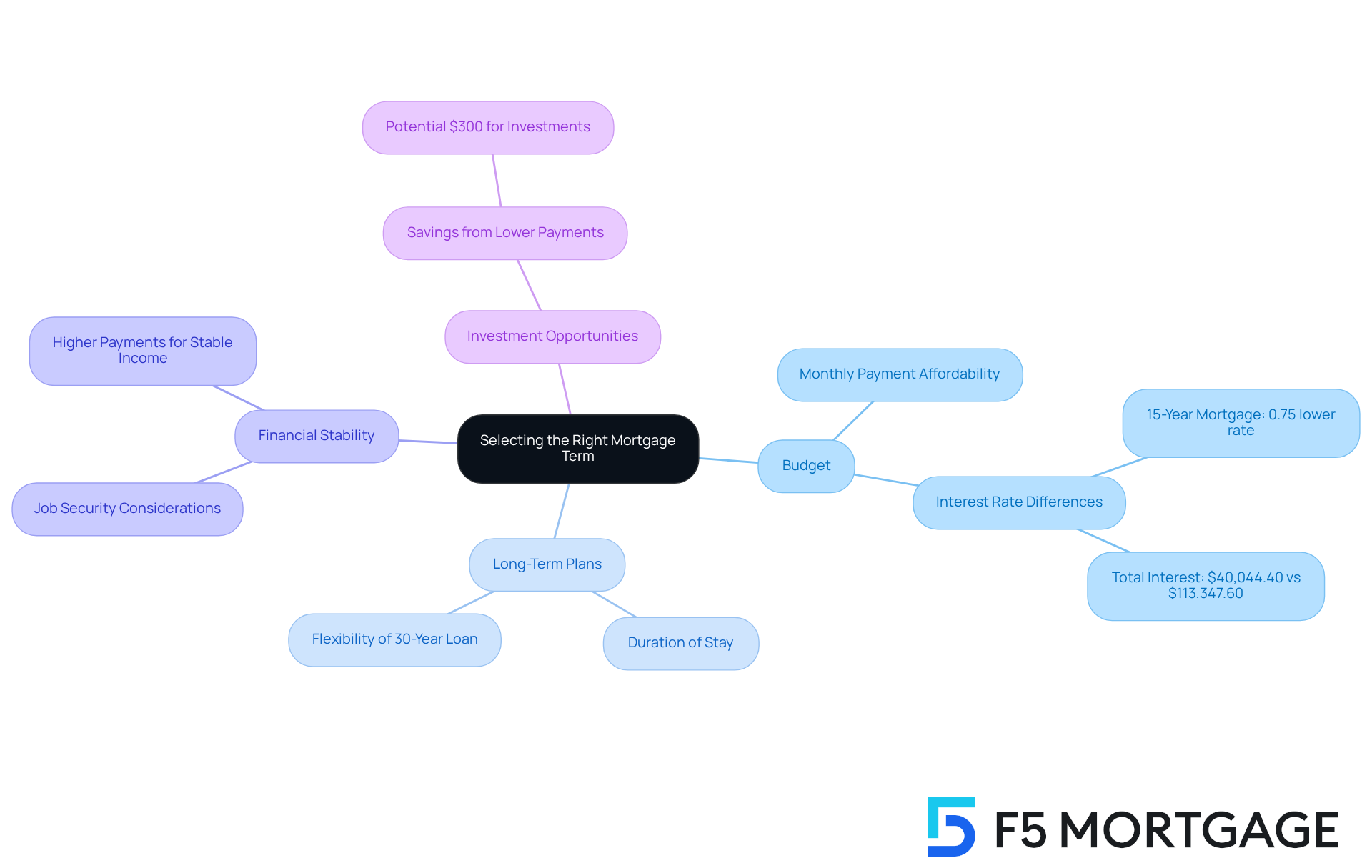
Selecting the right mortgage term can feel overwhelming, but understanding your .
Budget: We know how important it is to consider what you can afford in monthly payments. If your budget allows for larger contributions, a . Typically, it offers an interest rate that is 0.75% lower than a longer-term loan. This can lead to significant savings—total interest paid could reach $40,044.40 for a , with the costing $113,347.60. However, if you value smaller payments for , a 30-year loan could be a better option.
Long-Term Plans: Think about . If relocating in a few years is on your mind, a 30-year loan provides greater flexibility. Conversely, if you plan to stay put for a while, a . As Colin Robertson wisely noted, “Your choice can greatly impact how much interest is paid to the bank over time.”
Financial Stability: Evaluate your job security and income stability. If you enjoy a steady income, you might feel more comfortable with the higher payments associated with a 15 year vs 30 year mortgage. For instance, families with consistent earnings may find these increased costs manageable, while those facing uncertainty might prefer the lower payments associated with a 15 year vs 30 year mortgage option.
Investment Opportunities: Consider how the savings from could be invested for potential growth. The financial flexibility of a 30-year loan can empower families to set aside around $300 extra each month for savings or investments, enhancing their overall financial well-being.
By thoughtfully considering these factors and integrating relevant statistics and expert insights, you can choose a mortgage term that aligns with your financial goals and lifestyle. We’re here to support you every step of the way, ensuring a more secure and manageable .
Conclusion
Choosing the right mortgage term is a crucial decision that can significantly influence your family’s financial future. We understand how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way. When comparing a 15-year and a 30-year mortgage, it’s essential to recognize the distinct advantages and challenges each option presents.
- A 15-year mortgage offers lower interest rates and faster equity build-up, but it comes with higher monthly payments that may strain your budget.
- On the other hand, a 30-year mortgage provides lower monthly payments and greater financial flexibility, though it results in higher total interest payments over time.
As you navigate this decision, consider your personal financial situation, long-term plans, and budgetary constraints. It’s important to weigh the benefits of quicker debt repayment against the comfort of manageable monthly expenses. Understanding mortgage terms and amortization is vital for making informed choices that align with your financial goals.
Ultimately, whether you opt for a 15-year or a 30-year mortgage, your choice should reflect your family’s unique circumstances and aspirations. As financial landscapes evolve, the importance of strategic planning and informed decision-making cannot be overstated. We encourage you to assess your priorities carefully and seek expert guidance to ensure your mortgage choice supports your long-term financial well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are mortgage terms?
Mortgage terms define the duration over which a borrower commits to repaying a loan, commonly seen in 15-year and 30-year mortgages.
What is amortization?
Amortization is the organized method of settling a loan through regular payments that include both principal and interest.
What are the advantages of a 15-year mortgage?
A 15-year mortgage allows homeowners to pay off their debt in a shorter period, leading to higher regular payments but significantly reduced overall interest expenses.
What are the advantages of a 30-year mortgage?
A 30-year mortgage results in lower monthly installment amounts, making it more affordable in the short term, but it incurs higher total interest costs over the life of the loan.
What recent trends are observed in mortgage choices?
Recent trends indicate that about 90% of home purchasers opt for a 30-year fixed-rate loan, primarily due to the preference for lower monthly payments amid rising home costs.
How does the choice of mortgage impact a family’s budget?
The choice of mortgage directly affects a family’s financial well-being and long-term goals, making it essential to understand the implications of different loan options.
Can you provide an example of monthly payments for a 15-year vs 30-year mortgage?
For a family purchasing a house for $400,000 at an average interest rate of 6.9%, the monthly payment for a 30-year mortgage would be about $2,632, compared to roughly $3,500 for a 15-year mortgage.
What are adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs)?
ARMs typically offer lower introductory rates and may be suitable for those who plan to pay off their mortgage quickly or refinance in a few years, but they come with risks associated with variable rates.
How can borrowers calculate their break-even point for refinancing?
To calculate the break-even point, determine refinancing costs, calculate monthly savings by subtracting the new payment from the current payment, and divide the refinancing expenses by the monthly savings.
What factors should families consider when choosing a mortgage option?
Families should consider their financial situation, lifestyle, future aspirations, and the nuances of loan terms and amortization when selecting a mortgage option.








