Overview
This article offers essential insights into loan-to-value (LTV) ratios, a crucial aspect for homebuyers navigating the mortgage process. We understand how challenging this can be, and we want to empower you with knowledge. Maintaining a lower LTV, ideally below 80%, can significantly improve your loan terms, leading to lower interest rates and the avoidance of private mortgage insurance. By grasping these concepts, you can make informed financial decisions that benefit you and your family. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
Navigating the complex world of mortgages can be daunting, and understanding the intricacies of loan-to-value (LTV) ratios is crucial for homebuyers like you. This essential metric not only influences loan approval and interest rates but also directly impacts your overall financial health as a homeowner. As the housing market evolves, particularly as we approach 2025, grasping the nuances of LTV can empower you to make informed decisions that align with your financial goals.
We know how challenging this can be. How can you leverage this knowledge to secure better loan terms and avoid costly pitfalls? By understanding LTV ratios, you can take steps toward a more secure financial future.
F5 Mortgage: Your Partner for Understanding Loan-to-Value Ratios
Navigating the home loan landscape can be challenging, and we know how overwhelming it can feel, especially when it comes to understanding loan to value metrics. At F5 Mortgage, we prioritize your education and well-being. We offer personalized consultations to clarify the significance of loan to value (LTV) in your home buying or refinancing journey. The loan to value is an essential metric that lenders use to evaluate risk. A lower loan to value signifies more equity, which can lead to more advantageous loan terms. For instance, a loan to value ratio of 80% or lower may grant you access to competitive interest rates, while higher proportions might necessitate private insurance.
Our extensive network of lenders allows us to provide tailored advice that aligns with your unique financial goals. By understanding loan to value, you can make informed decisions regarding down payments and property negotiations. Imagine obtaining financing of $150,000 on a property valued at $200,000; your loan to value would be 75%, placing you in a favorable position with lenders.
As we look ahead to 2025, the importance of loan to value measurements in mortgage approvals remains crucial. Lenders are increasingly examining the loan to value metric alongside credit scores and debt-to-income ratios. Our commitment to empowering you with knowledge ensures that you are well-equipped to navigate these complexities. With over 1,000 families helped and a customer satisfaction rate of 94%, F5 Mortgage stands out as a trusted partner in achieving your homeownership dreams. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding Loan-to-Value Ratio: Definition and Importance
Understanding the debt-to-value proportion, specifically the loan to value (LTV) ratio, is essential for anyone navigating the mortgage process. This financial term helps you see the relationship between the amount you borrow and the worth of the asset you’re acquiring. Essentially, it’s calculated by dividing the amount borrowed by the appraised value of the property. A lower LTV ratio can significantly reduce risk for lenders, which often leads to better financing terms for you, the borrower.
We know how challenging this can be, especially for first-time homebuyers. Comprehending loan to value can directly impact your loan approval, interest rates, and even the necessity for loan insurance. It’s a crucial piece of the puzzle that can empower you in your home-buying journey.
Additionally, it’s important to keep in mind that approval letters for financing typically become invalid after 90 days. This timeframe can vary depending on your type of credit. If you haven’t made an offer within this period, it’s vital to renew your approval before moving forward with your home purchase. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Calculating Your Loan-to-Value Ratio: A Step-by-Step Guide
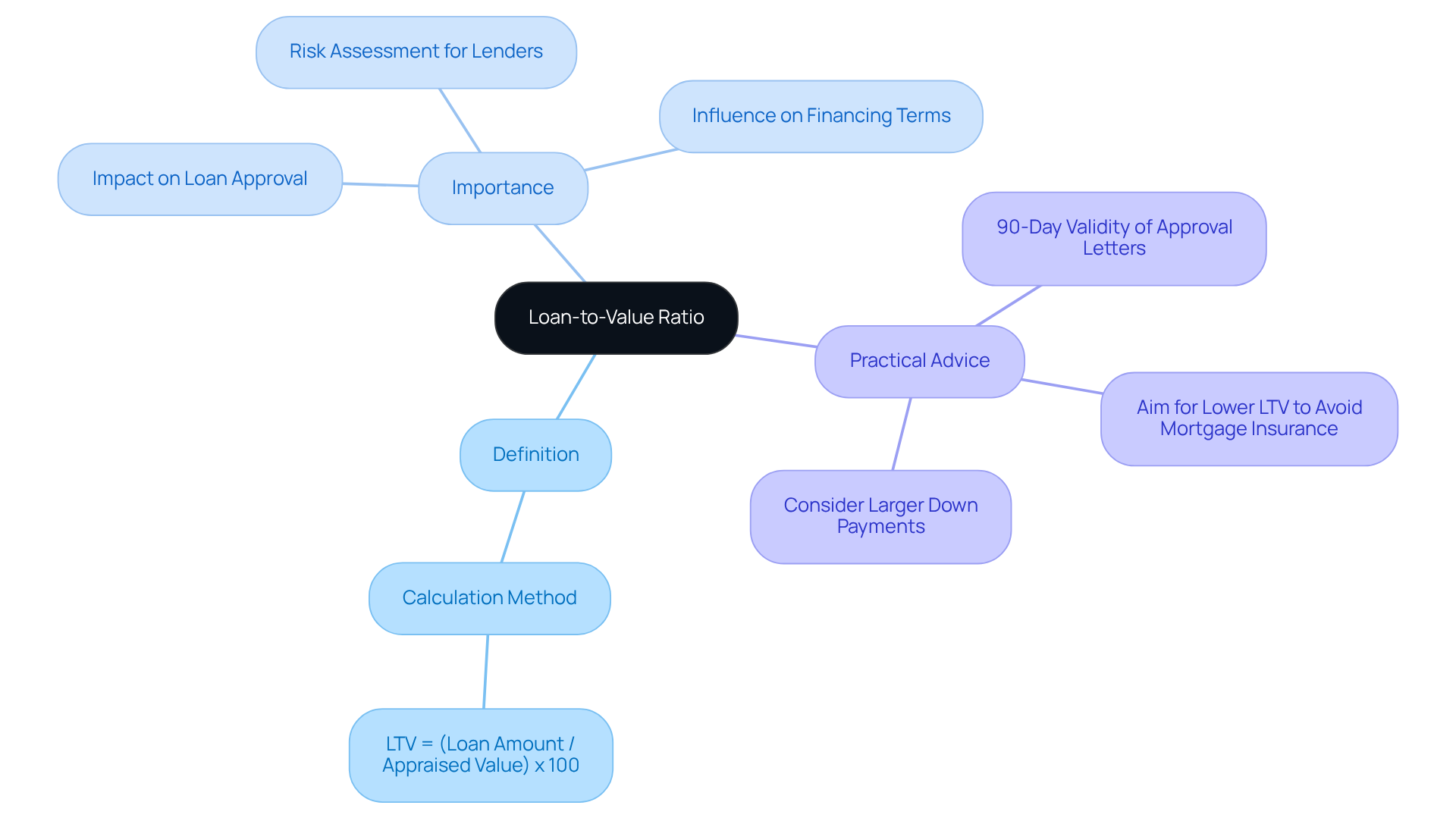
Understanding your loan to value ratio is essential for navigating your financing options with confidence. We know how challenging this can be, but by following these straightforward steps, you can determine your LTV:
- Start by establishing the appraised value of your property.
- Next, identify the total amount you plan to borrow.
- Finally, apply the formula: LTV = (Loan Amount / Appraised Value) x 100.
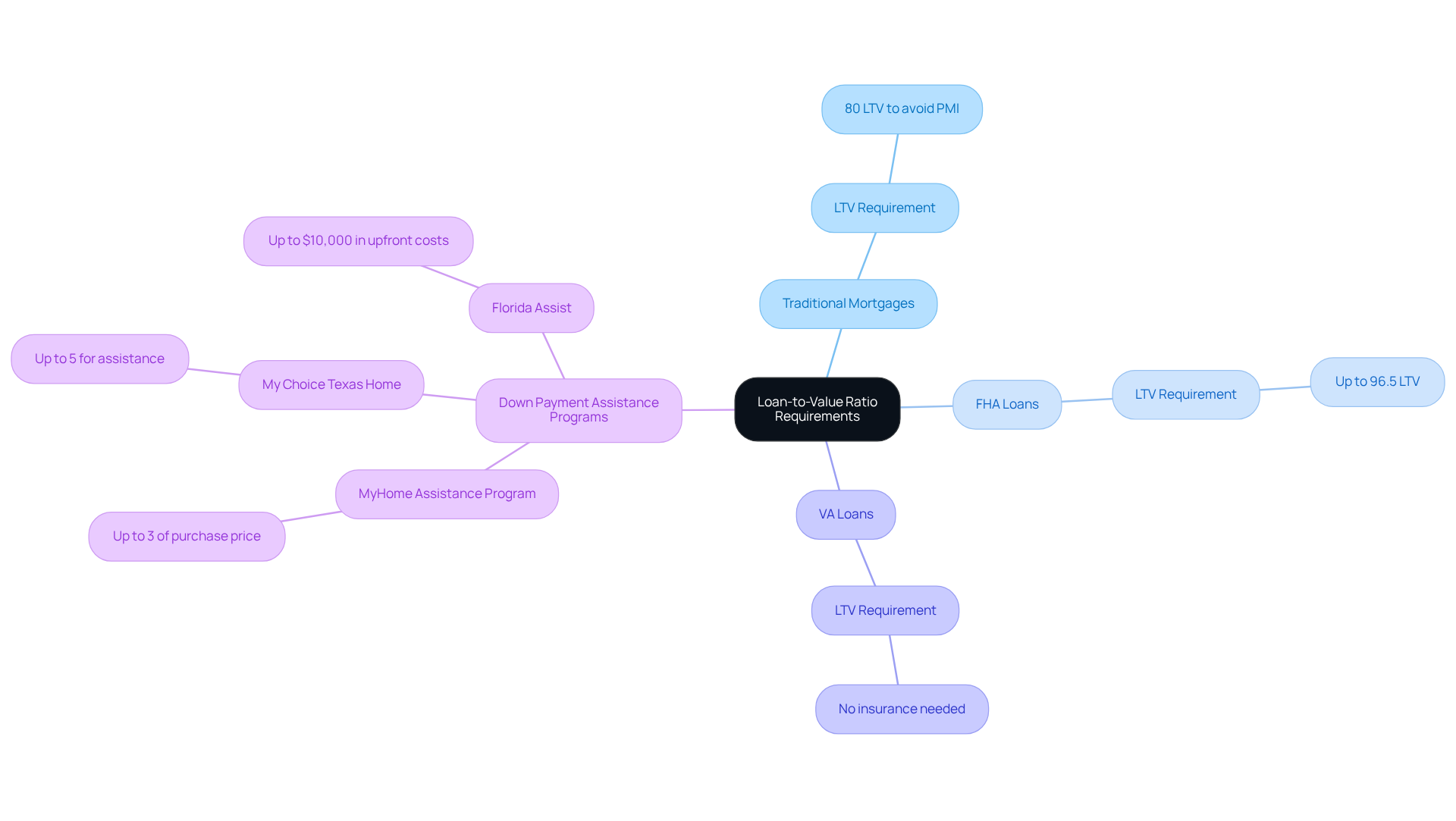
For example, if you borrow $200,000 for a home valued at $250,000, your LTV would be 80%. This loan to value ratio is crucial, as many lenders typically require a maximum loan to value of 80% to avoid private insurance. In contrast, FHA loans can allow for a maximum loan to value (LTV) of 96.5%.
Understanding your loan to value can significantly influence both your borrowing costs and your chances of approval. By grasping this vital metric, you empower yourself in the home buying process, ensuring you make informed decisions every step of the way.
The Role of Loan-to-Value Ratio in Mortgage Approval and Interest Rates
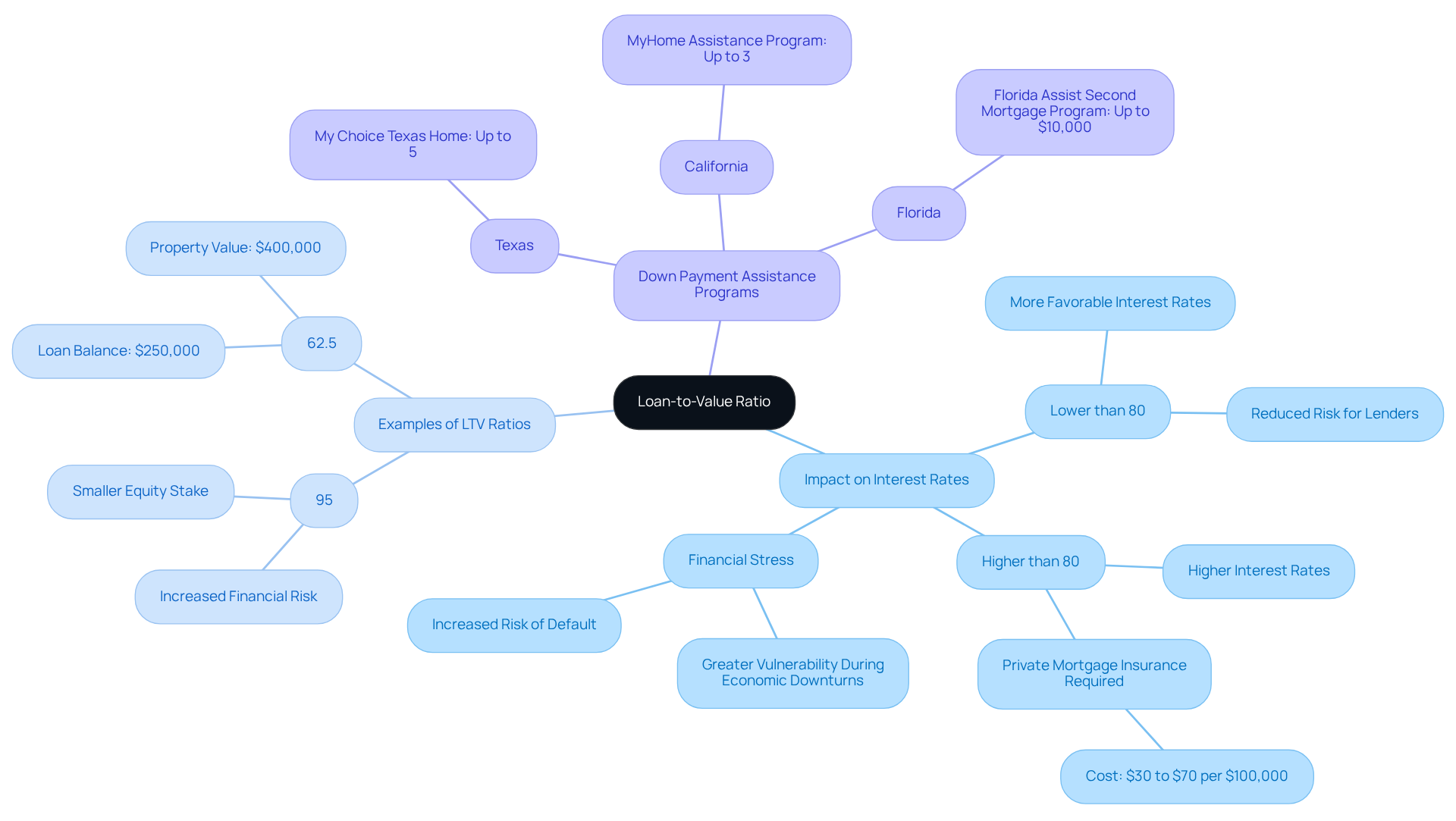
The loan to value (LTV) proportion is a crucial factor in home loan approval and significantly impacts interest rates. We understand that lenders often prefer lower loan to value levels, as these levels signal reduced risk. For instance, if your loan to value ratio is 80% or lower, you may qualify for more favorable interest rates. On the other hand, if your ratio exceeds 80%, you might face higher rates and be required to pay private insurance, which can add an extra $30 to $70 monthly for every $100,000 borrowed. This added cost can affect your overall affordability.
Research shows that homebuyers with higher loan to value ratios may experience greater financial stress, especially during economic downturns or when interest rates rise. Consider a scenario where a borrower holds a loan balance of $250,000 on a property valued at $400,000, resulting in an LTV of 62.5%. This is generally seen as manageable. In contrast, a loan to value (LTV) of 95% reflects a smaller equity stake and increased financial risk, often leading to higher interest rates.
Understanding how loan to value (LTV) relates to interest rates is vital for homebuyers. A lower loan to value not only increases the chances of securing financing but also opens the door to better loan conditions. As loan rates fluctuate, keeping a manageable loan to value can provide a strategic advantage in obtaining favorable financing options.
For families looking to enhance their homes, down payment assistance programs can play a significant role in improving LTV figures by providing funds that reduce the required down payment. For example:
- California’s MyHome Assistance Program offers up to 3% of the home’s purchase price.
- Texas’s My Choice Texas Home program provides up to 5% for down payment and closing assistance.
- In Florida, programs like the Florida Assist Second Mortgage Program can provide up to $10,000 in upfront costs.
These initiatives help lower the loan to value ratio, making it easier for families to qualify for better loan conditions. As Neil Peterson, Chief Credit Officer, wisely states, “Determining how much loan you can afford is a crucial step in the homebuying process.
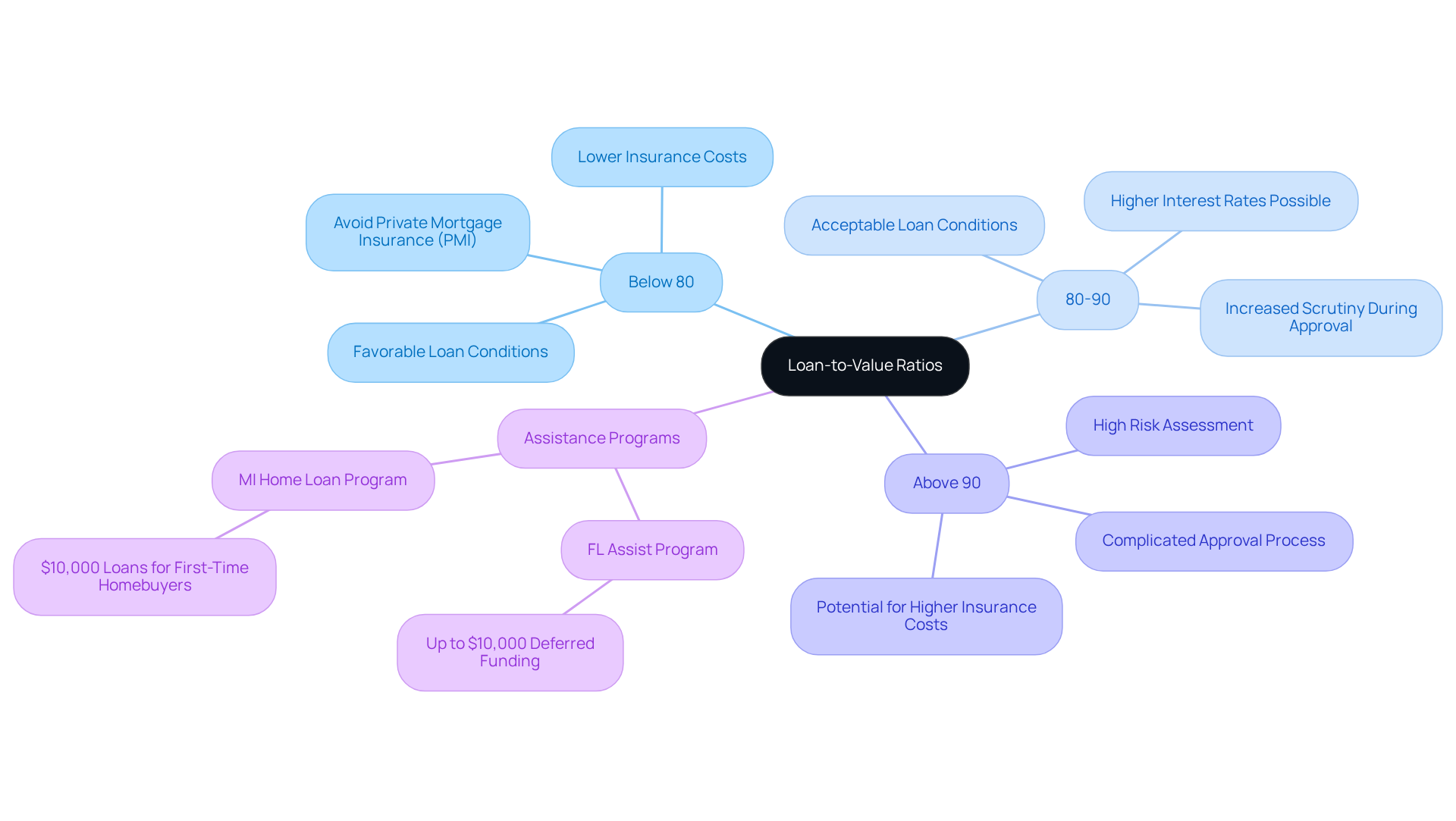
What is a Good Loan-to-Value Ratio? Key Benchmarks for Homebuyers
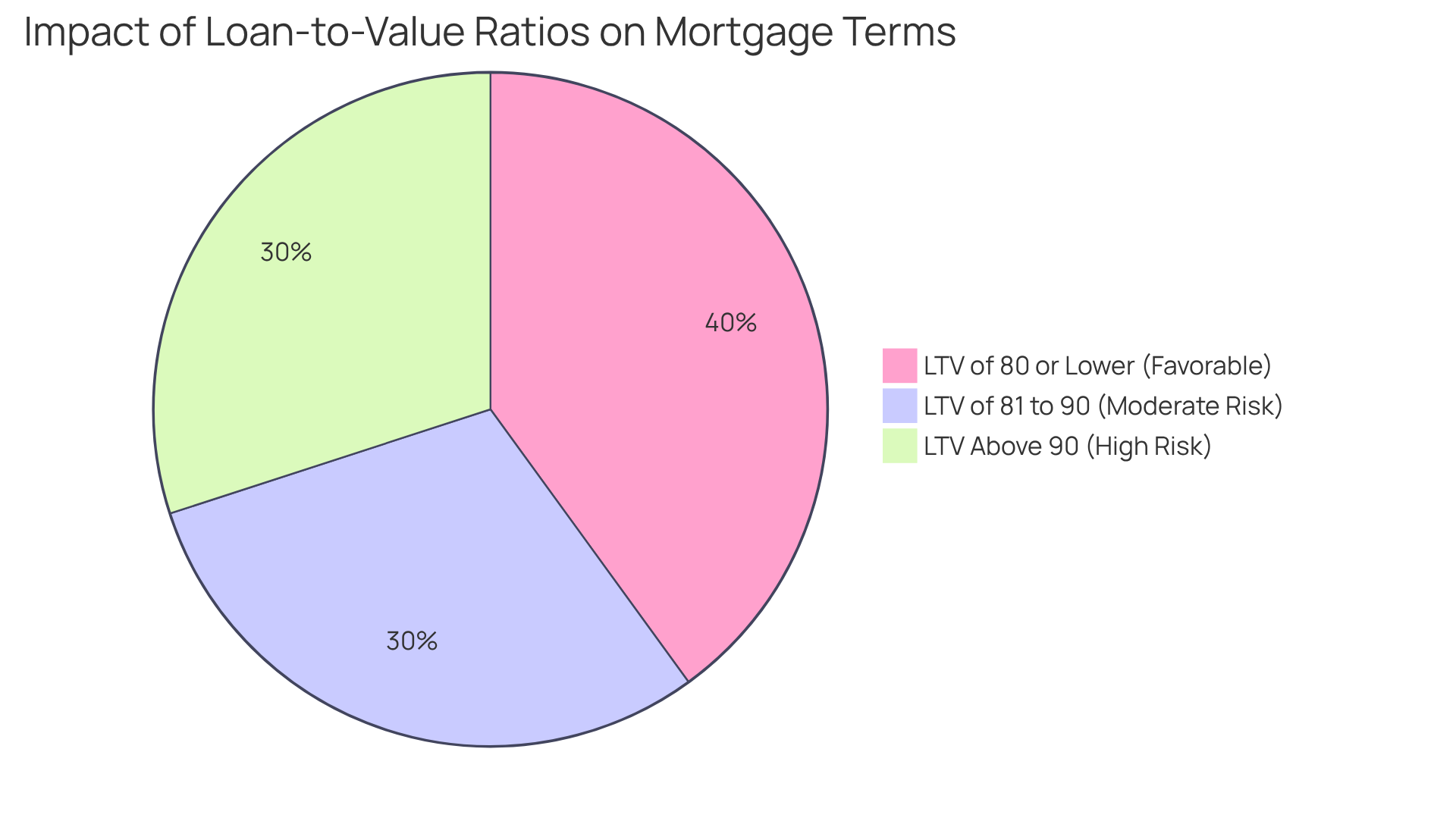
A favorable loan to value ratio is generally considered to be below 80%. This benchmark is crucial; it often relates to better loan conditions and lower insurance costs. Ratios between 80% and 90% can still be acceptable, but they may lead to higher interest rates and more scrutiny during the approval process. When ratios exceed 90%, they are typically viewed as high risk, complicating the approval journey for borrowers.
For instance, a homebuyer securing financing with a 75% LTV may benefit from lower monthly payments and avoid private mortgage insurance (PMI), positively impacting their overall financial situation. Understanding these benchmarks allows homebuyers to set realistic expectations and navigate the financing landscape, particularly concerning loan to value ratios, more effectively. As industry experts suggest, maintaining a loan to value ratio of 80% or lower is advisable for securing favorable financing terms, underscoring the importance of the loan to value metric in the home buying process.
At F5 Mortgage, we know how challenging this can be, especially for families looking to upgrade their homes. Many families may find value in down payment assistance programs. For example, Florida offers various initiatives, such as the FL Assist program, which provides up to $10,000 as a deferred second funding option for different credit types. Similarly, Michigan’s MI Home Loan program offers $10,000 loans for first-time homebuyers, with repayment postponed until the home is sold or the primary loan is settled.
These programs can significantly enhance home buying opportunities, making it easier for families to achieve their dream of homeownership. Our clients have expressed exceptional satisfaction with our services, as reflected in their testimonials. They appreciate our support during the mortgage process, ensuring they can fully utilize available assistance programs while maintaining a favorable loan to value. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
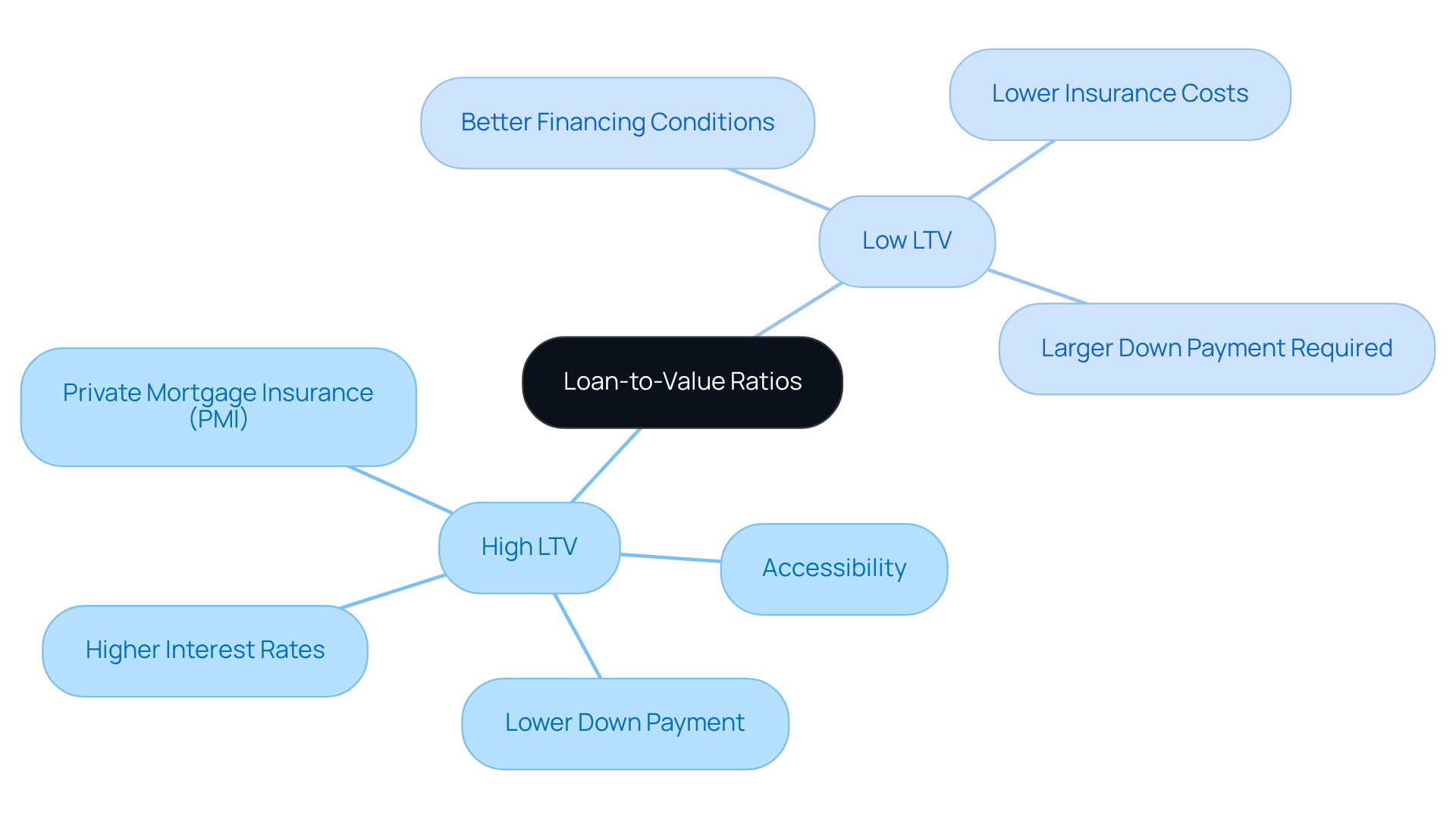
High vs. Low Loan-to-Value Ratios: Risks and Benefits Explained
High loan to value ratios can make homeownership more accessible, lowering upfront costs and allowing buyers to enter the market with smaller down payments. For instance, a traditional mortgage can require as little as a 3% down payment, resulting in an LTV of 97%. However, we know how challenging this can be, as this accessibility comes with significant risks. Higher interest rates and the necessity for private mortgage insurance (PMI) if the LTV exceeds 80% can add to monthly payments, impacting overall affordability.
In contrast, low LTV ratios can lead to more advantageous financing conditions and lower insurance expenses. A lower LTV, such as 80% or below, often qualifies borrowers for better interest rates and eliminates the need for PMI. This can save thousands over the life of the loan. However, achieving a low loan to value (LTV) typically requires a larger down payment, which can be a barrier for some buyers.
As you navigate this journey, it’s important to weigh these factors carefully when crafting your financing strategy. For example, families looking to upgrade their homes may find that while a high loan to value allows them to purchase sooner, the long-term costs associated with higher interest rates and PMI could outweigh the initial benefits. Conversely, those who can afford a larger down payment may benefit from the stability and savings associated with a low LTV, ultimately leading to a more manageable mortgage experience.
We’re here to support you every step of the way as you explore your options. Take the time to consider what works best for your family, and remember that understanding your financing strategy can empower you to make the best decision for your future.
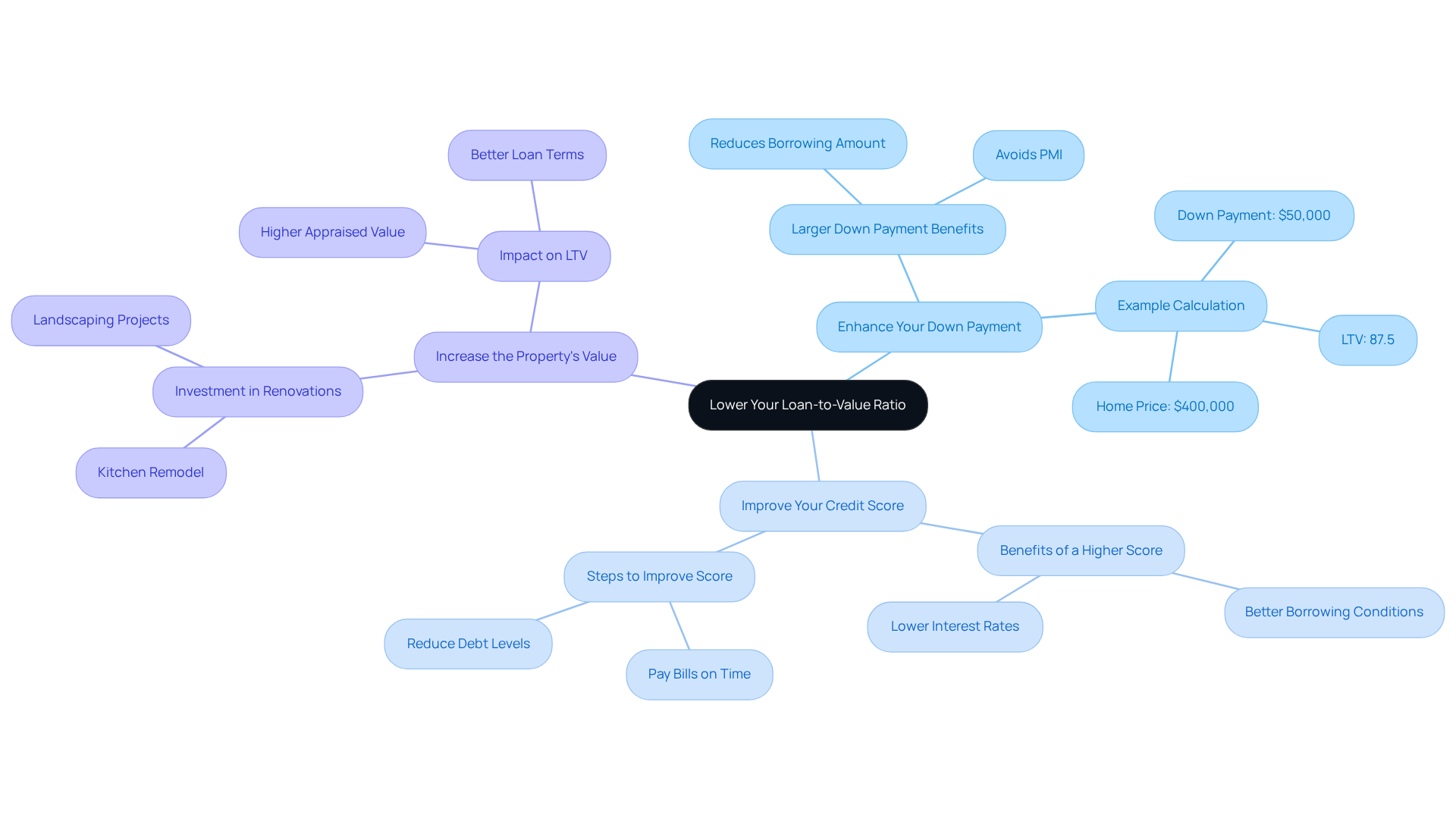
How to Lower Your Loan-to-Value Ratio: Effective Strategies
To effectively lower your loan to value ratio, we understand how important it is to explore strategies that can ease your financial journey. Here are some thoughtful approaches you might consider:
-
Enhance Your Down Payment: A larger down payment directly reduces the amount you need to borrow compared to the property’s value. For example, if you buy a $400,000 home with a $50,000 down payment, your LTV would be 87.5%. Striving for a down payment of 20% or more can help you avoid private mortgage insurance (PMI), which is often required for loan to value ratios exceeding 80%. This can save you money in the long run.
-
Improve Your Credit Score: Elevating your credit score can lead to better borrowing conditions, allowing you to secure a lower loan amount. Lenders typically reward higher credit scores with more favorable interest rates, which can significantly decrease your overall borrowing costs. We know how challenging this can be, but every step you take towards improving your credit can make a difference.
-
Increase the Property’s Value: Investing in renovations or improvements can boost your home’s appraised value, thus lowering your LTV. For instance, a well-planned kitchen remodel or landscaping project can greatly enhance your home’s market worth, opening doors to better loan terms.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve your financing options and potentially save thousands over the life of your loan. Remember, understanding how each of these factors relates to your overall financial situation is vital for achieving your homeownership goals. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
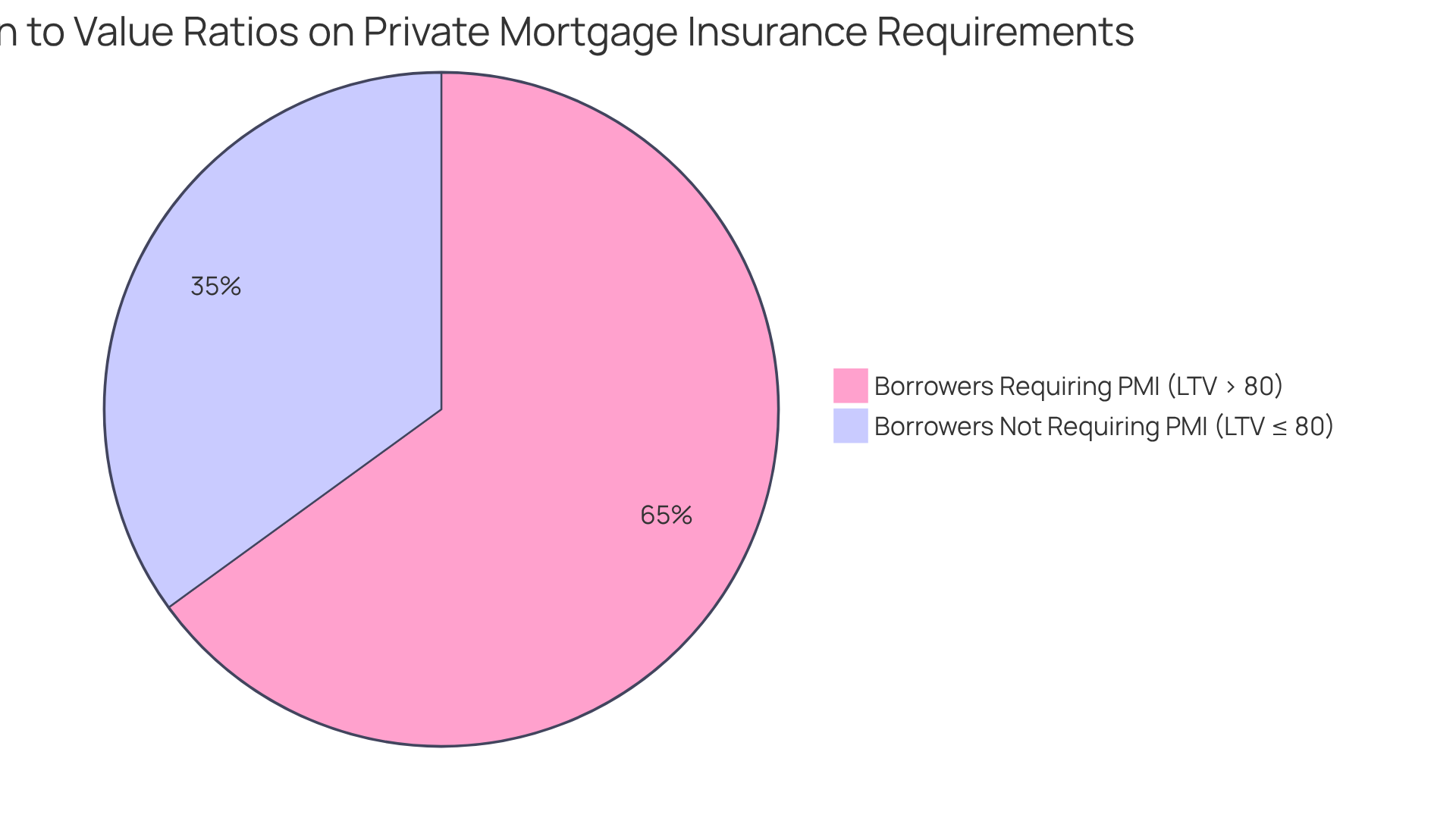
Loan-to-Value Ratio and Mortgage Insurance: What You Need to Know
The loan to value (LTV) ratio is a significant factor in determining whether private mortgage insurance (PMI) is necessary. When your loan to value exceeds 80%, lenders typically require PMI to help protect against the risk of default. This requirement can lead to a noticeable increase in your monthly loan payment, making it essential for homebuyers to grasp this relationship, as it directly influences their overall budget and financing strategy.
Consider this: a borrower with a home valued at $400,000 and a loan amount of $360,000 has a loan to value ratio of 90%, which necessitates PMI. On the other hand, making a down payment of 20% or more results in a loan to value (LTV) ratio of 80% or lower, allowing you to avoid these additional costs.
Effectively managing PMI costs is crucial for homebuyers. Strategies such as making extra payments toward the principal can reduce the loan balance and improve the loan to value over time. This may even lead to PMI cancellation once the loan balance reaches 78% of the property’s value.
Insurance professionals highlight the importance of understanding loan to value in navigating mortgage requirements. As one expert noted, ‘Lowering your loan to value ratio may be easier said than done.’ This statement underscores the challenges many face in securing favorable financing terms.
In 2022, the average borrowing amount with PMI was approximately $341,716, showcasing the financial implications of high loan to value levels. With nearly 2 million low down payment borrowers obtaining financing in 2021, understanding the loan to value ratio and its effects on PMI costs is more important than ever. By staying informed, homebuyers can make strategic decisions that align with their financial aspirations.
Loan-to-Value Ratio Requirements by Loan Type: A Comparative Overview
Loan types exhibit distinct loan to value (LTV) ratio requirements that significantly influence your borrowing options. We understand how daunting this process can feel. Traditional financing usually requires a loan to value of 80% or less to bypass private insurance, which can significantly increase monthly expenses. In contrast, FHA mortgages accommodate higher loan to value ratios, allowing you to secure financing with a loan to value of up to 96.5%. This flexibility can be particularly beneficial for first-time homebuyers who may have limited funds for a down payment. VA loans stand out, as they do not require insurance at all, regardless of the loan to value, making them an appealing choice for qualified veterans and active-duty military personnel.
Mortgage professionals emphasize the importance of understanding these differences. As one specialist pointed out, ‘Lenders utilize your loan to value ratio during loan qualification to evaluate the risk of providing you funds and to decide if you’ll require to pay insurance for the loan.’ This insight highlights the essential role of loan to value (LTV) in the total expense of a home loan.
For instance, imagine a homebuyer contemplating an FHA mortgage with a purchase price of $350,000 and a down payment of $10,000. You would encounter an LTV of roughly 97%. This high loan to value could result in higher monthly mortgage insurance premiums. On the other hand, a traditional mortgage with a $50,000 down payment on the same property would produce a loan to value (LTV) of 86%, which could lead to reduced overall expenses if you can maintain the loan to value under 80% to prevent PMI.
Alongside these credit types, down payment assistance programs can greatly reduce the effective LTV for borrowers. For instance, the MyHome Assistance Program in California provides up to 3% of the home’s purchase price, while Texas’s My Choice Texas Home program offers up to 5% for down payment and closing assistance. Florida’s programs, such as the Florida Assist Second Mortgage Program, can provide up to $10,000 in upfront costs. These assistance options can make homeownership more accessible by reducing the loan to value ratio.
Navigating these loan to value differences is essential for homebuyers, especially those exploring FHA and VA loan options. By comprehending the consequences of LTV metrics and utilizing available support programs, you can make informed choices that align with your financial circumstances and homeownership objectives. Additionally, F5 Mortgage’s fast closing process can help streamline the approval and closing stages, making it easier for you to secure your desired financing.
Loan-to-Value Ratio FAQs: Answers to Common Homebuyer Questions
-
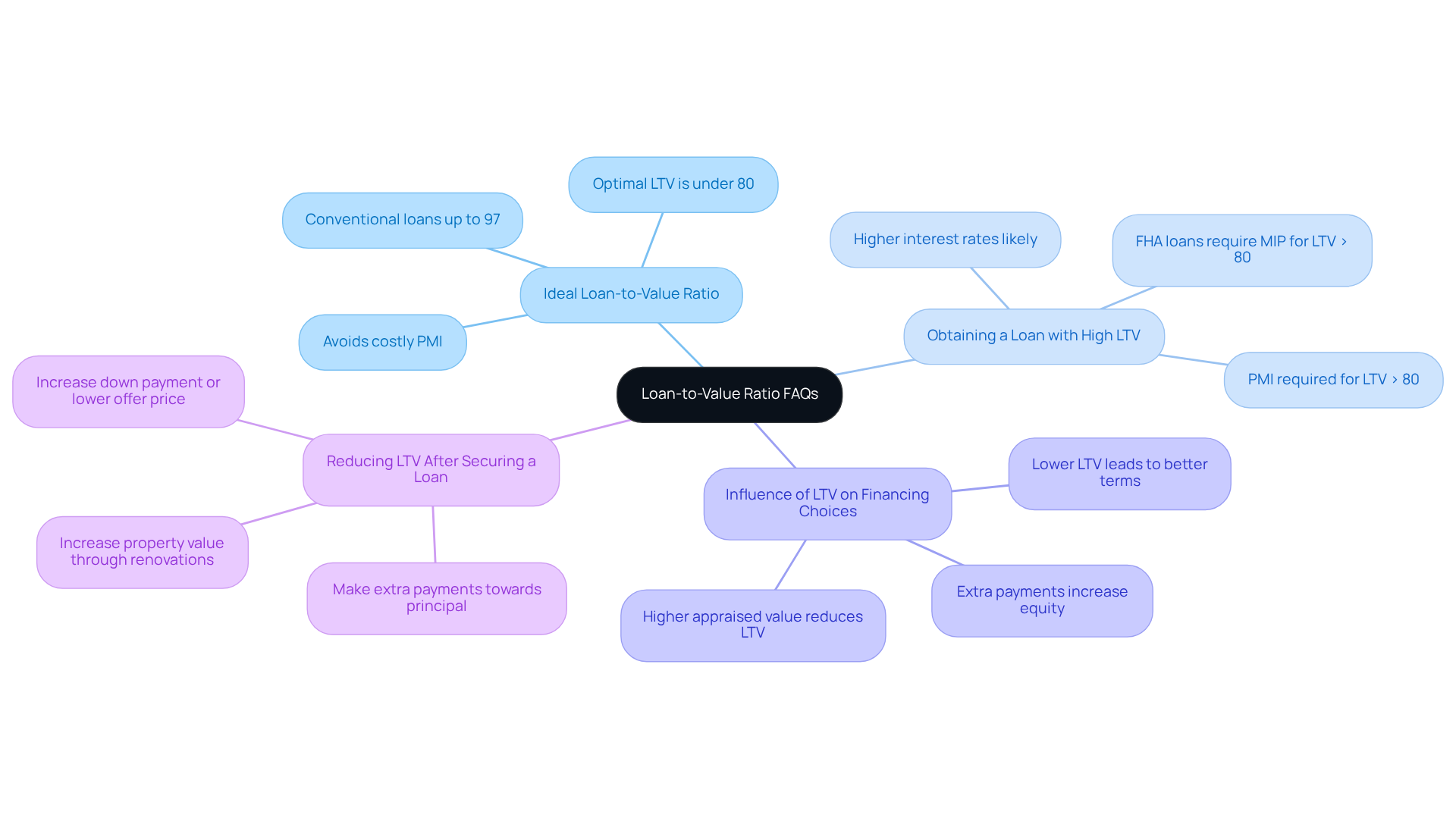
What is the ideal loan-to-value ratio? We understand that navigating the mortgage landscape can be overwhelming. The optimal loan to value ratio is usually under 80%. This limit not only helps you secure better loan conditions but also allows you to avoid costly private mortgage insurance (PMI). At F5 Mortgage, we are here to help you explore these options and find competitive rates that align with your financial needs. While conventional loans backed by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac accept loan to value ratios up to 97%, it’s important to note that higher loan to value ratios often come with increased costs.
-
Can I obtain a loan with a high LTV? Yes, loans with high loan to value ratios are available, but we want you to be aware that they often come with elevated interest rates and may require PMI. This insurance safeguards lenders in the event of default. Additionally, FHA financing necessitates mortgage insurance premiums (MIP) for loan to value (LTV) ratios exceeding 80%. Understanding these implications is crucial, and at F5 Mortgage, we offer personalized service to help you make informed decisions that suit your situation.
-
How does LTV influence my financing choices? A lower loan to value typically results in better loan terms, such as lower interest rates and reduced insurance costs, making homeownership more affordable for you. Moreover, a greater appraised value of your home can reduce the loan to value ratio, potentially enhancing your financing options. We are here to help you comprehend how home appraisals affect your equity and loan rates, ensuring you feel confident in your choices.
-
Is it possible to reduce my LTV after securing a loan? Yes, homeowners can lower their loan to value by making extra payments towards the principal, increasing the property’s value through renovations, or employing strategies such as increasing the down payment or lowering the offer price. These actions can enhance your equity and improve refinancing options. At F5 Mortgage, we are dedicated to guiding you through these strategies, supporting you every step of the way.
These FAQs address common concerns and help demystify the loan-to-value ratio for homebuyers. We aim to provide essential insights into navigating the mortgage landscape with the compassionate support of F5 Mortgage.
Conclusion
Understanding the loan to value (LTV) ratio is crucial for homebuyers who aim to navigate the complexities of mortgage financing successfully. This essential metric not only influences loan approval and interest rates but also plays a significant role in determining overall affordability. By grasping the nuances of LTV, potential homeowners can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals, ultimately paving the way for a smoother home buying experience.
Throughout this article, we’ve shared key insights to illuminate the importance of LTV in the mortgage process. A lower LTV ratio often translates to better loan terms, reduced insurance costs, and increased chances of approval. Conversely, higher LTV ratios can lead to elevated interest rates and the necessity for private mortgage insurance, which can strain a buyer’s budget. We also discussed strategies for lowering LTV, such as enhancing down payments or improving credit scores, as vital steps toward achieving favorable financing.
As you prepare for your journey, it’s imperative to consider the implications of LTV on your financial future. By utilizing available resources, such as down payment assistance programs and expert guidance from organizations like F5 Mortgage, you can empower yourself to make strategic choices. Embracing this knowledge will not only facilitate a successful home buying experience but also foster long-term financial stability. Remember, we know how challenging this can be, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio?
The loan-to-value (LTV) ratio is a financial term that represents the relationship between the amount borrowed and the appraised value of the property. It is calculated by dividing the loan amount by the appraised value and multiplying by 100.
Why is the LTV ratio important?
The LTV ratio is important because it helps lenders evaluate risk. A lower LTV ratio indicates more equity in the property, which can lead to better financing terms for borrowers, such as lower interest rates and reduced need for private insurance.
How do I calculate my LTV ratio?
To calculate your LTV ratio, follow these steps: 1. Establish the appraised value of your property. 2. Identify the total amount you plan to borrow. 3. Use the formula: LTV = (Loan Amount / Appraised Value) x 100. For example, borrowing $200,000 for a home valued at $250,000 results in an LTV of 80%.
What LTV ratio is considered favorable?
An LTV ratio of 80% or lower is generally considered favorable, as it may grant access to competitive interest rates. Higher LTV ratios may necessitate private insurance.
How does LTV affect loan approval and interest rates?
LTV can significantly impact loan approval and interest rates. A lower LTV ratio can lead to better financing terms and increase the likelihood of loan approval, while a higher LTV may result in higher interest rates and additional insurance requirements.
How long are loan approval letters valid?
Loan approval letters typically become invalid after 90 days. It is important to renew your approval if you haven’t made an offer within this timeframe.
What should I do if I need assistance with understanding LTV?
F5 Mortgage offers personalized consultations to help clarify the significance of loan-to-value ratios and provide tailored advice to align with your financial goals. They aim to empower you with the knowledge needed to navigate the mortgage process effectively.








